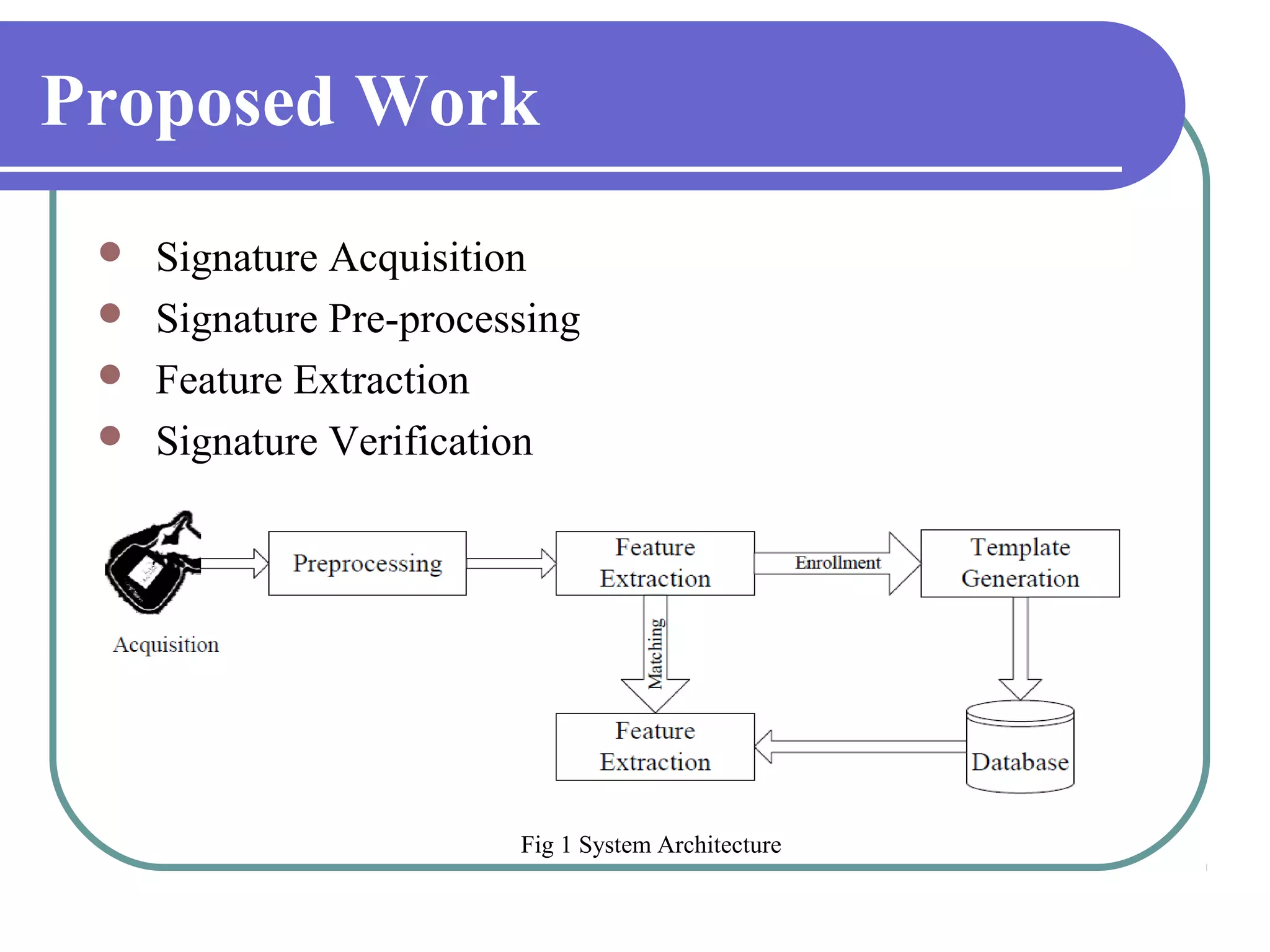
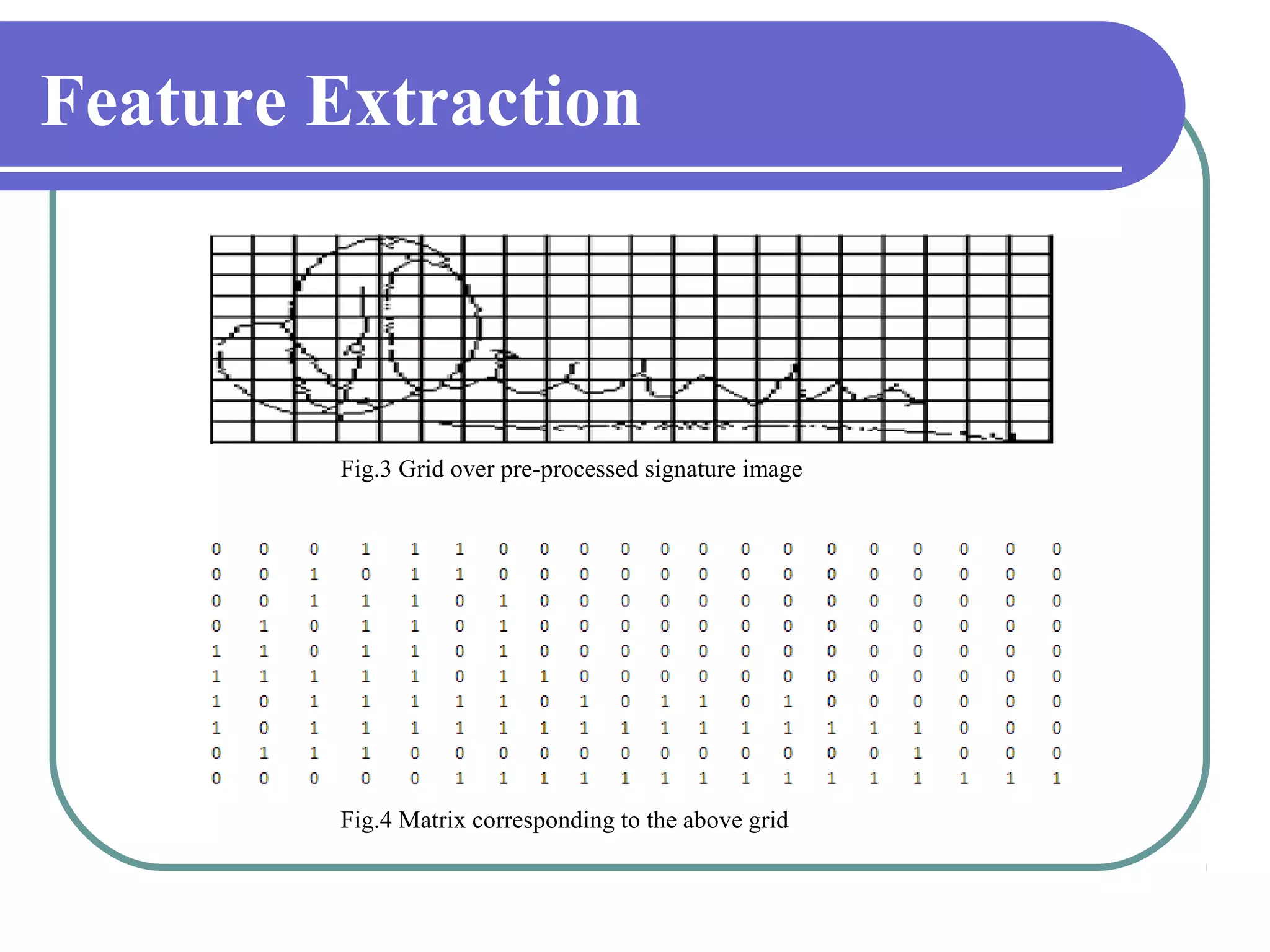
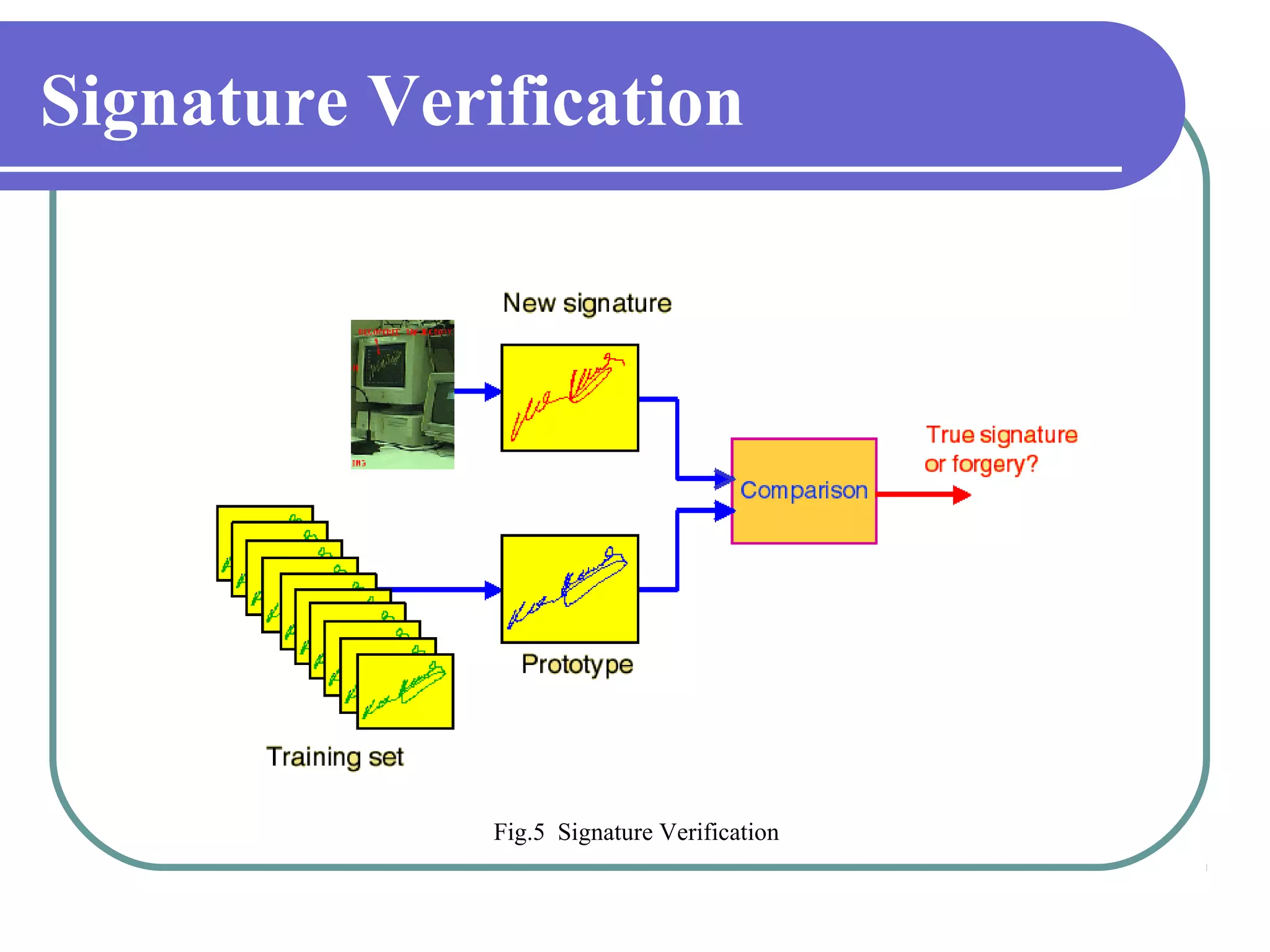
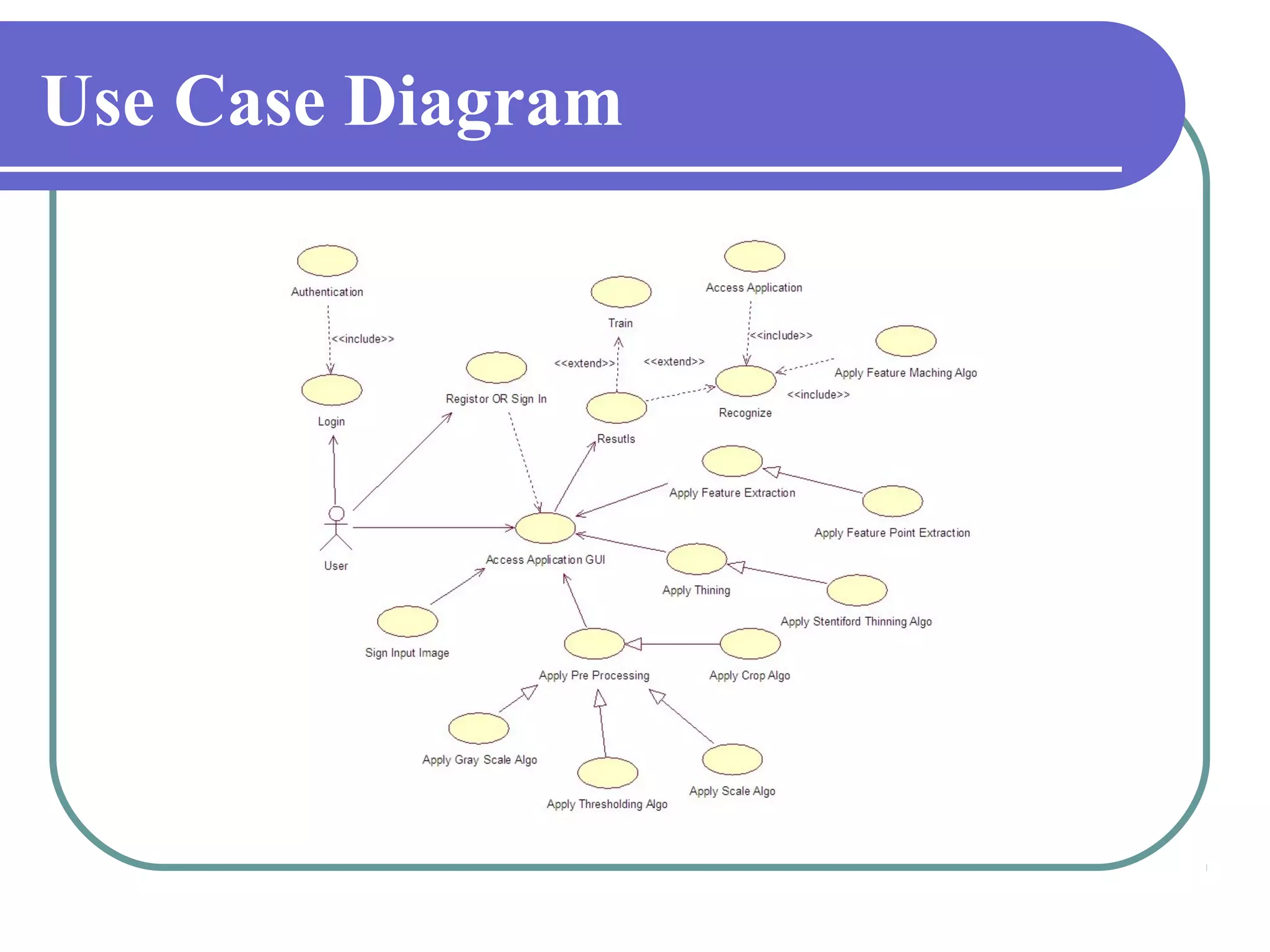
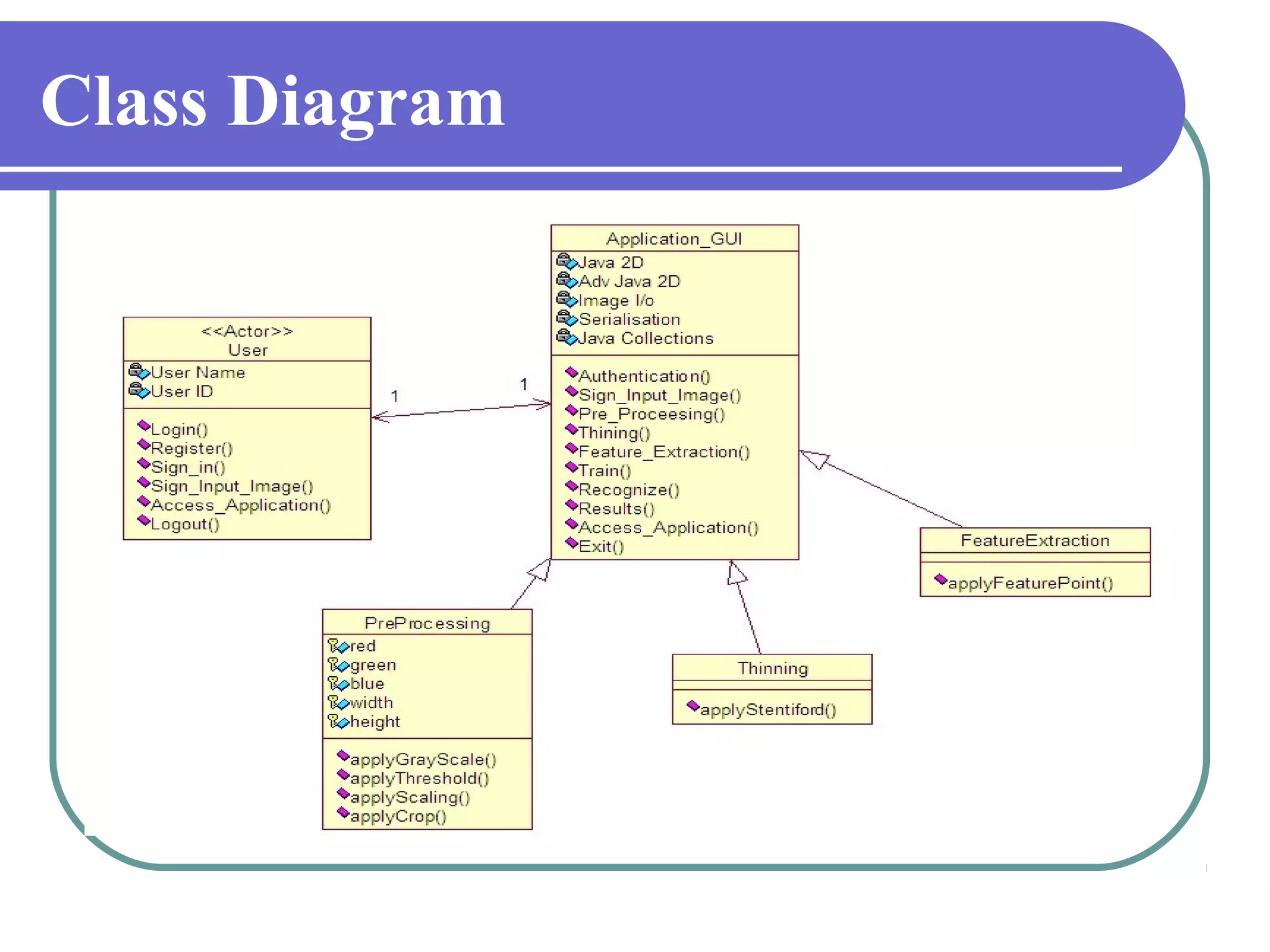
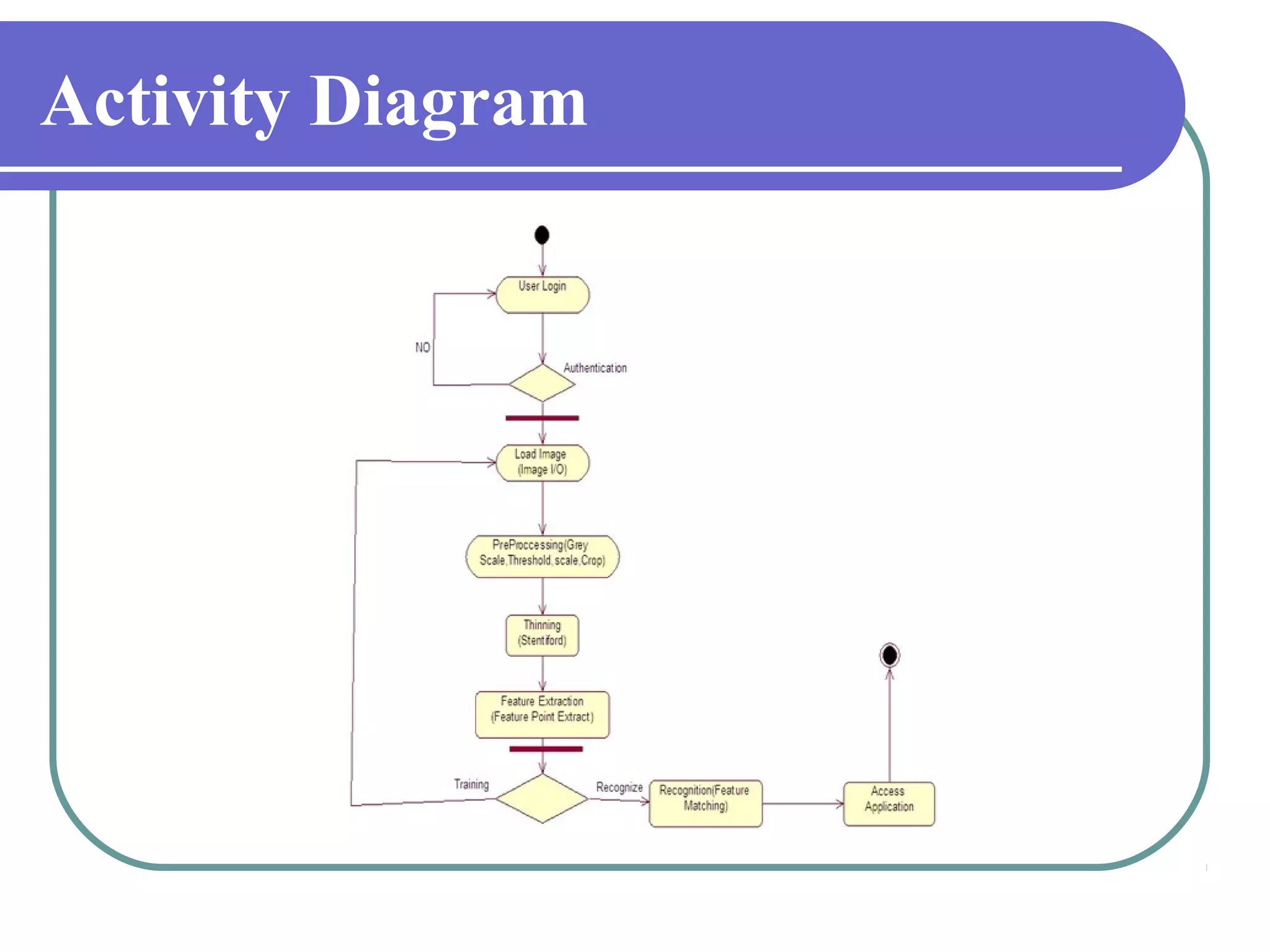
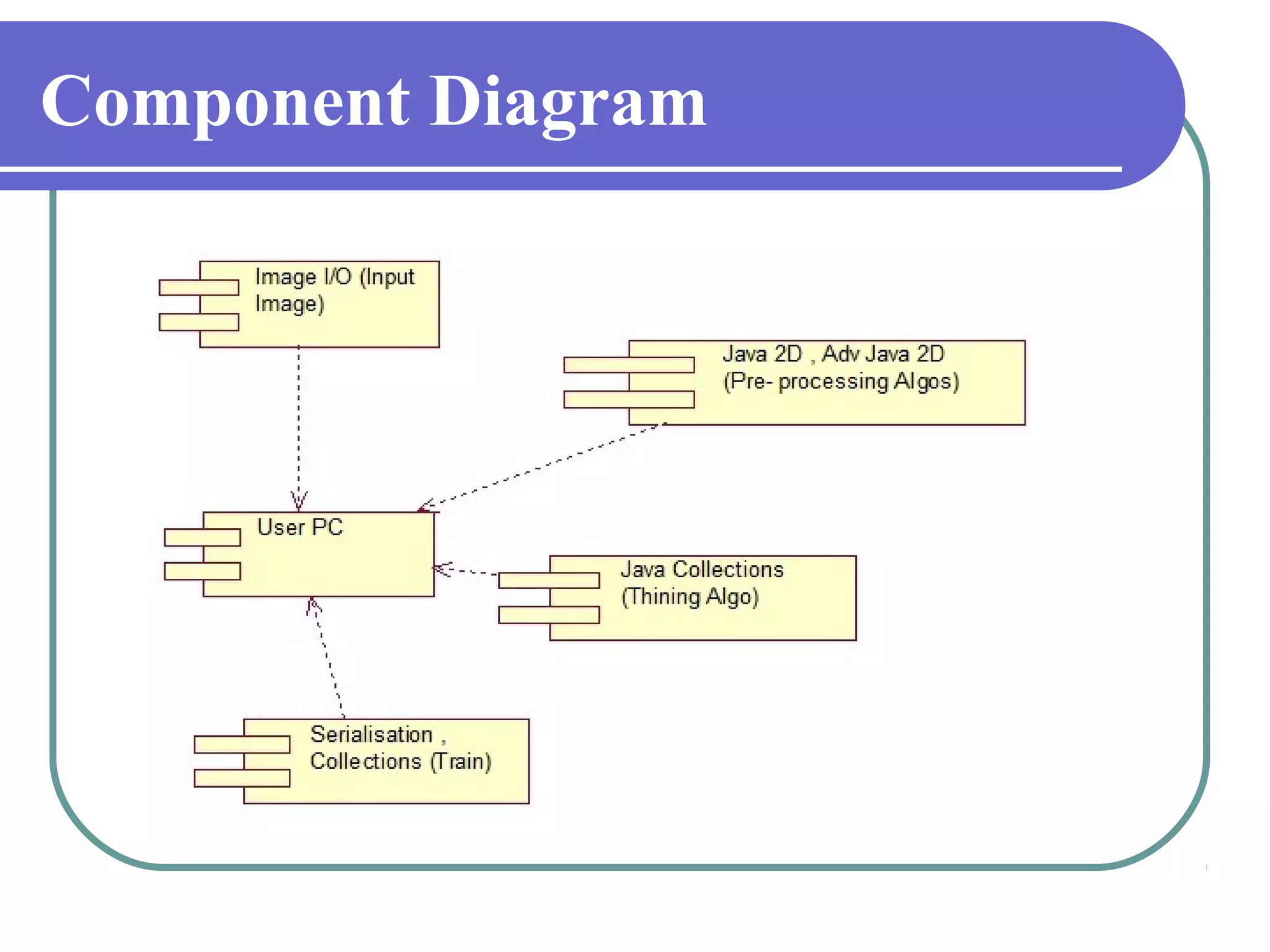
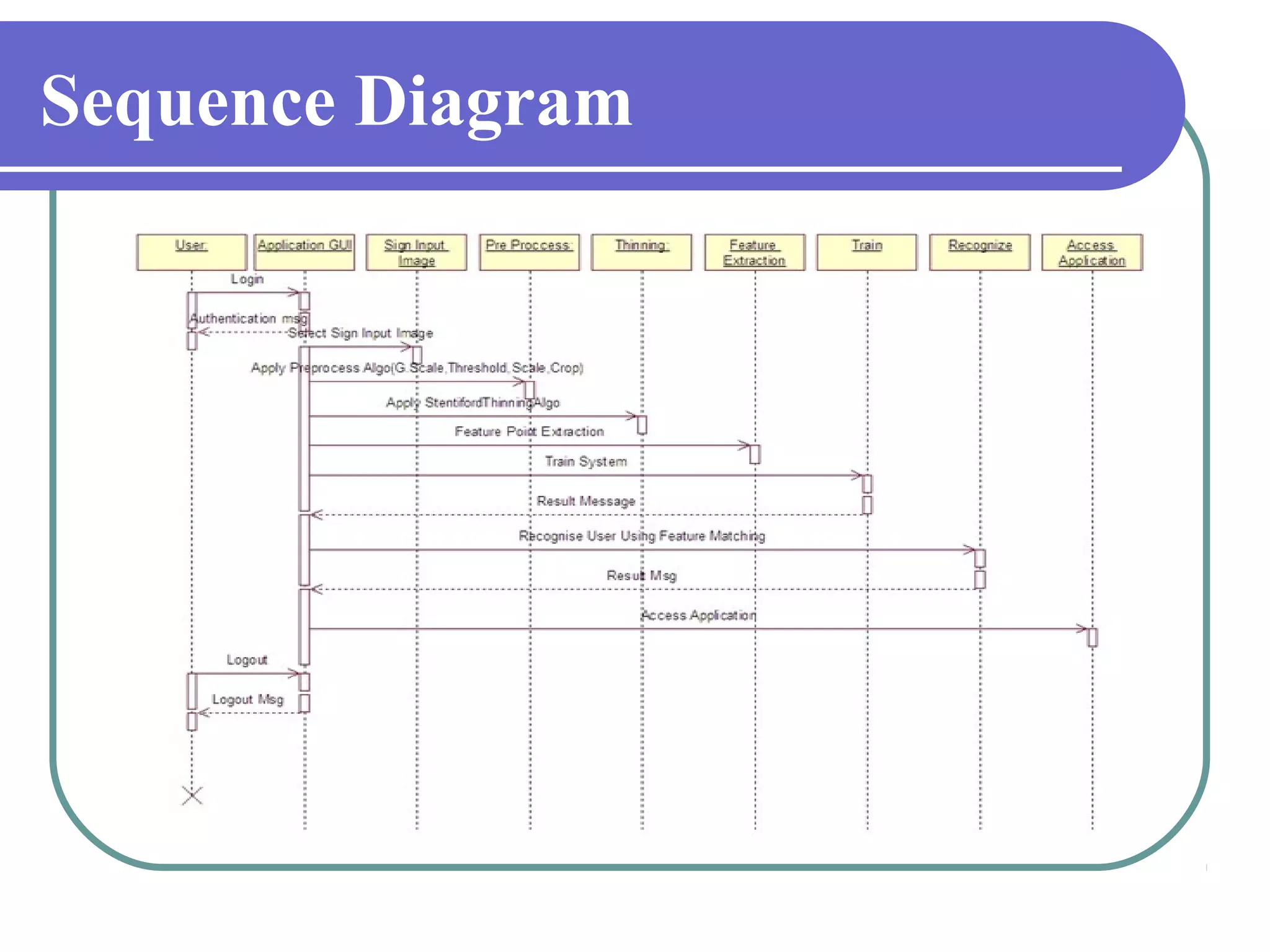
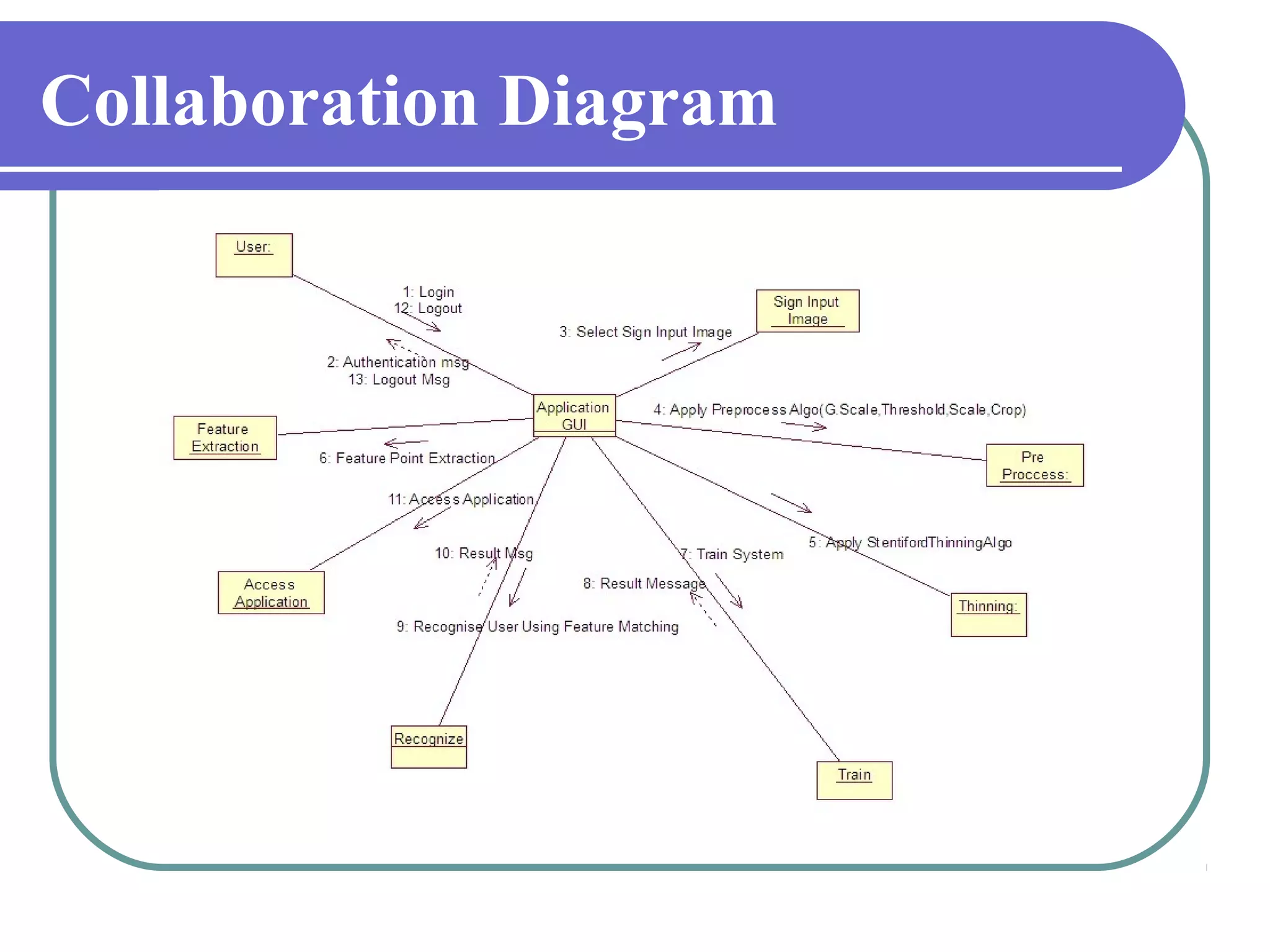
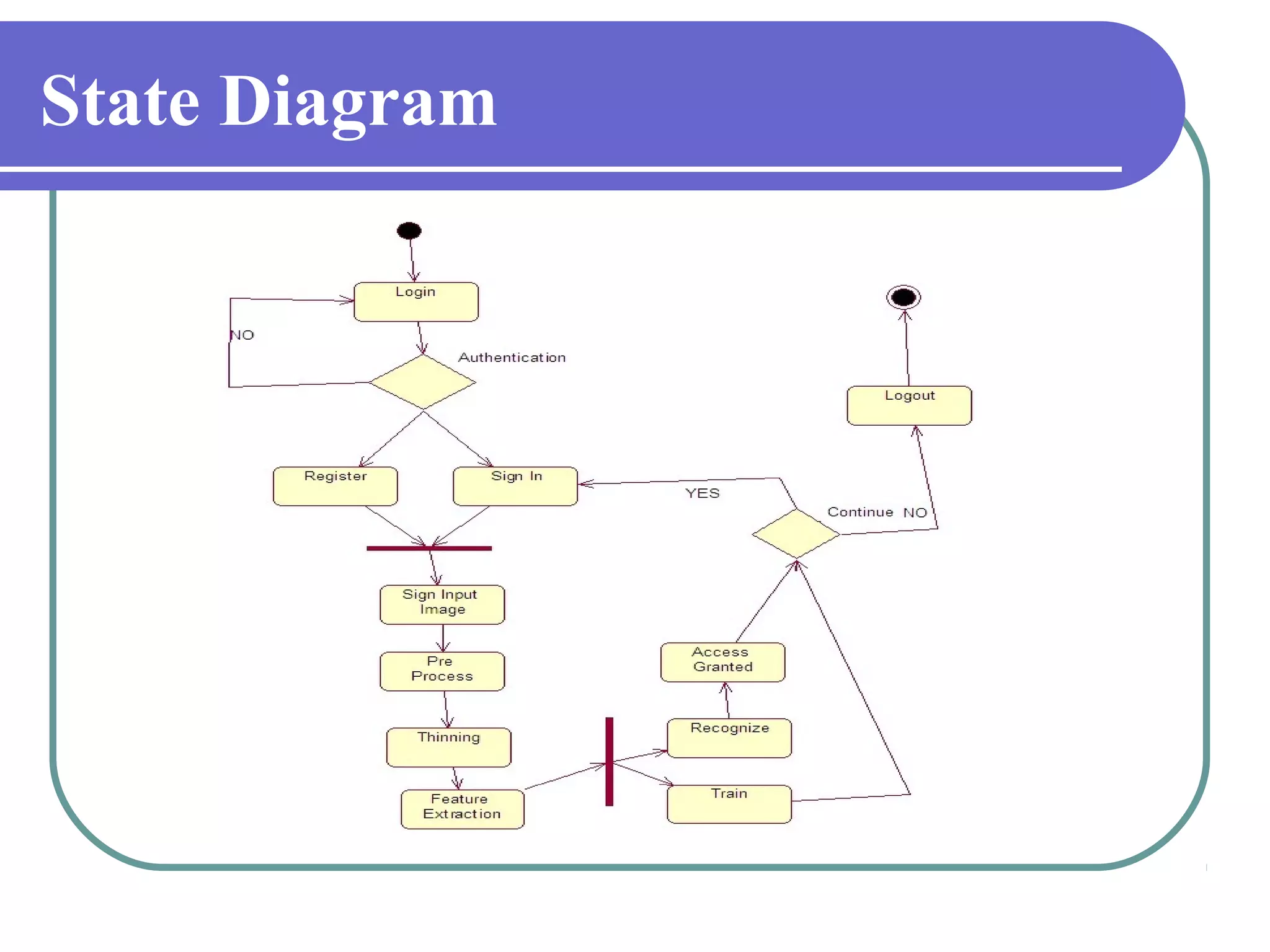
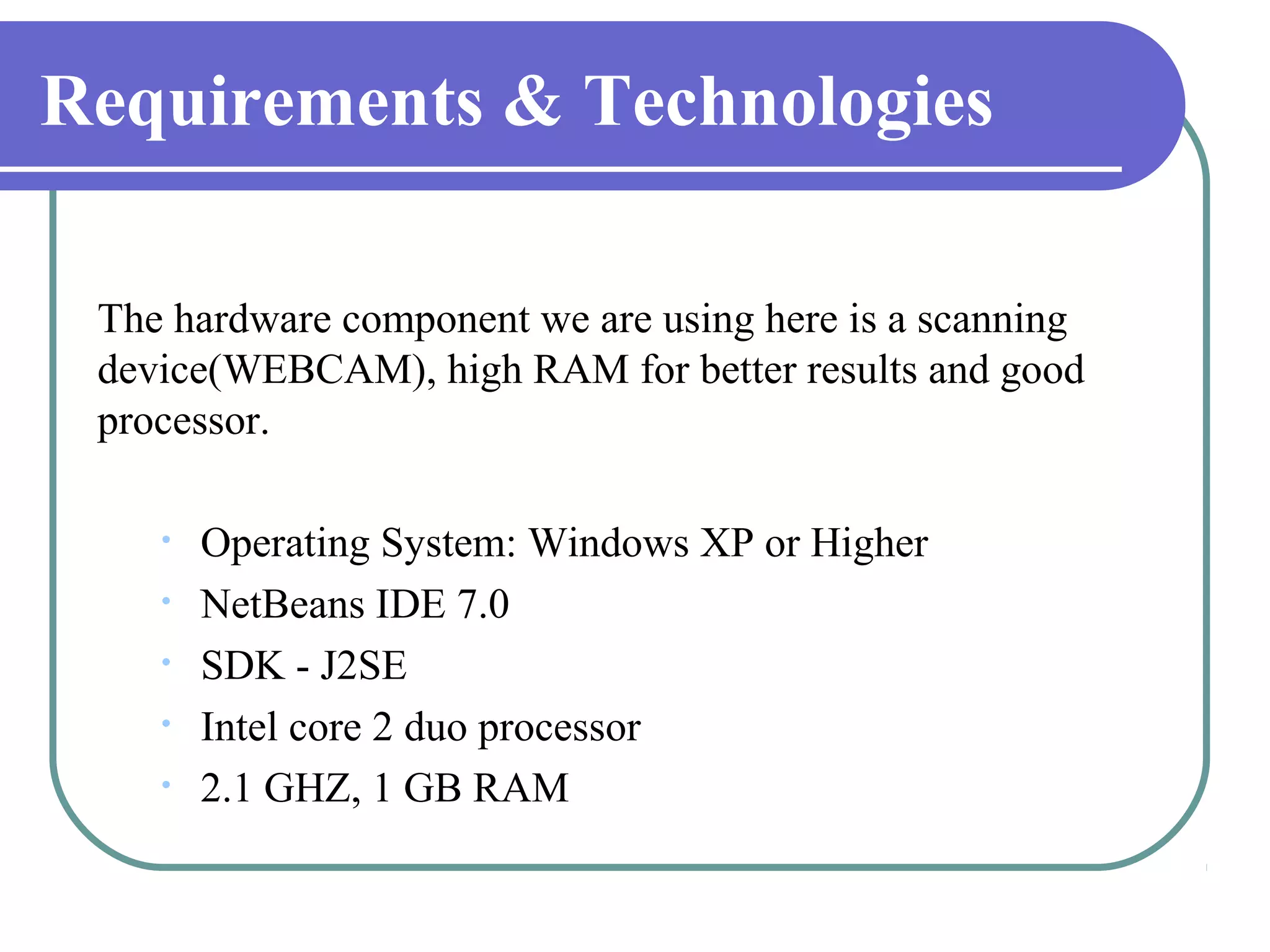
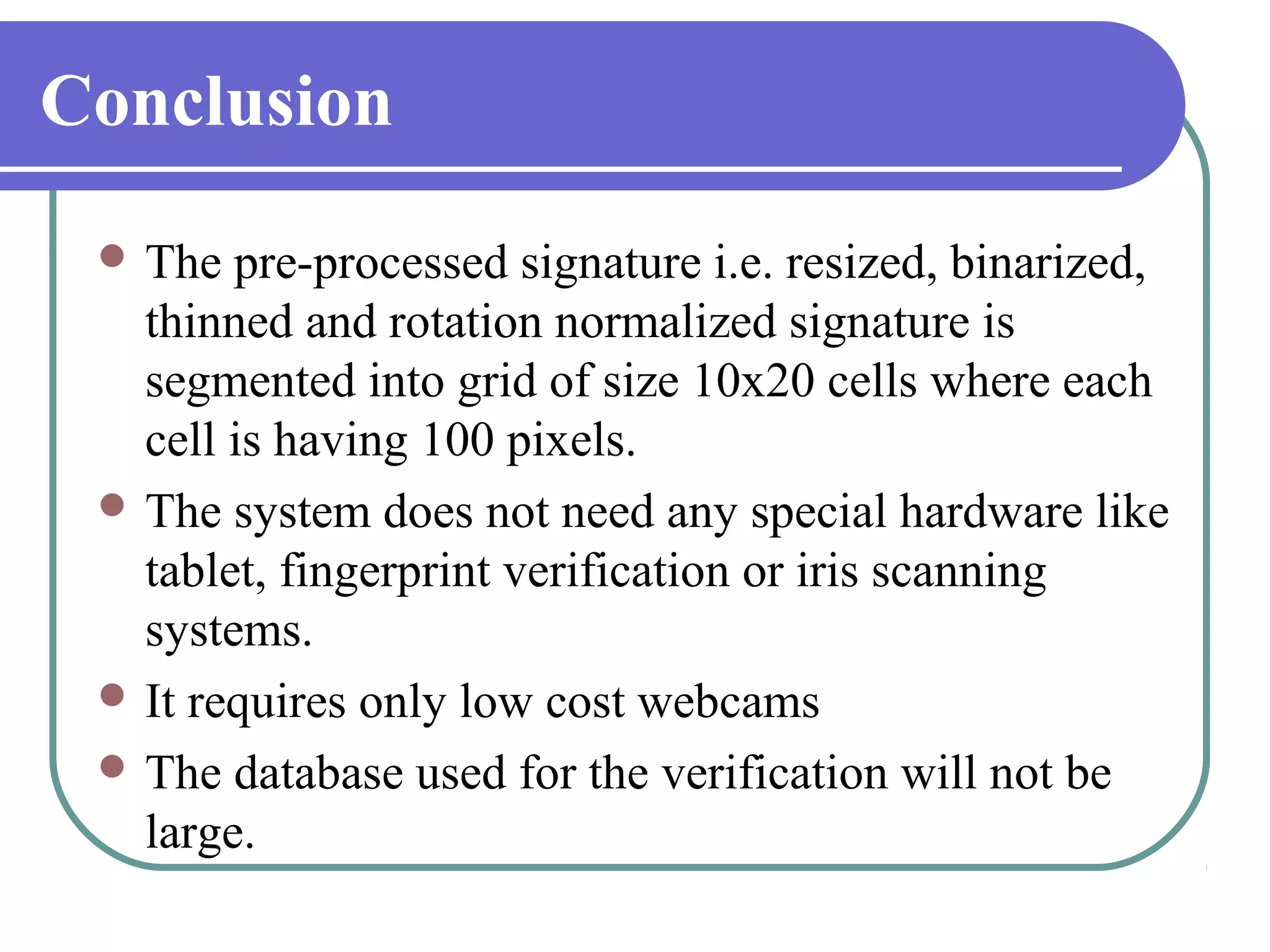
This document proposes a grid-based feature extraction method for offline signature verification. It begins with an introduction and discusses existing techniques and their limitations. It then presents the proposed work, which involves signature acquisition, preprocessing, feature extraction by segmenting the signature image into a grid, and verification. The algorithms, mathematical model, advantages and applications are described. The document concludes that the proposed method requires only low-cost hardware and has a low error rate for signature verification.