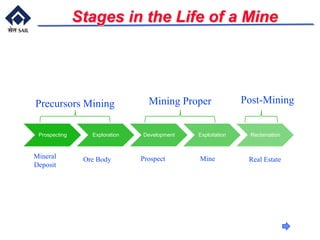
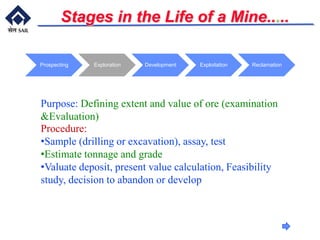
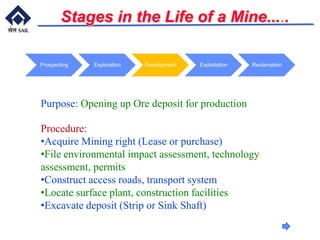
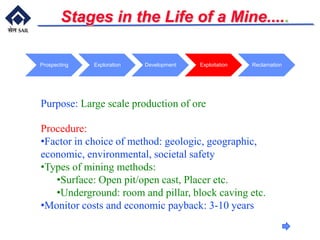
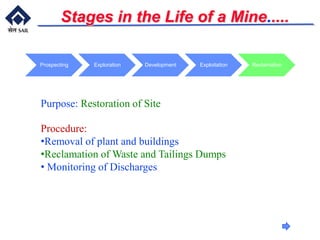
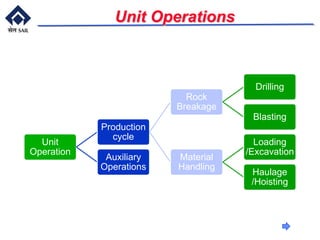
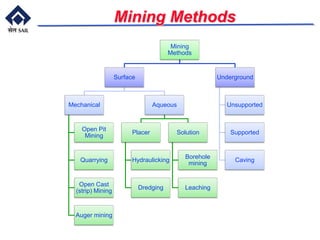
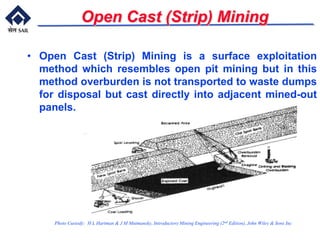
This document provides an overview of introductory mining concepts. It discusses how mining has paralleled the development of civilization throughout history. Various eras such as the Stone Age, Bronze Age, and Iron Age are identified based on the dominant minerals used during those times. Key terminology related to mining like mine, ore, waste, and gangue are defined. The document outlines the major stages in the life of a mine from prospecting to exploitation to reclamation. It also describes common mining methods including open pit mining, quarrying, open cast mining, and auger mining. Finally, photos of mining equipment and operations at active mines are presented.