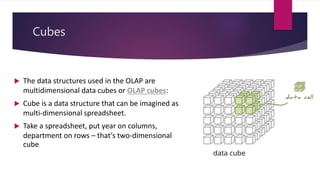
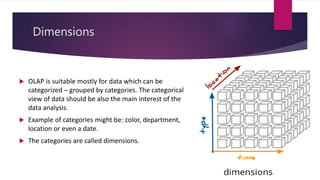
OLAP (online analytical processing) allows users to easily extract and view data from different perspectives. It was invented by Edgar Codd in the 1980s and uses multidimensional data structures called cubes to store and analyze data. OLAP utilizes either a multidimensional (MOLAP), relational (ROLAP), or hybrid (HOLAP) approach to store cube data in databases and provide interactive analysis of data.