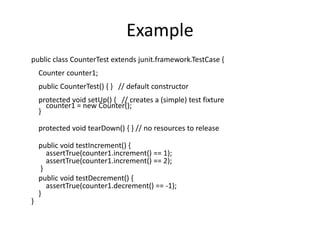
This document provides an overview of how to create test classes and methods in JUnit and mock objects using frameworks like PowerMock and EasyMock. It describes how to define a test class that extends TestCase and overrides setUp(), tearDown(), and testXXX() methods. It also explains how PowerMock allows mocking static methods, private methods, final classes/methods by using annotations and bytecode manipulation.