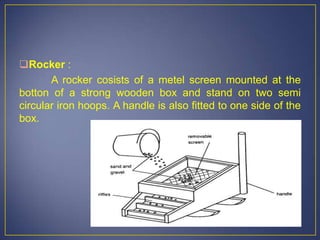
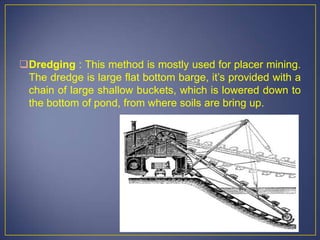
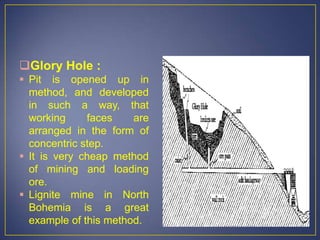
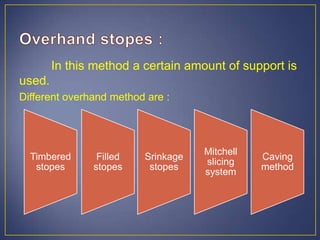
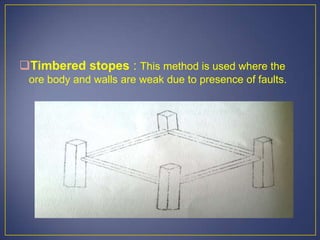
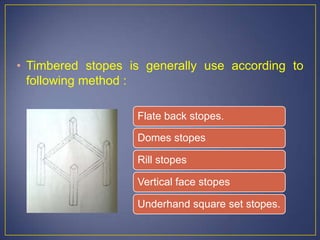
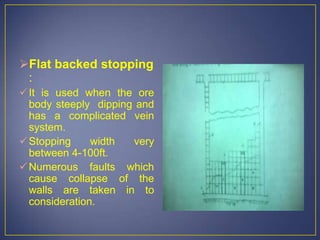
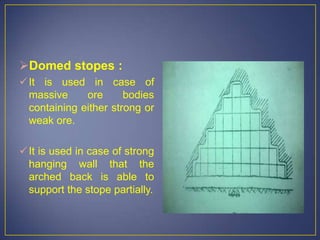
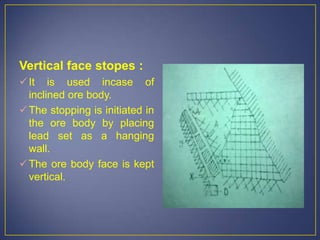
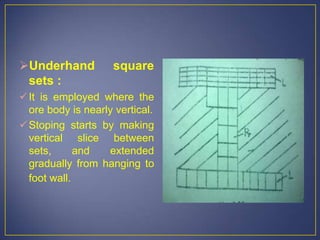
This document discusses various mining methods including surface mining techniques like alluvial mining and open-cast mining as well as underground mining techniques. It describes alluvial mining methods like using pans, rockers, and sluicing. For open-cast mining it discusses loading by hand or machine and different open-cast mining methods. Underground mining techniques discussed include room and pillar mining, open stoping methods using timber supports or waste filling, shrinkage stoping, and caving methods like top slicing and block caving.