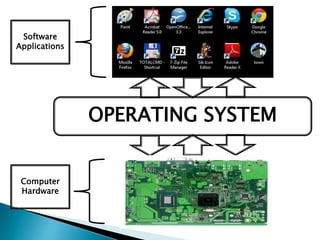
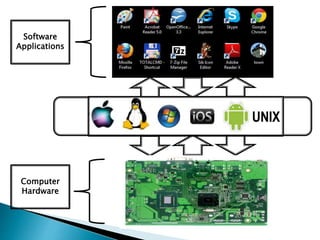
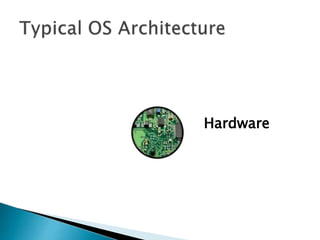
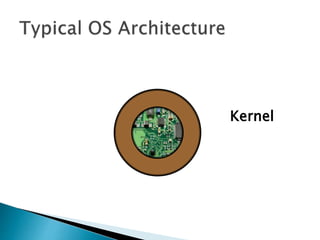
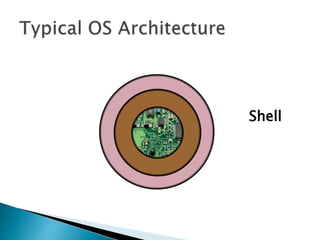
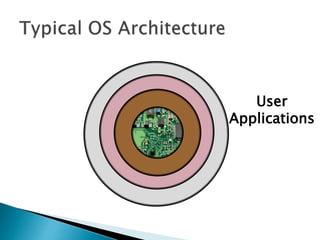
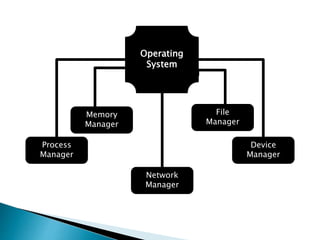
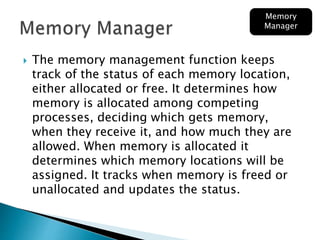
The document discusses the components and functions of an operating system. It explains that hardware is the physical elements of a computer system, while the kernel manages processes and resource allocation. The shell provides an interface to access operating system services through either a command-line or graphical user interface. User applications are programs designed for user benefit. It then provides details about specific operating systems like UNIX, Windows, MacOS, Linux, Android and iOS.