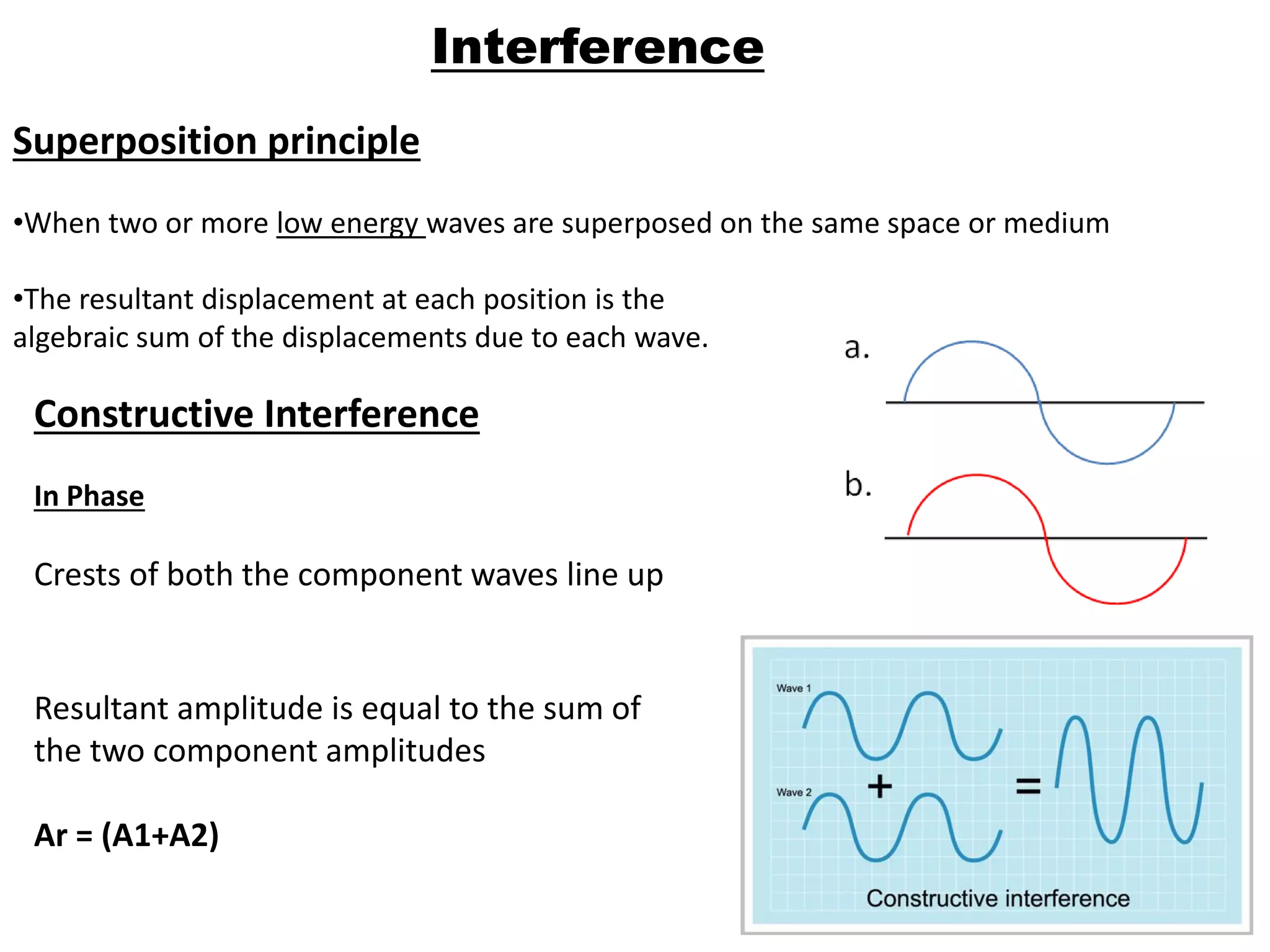
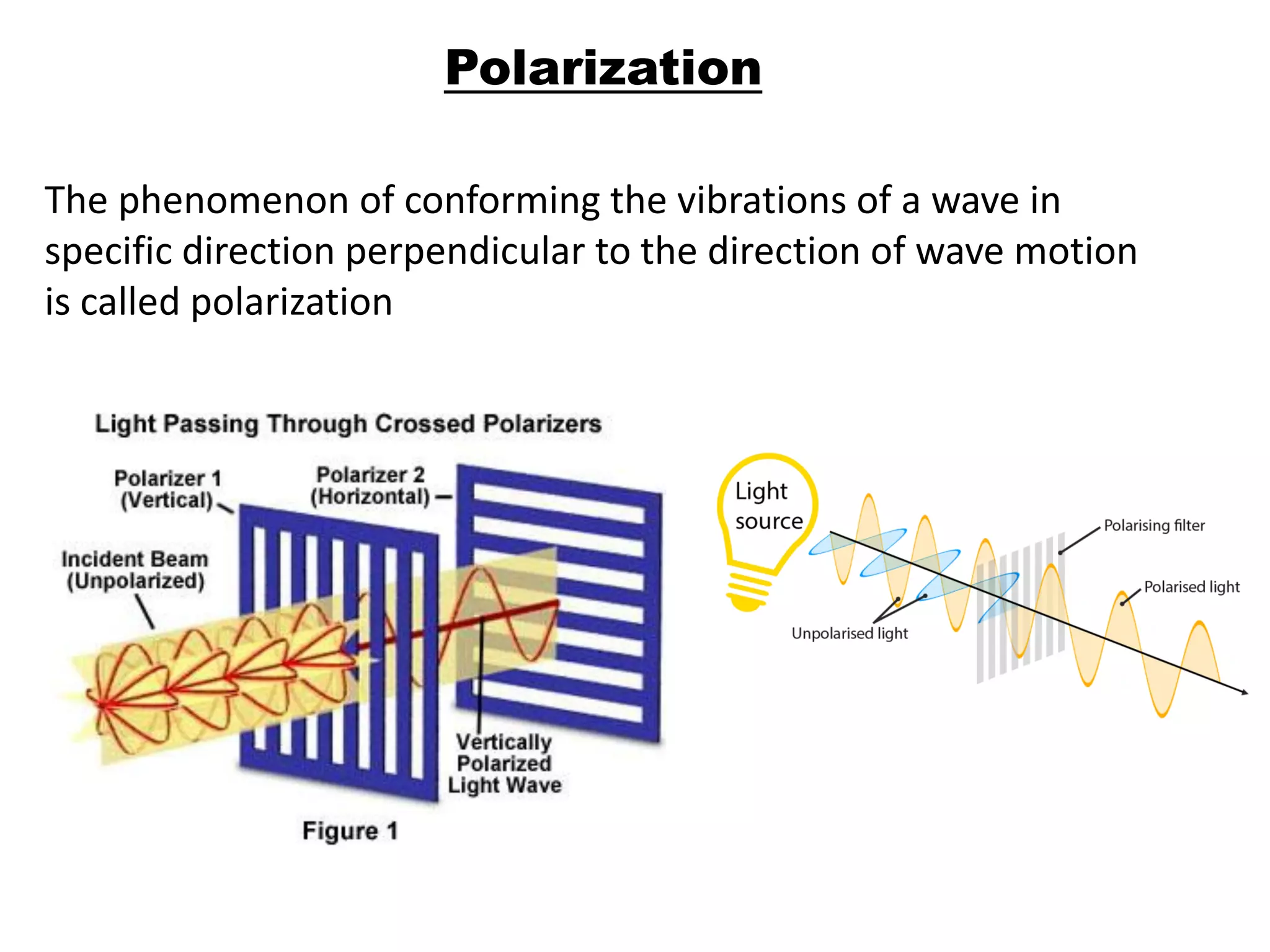
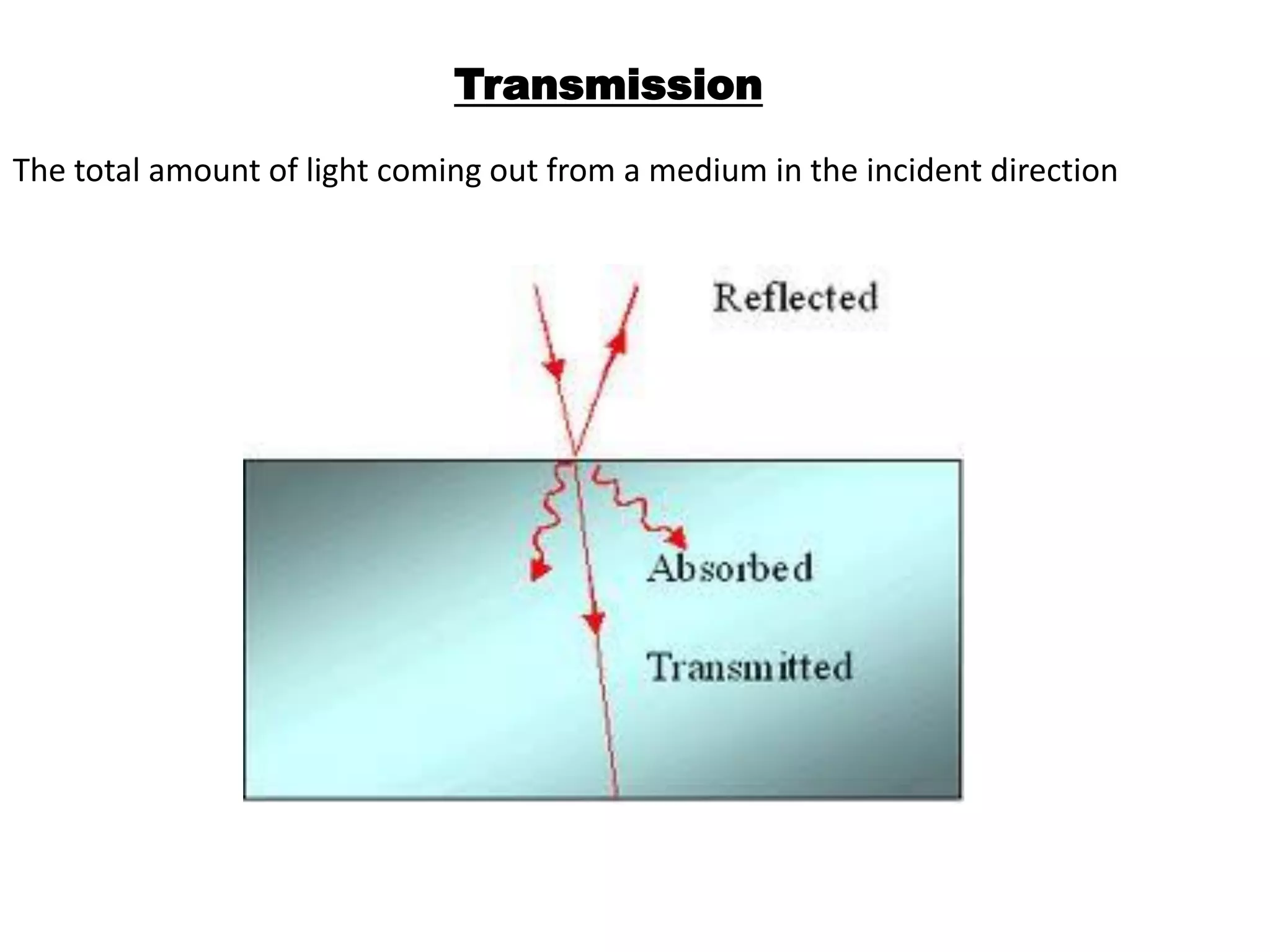
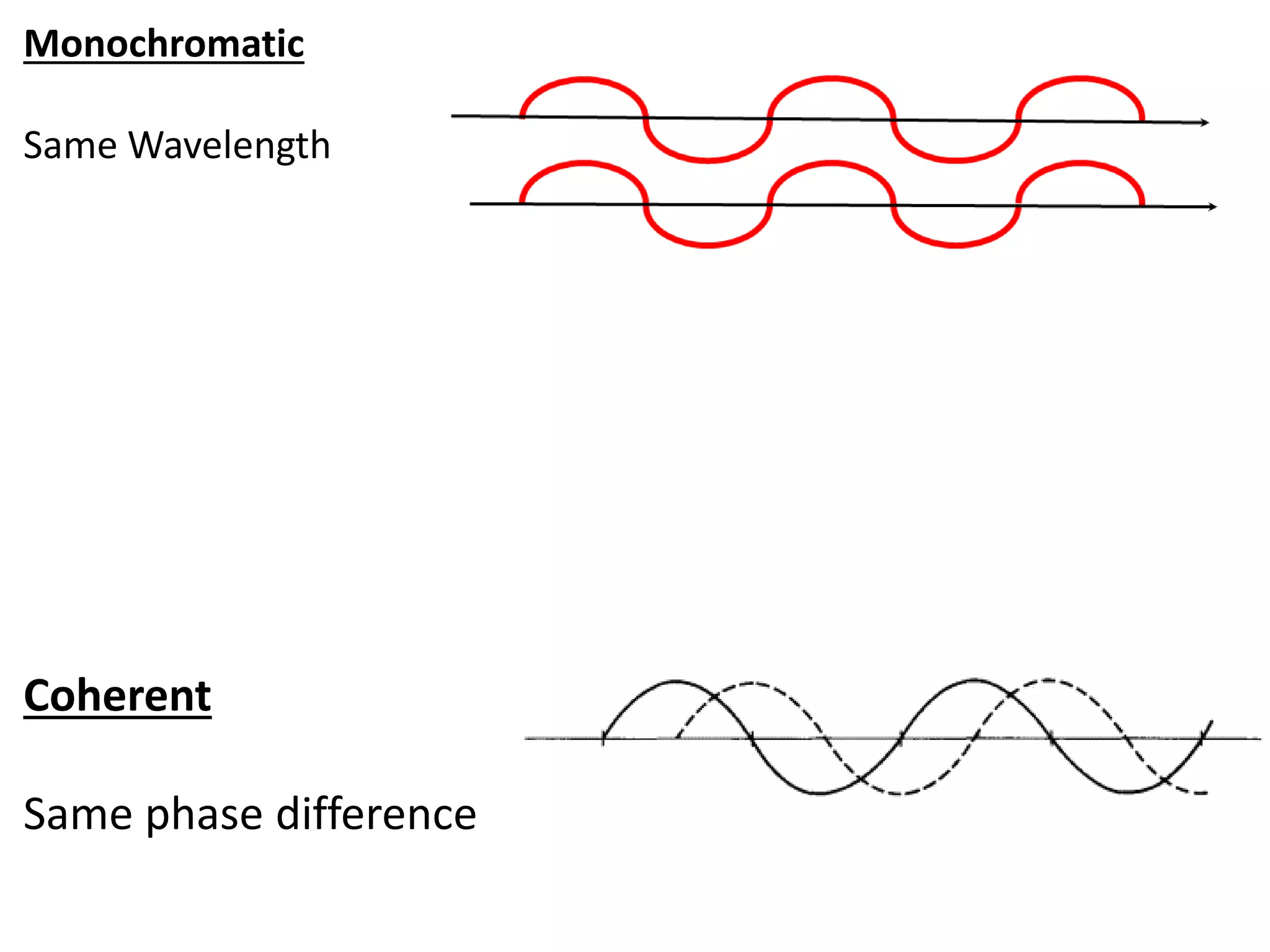
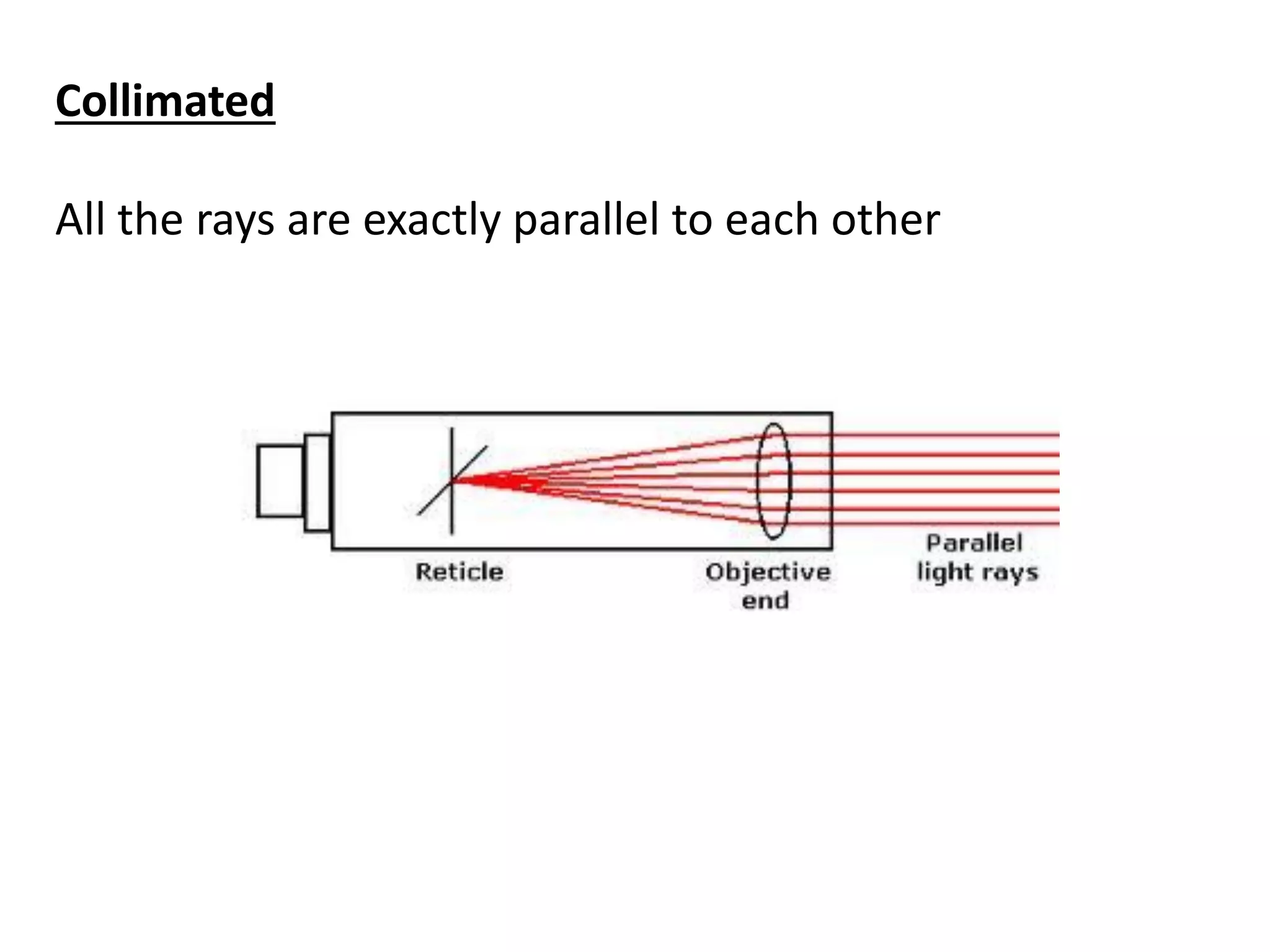
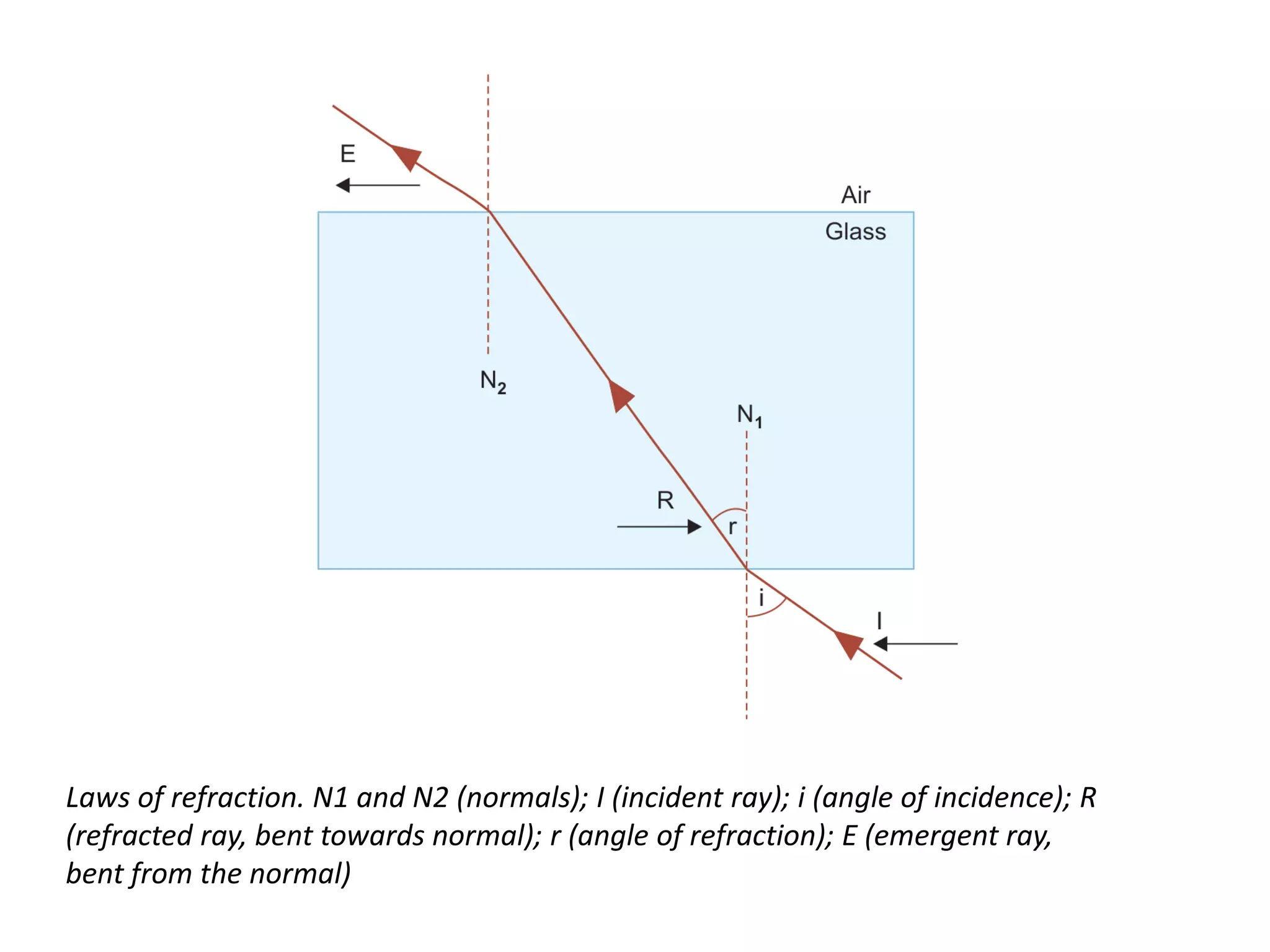
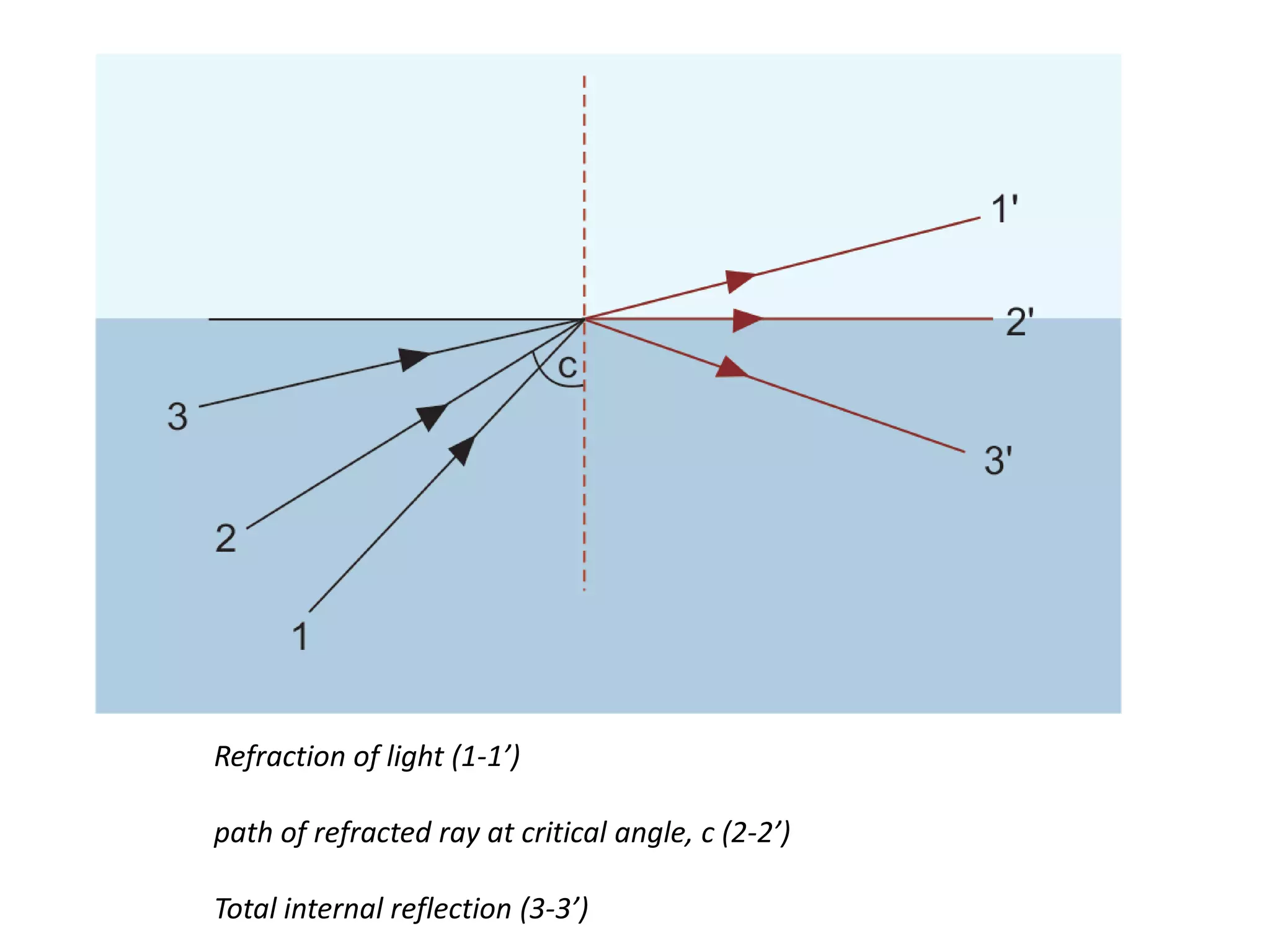
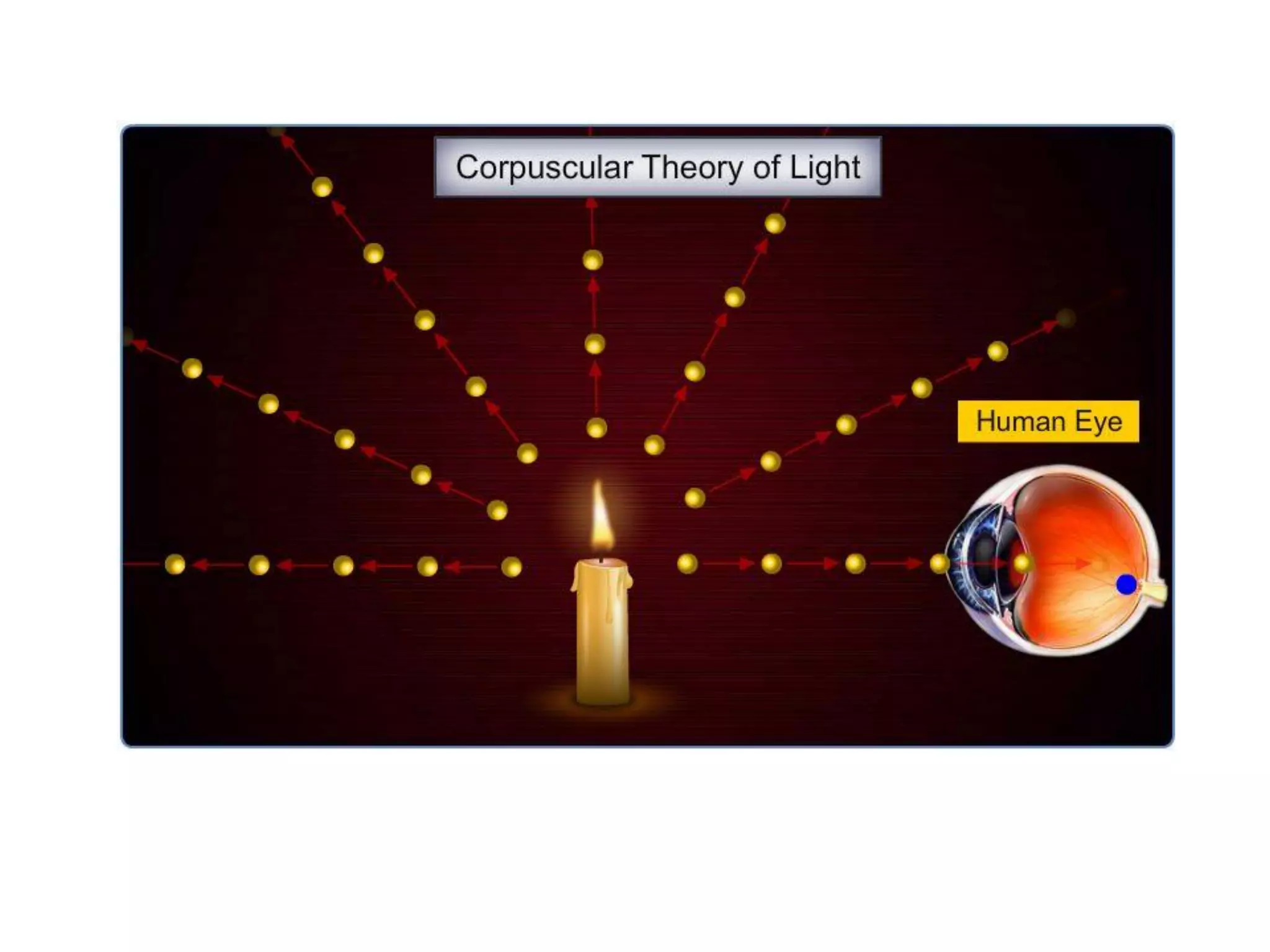
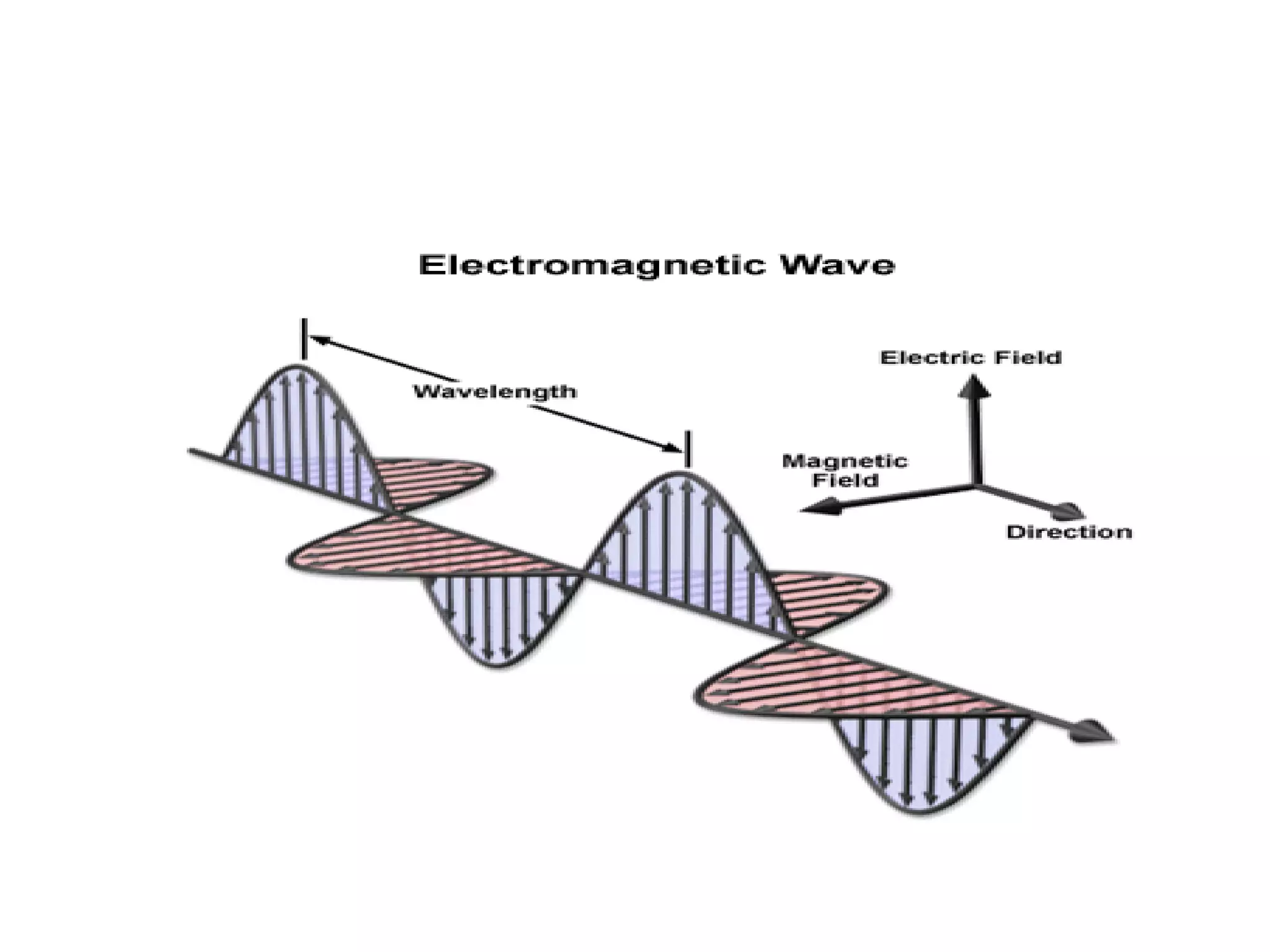
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that interacts with the retina to produce the sensation of sight. It is the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, ranging from 400-700 nm. Light travels as a transverse wave and exhibits properties of both waves and particles. The interaction of light with matter can be explained using wave optics concepts like interference and diffraction, or quantum optics concepts like absorption and scattering. Geometrical optics describes how lenses and mirrors form images through reflection and refraction according to Snell's law. Total internal reflection occurs when light passes from an optically dense to rare medium at an angle greater than the critical angle.


















![Frequency
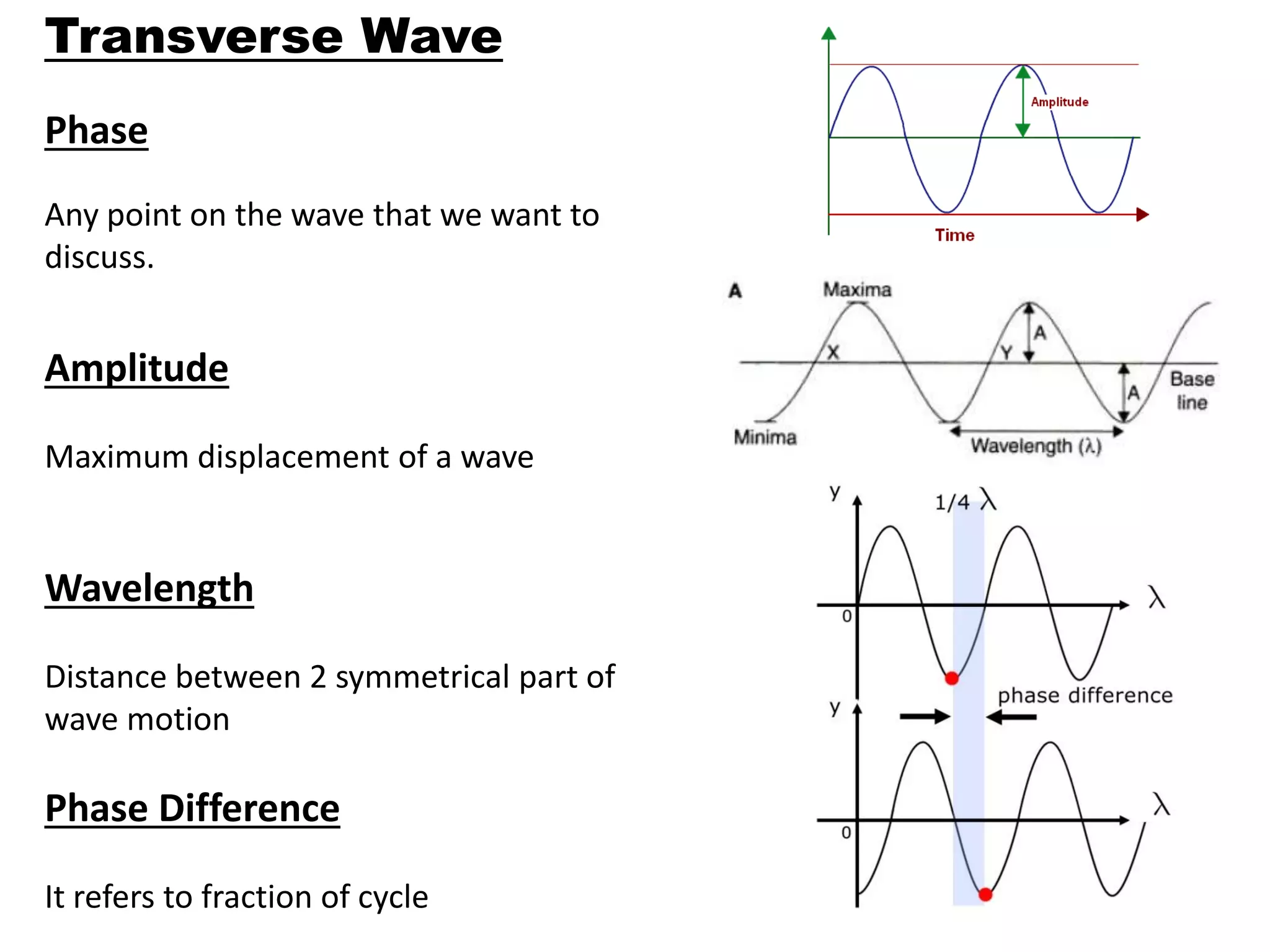
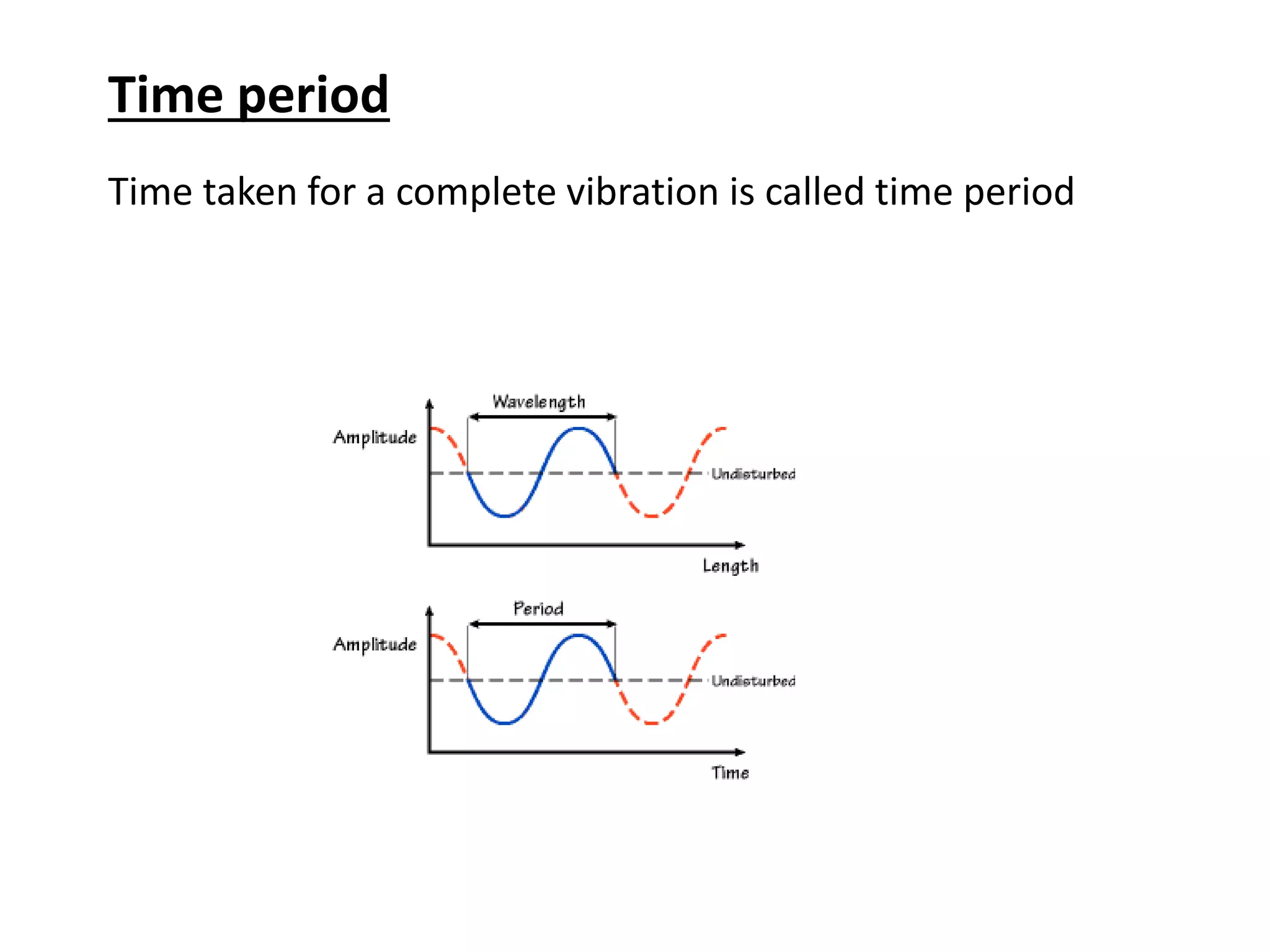
Number of oscillations/cycles per unit time is called
frequency
Unit = hertz
Never changes when light moves from one medium to
another (5.45x1014 Hz)
Intensity
Energy delivered or carried by the wave per unit area per
unit time
I = (energy delivered)/[(area/time)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/light-230203142815-008c1629/75/LIGHT-pdf-23-2048.jpg)