This document discusses open pit mining and provides details on:
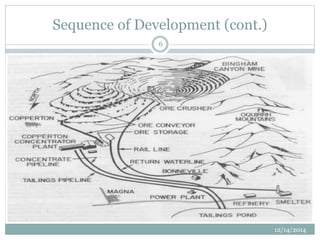
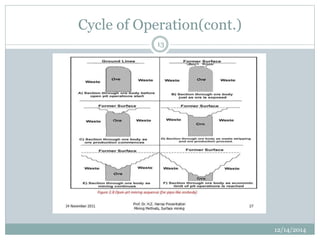
- The sequence of development including land clearance, plant location, and establishing the first bench.
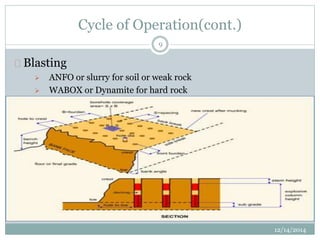
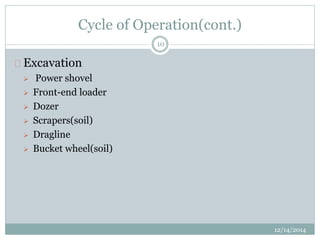
- The cycle of operations including drilling, blasting, excavation, and haulage using various equipment like power shovels and trucks.
- Auxiliary operations that support open pit mining such as health and safety, environmental control, and maintenance.