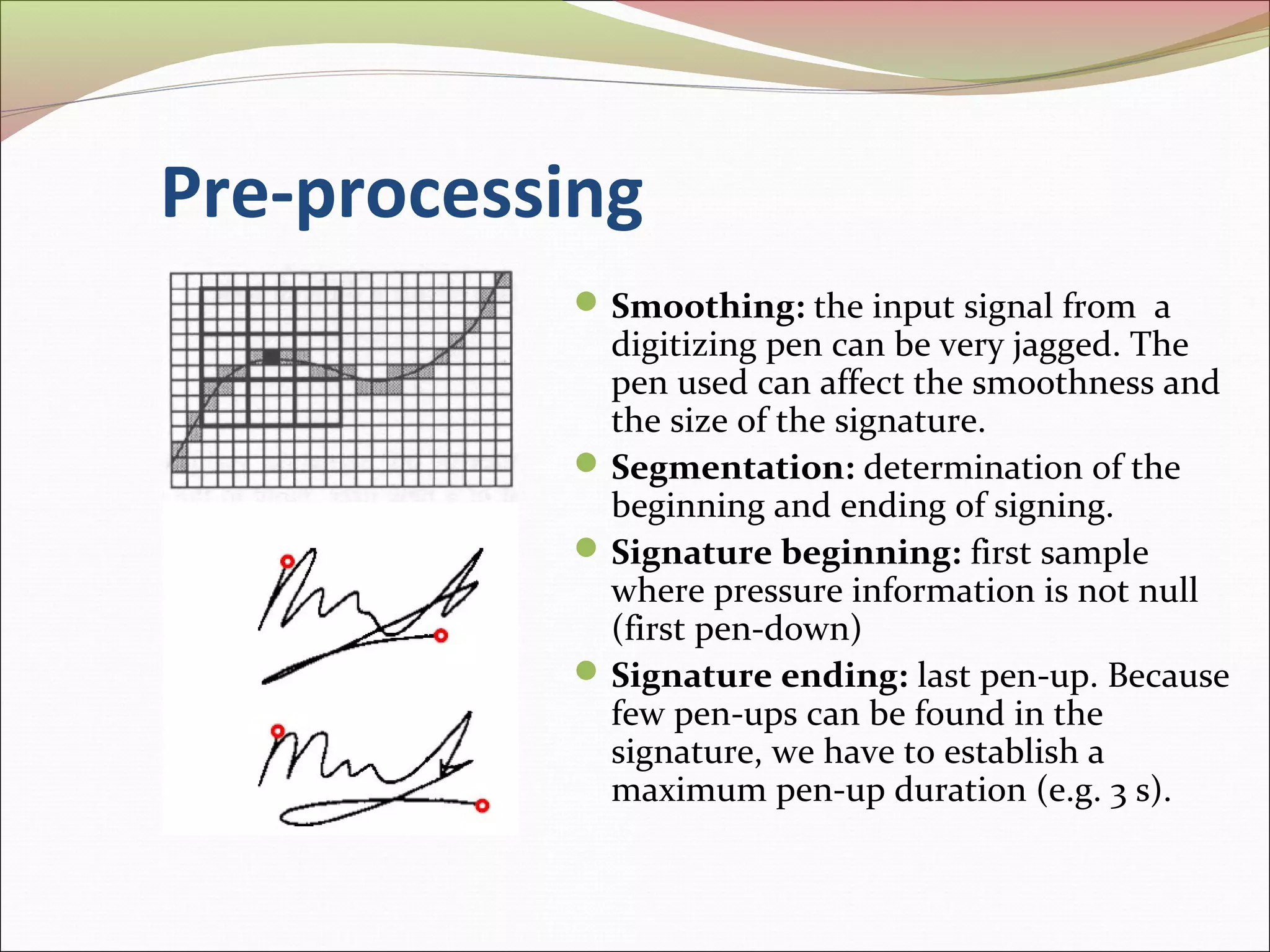
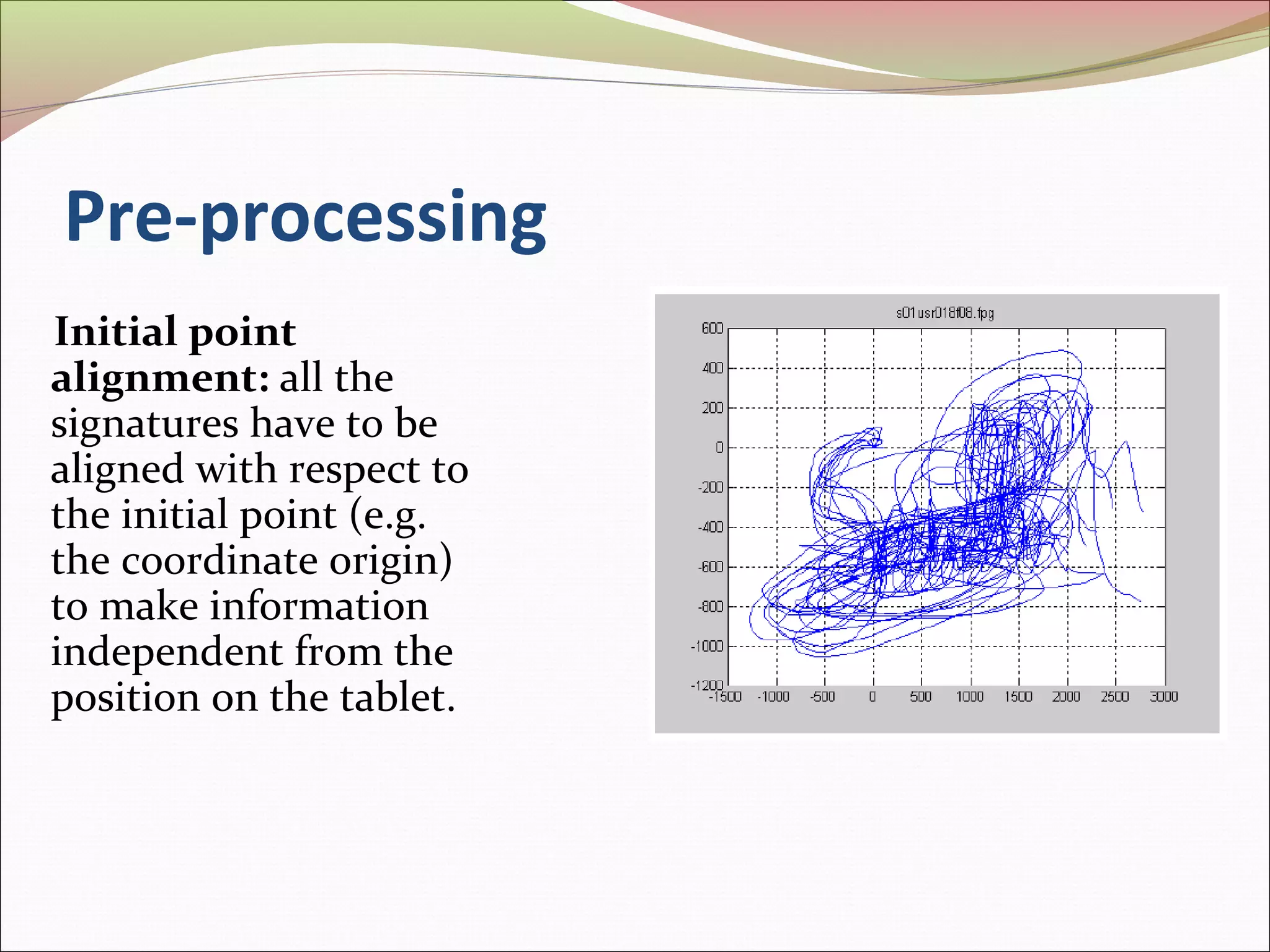
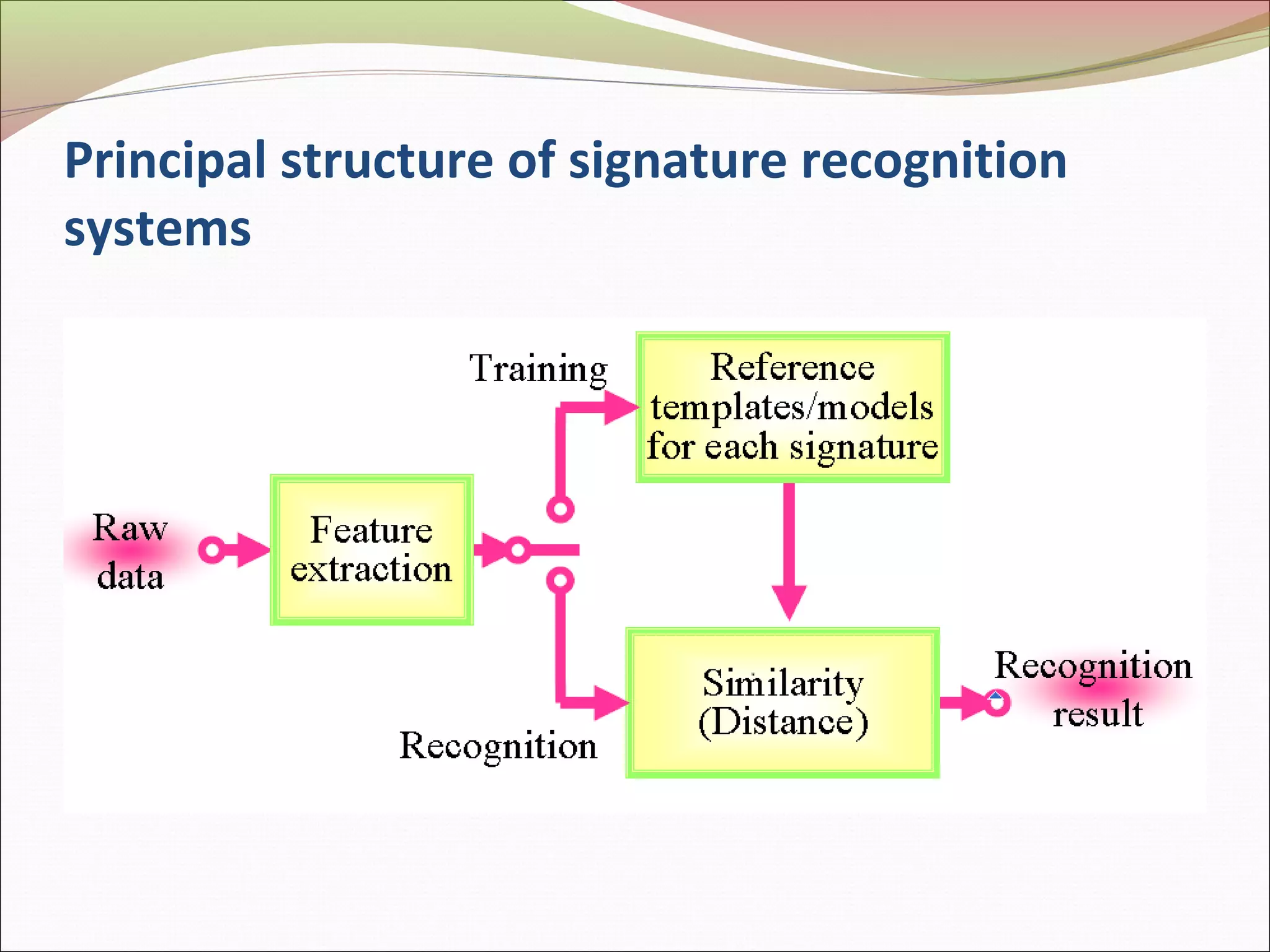
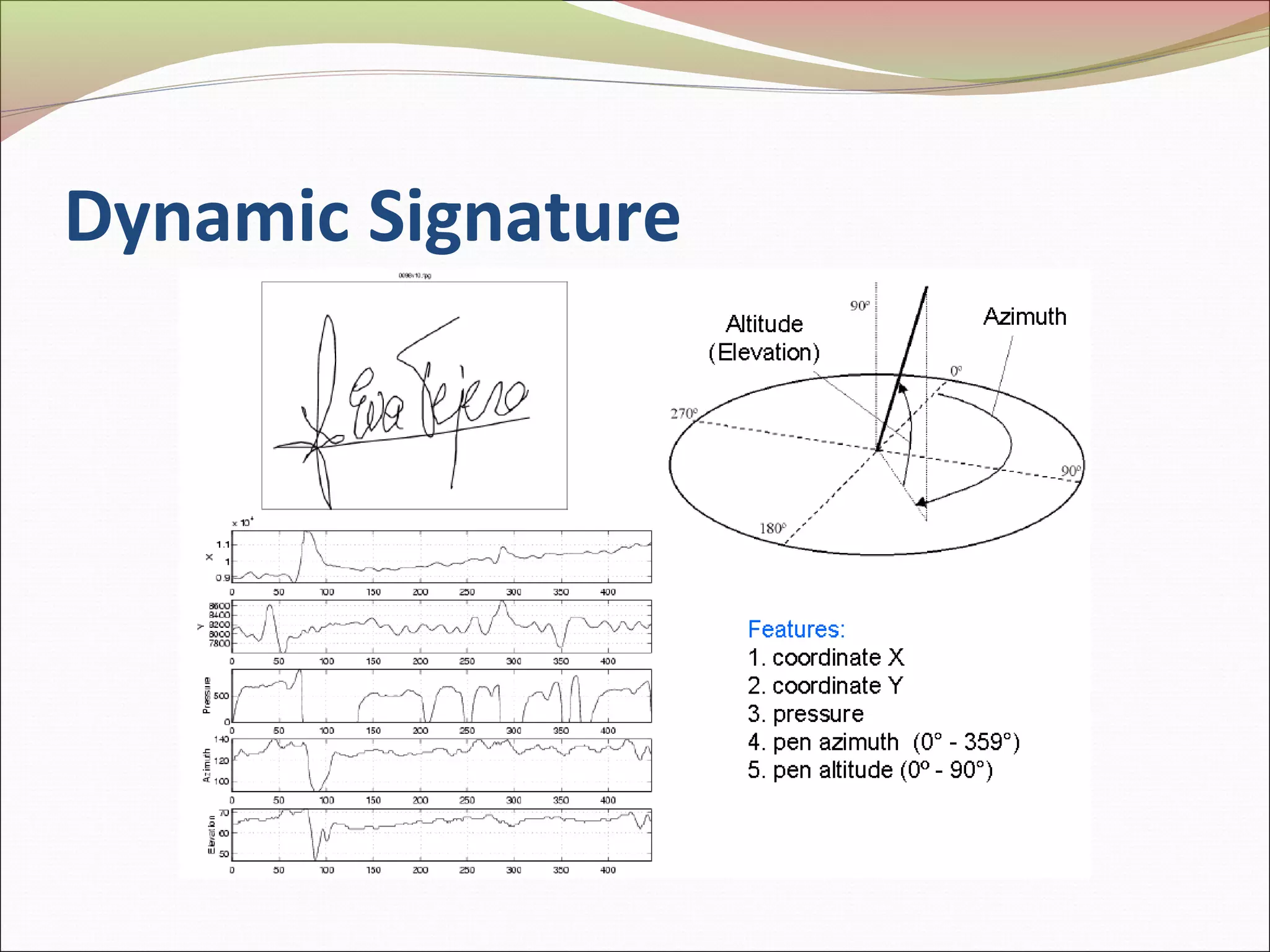
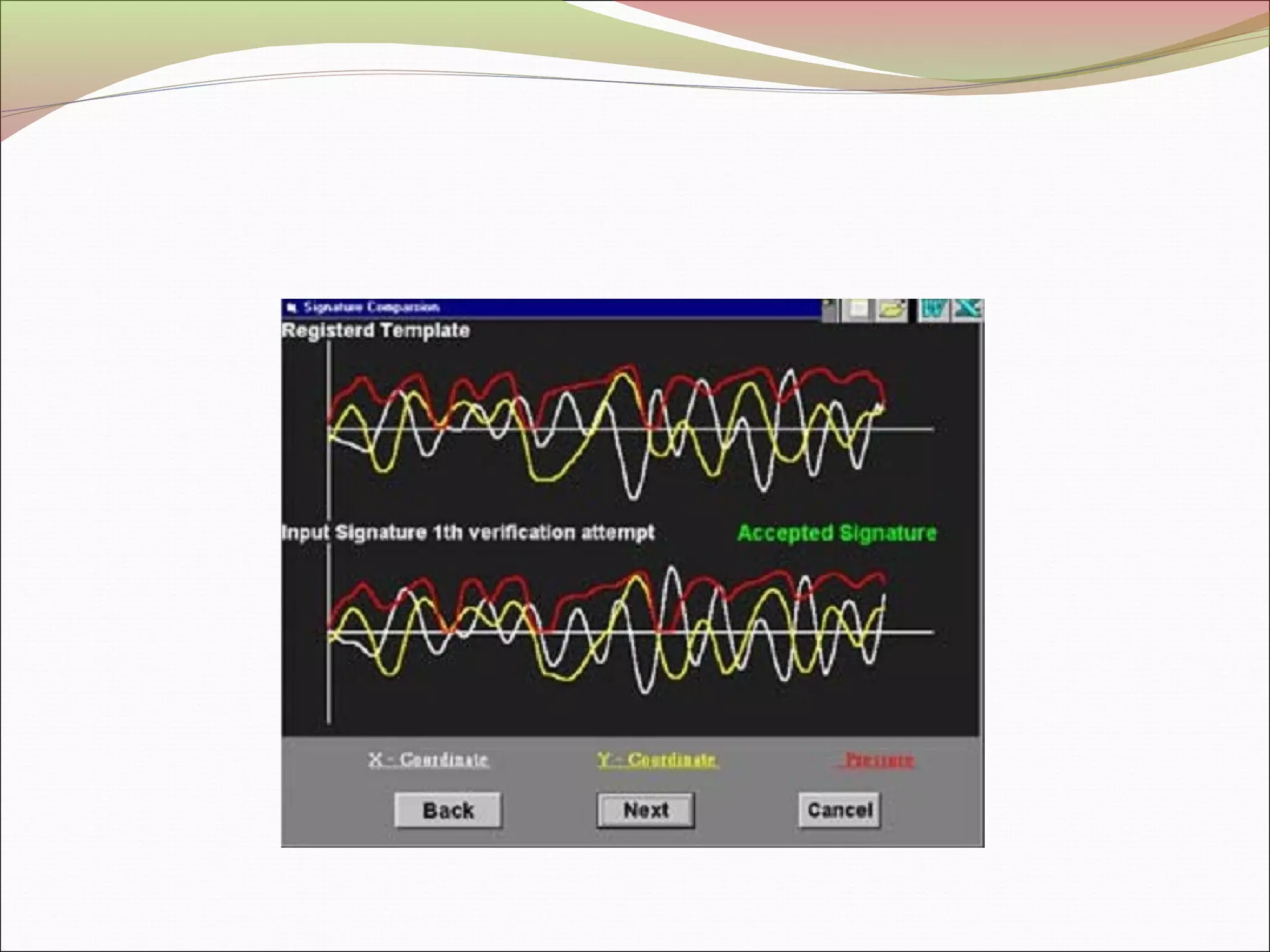
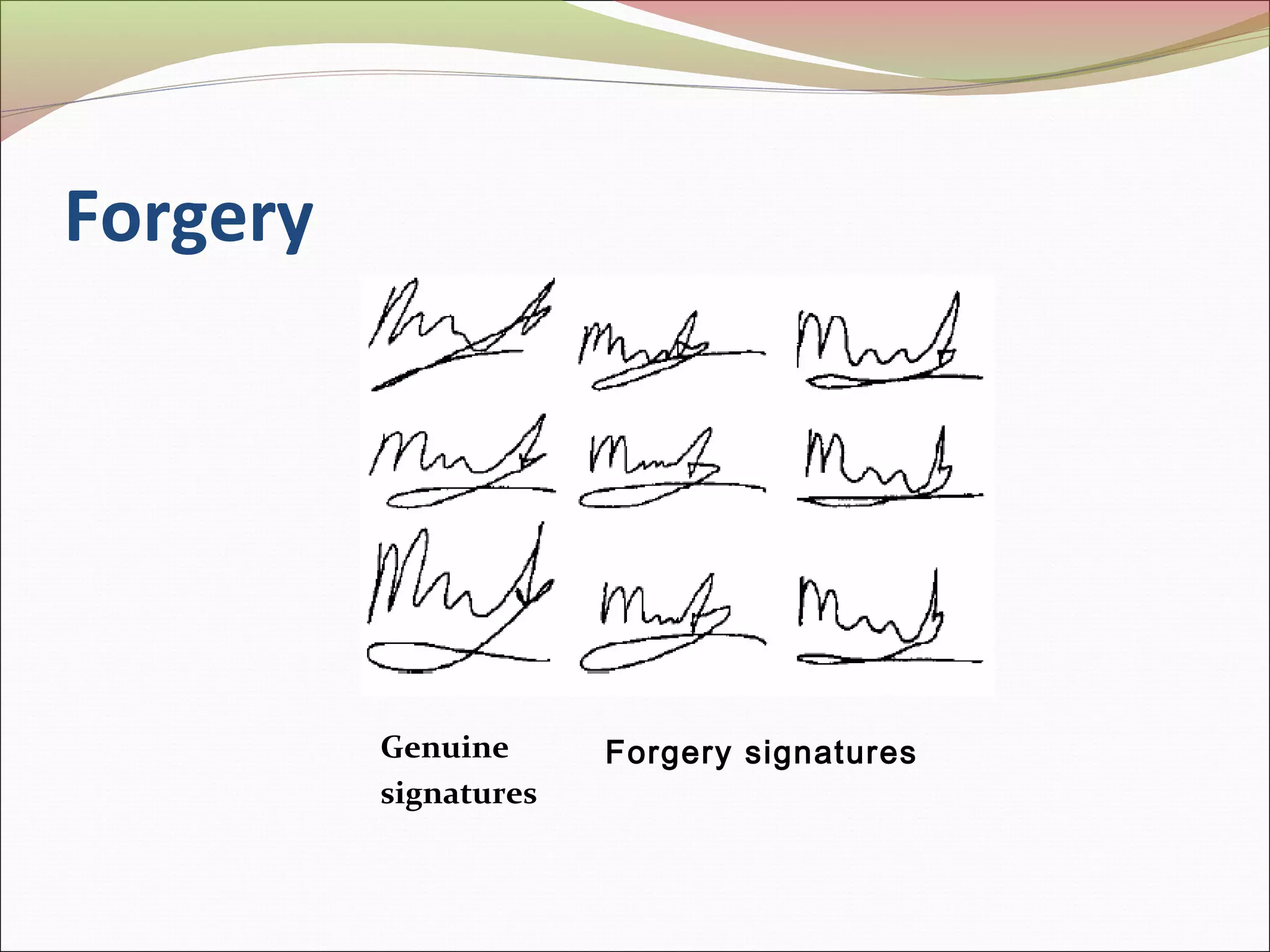
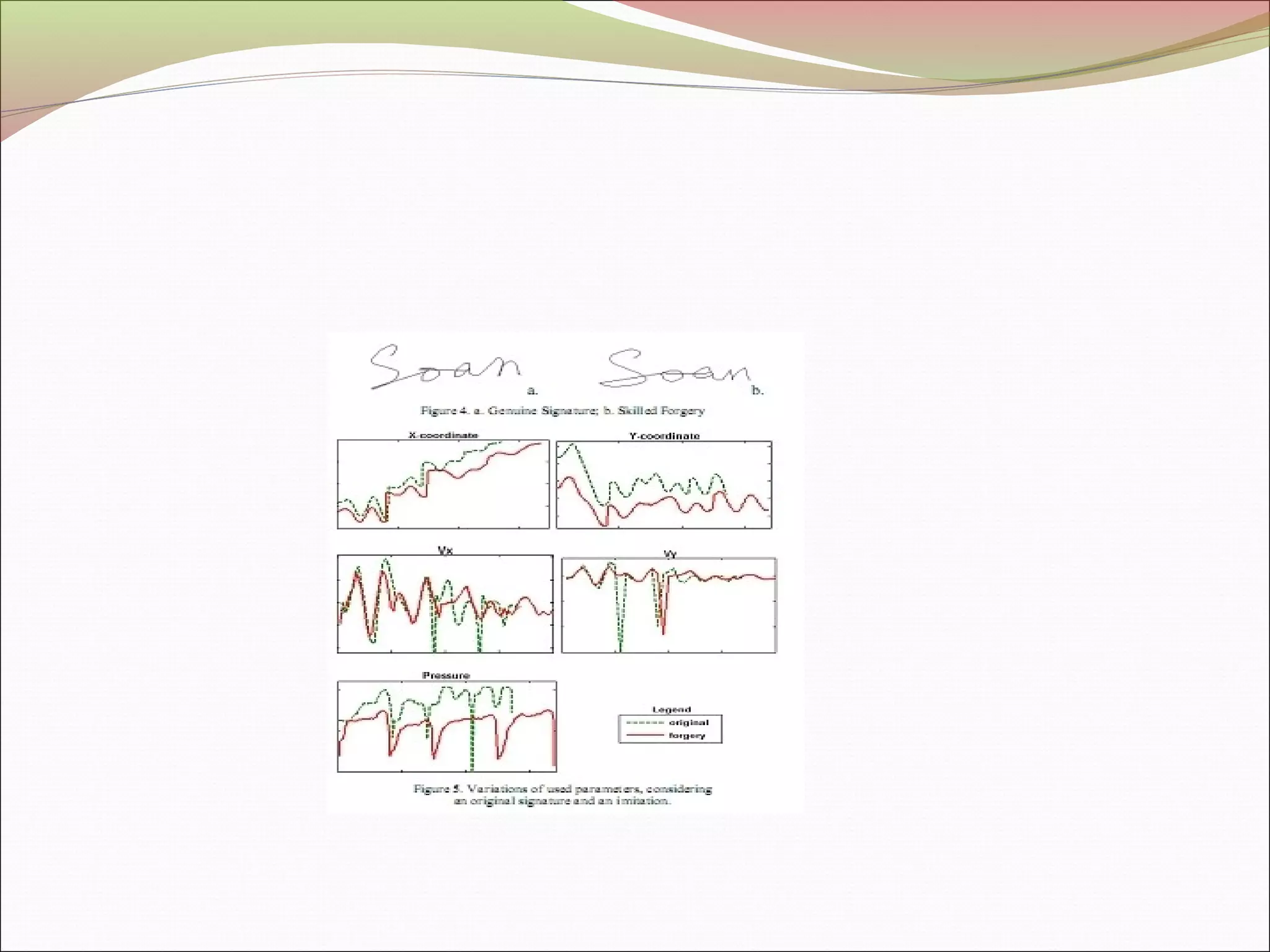
This document discusses signature recognition as a biometric for identity verification. It defines offline and online signatures, and describes how pen tablets digitize dynamic signatures. The document outlines the key steps of signature recognition systems, including pre-processing, feature extraction of local and global traits, modeling signatures, and detecting forgeries. It notes advantages of signatures being intuitive and independent of language, but also challenges around hardware costs and inconsistent writing abilities.