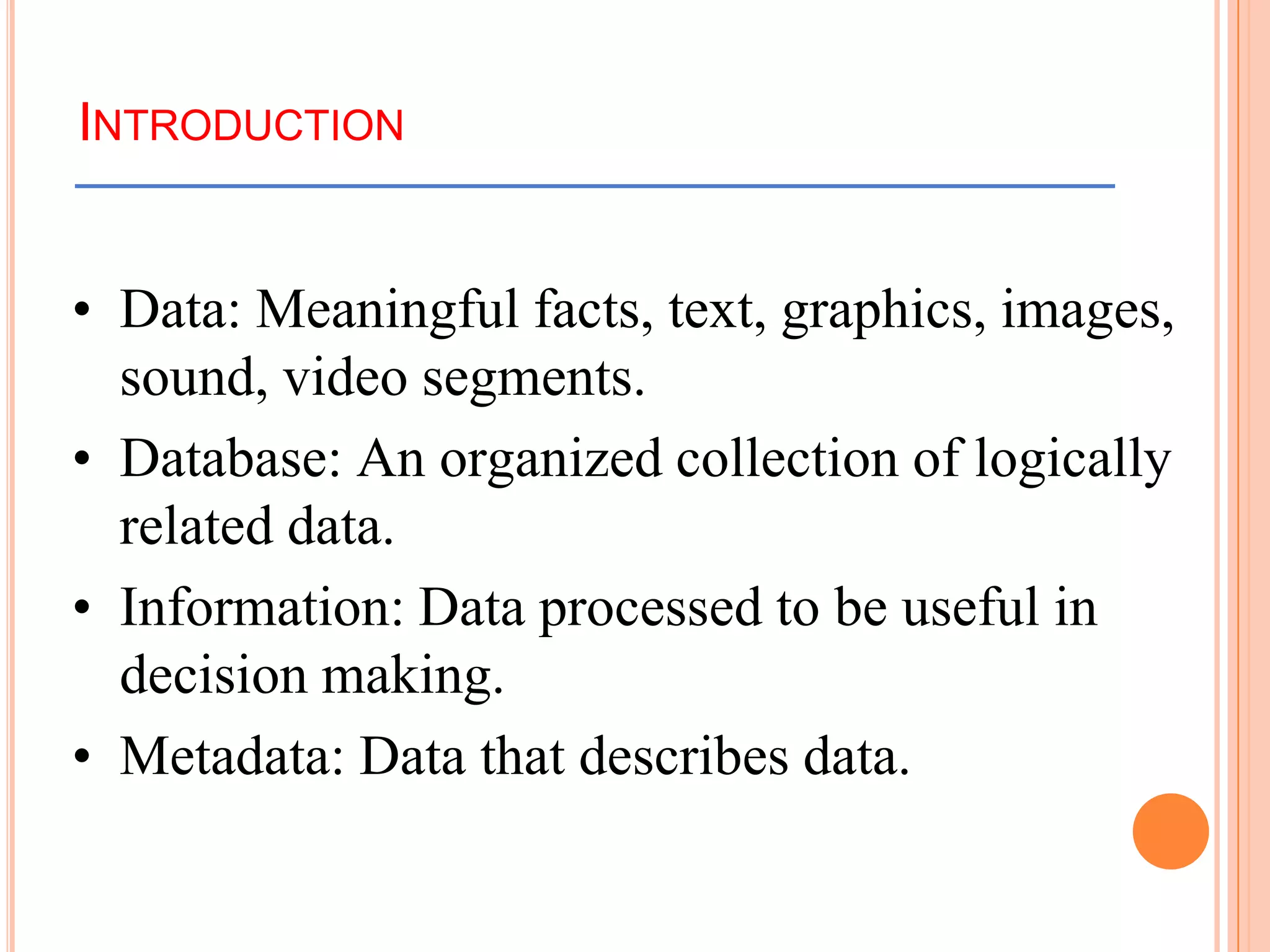
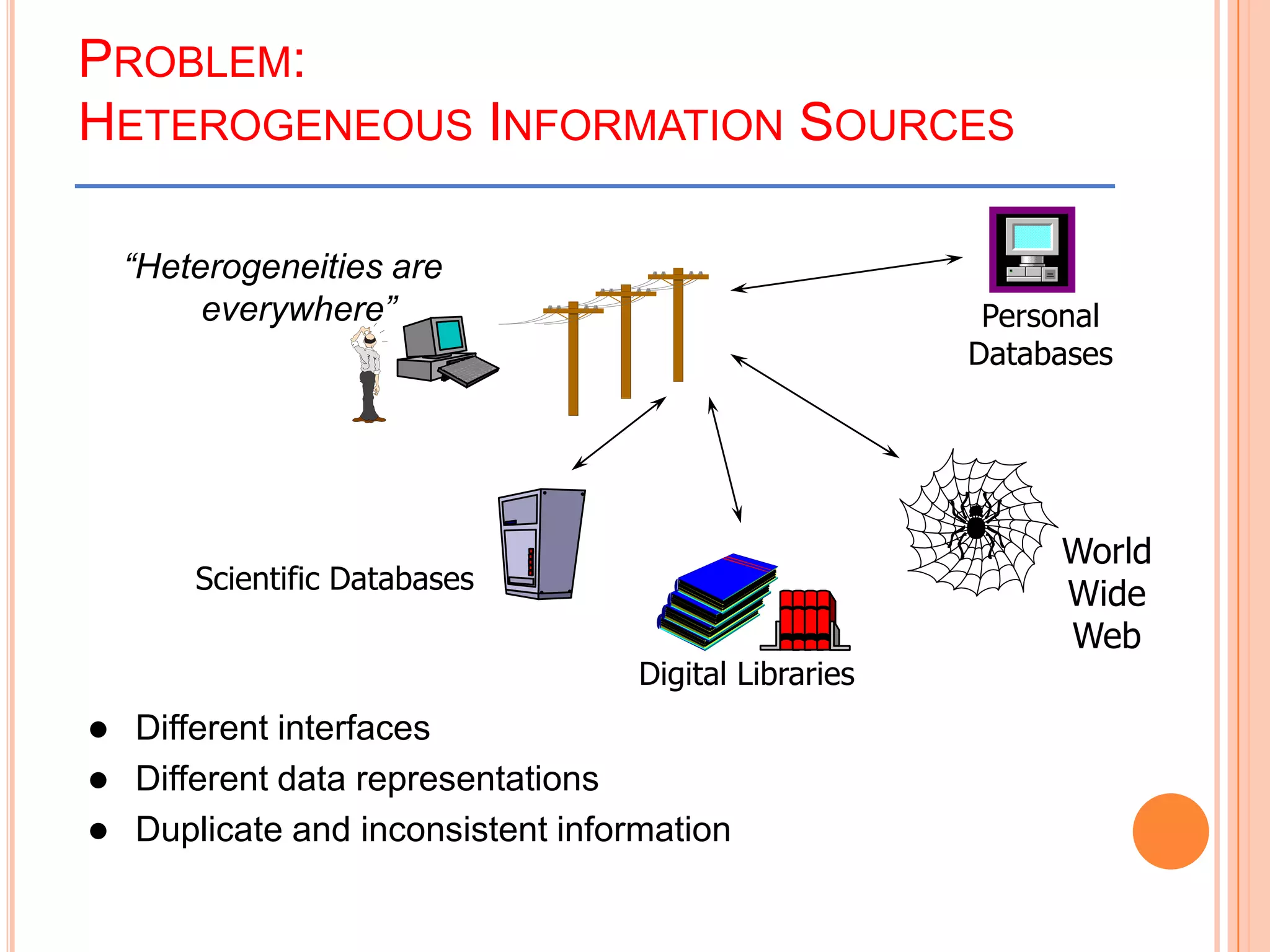
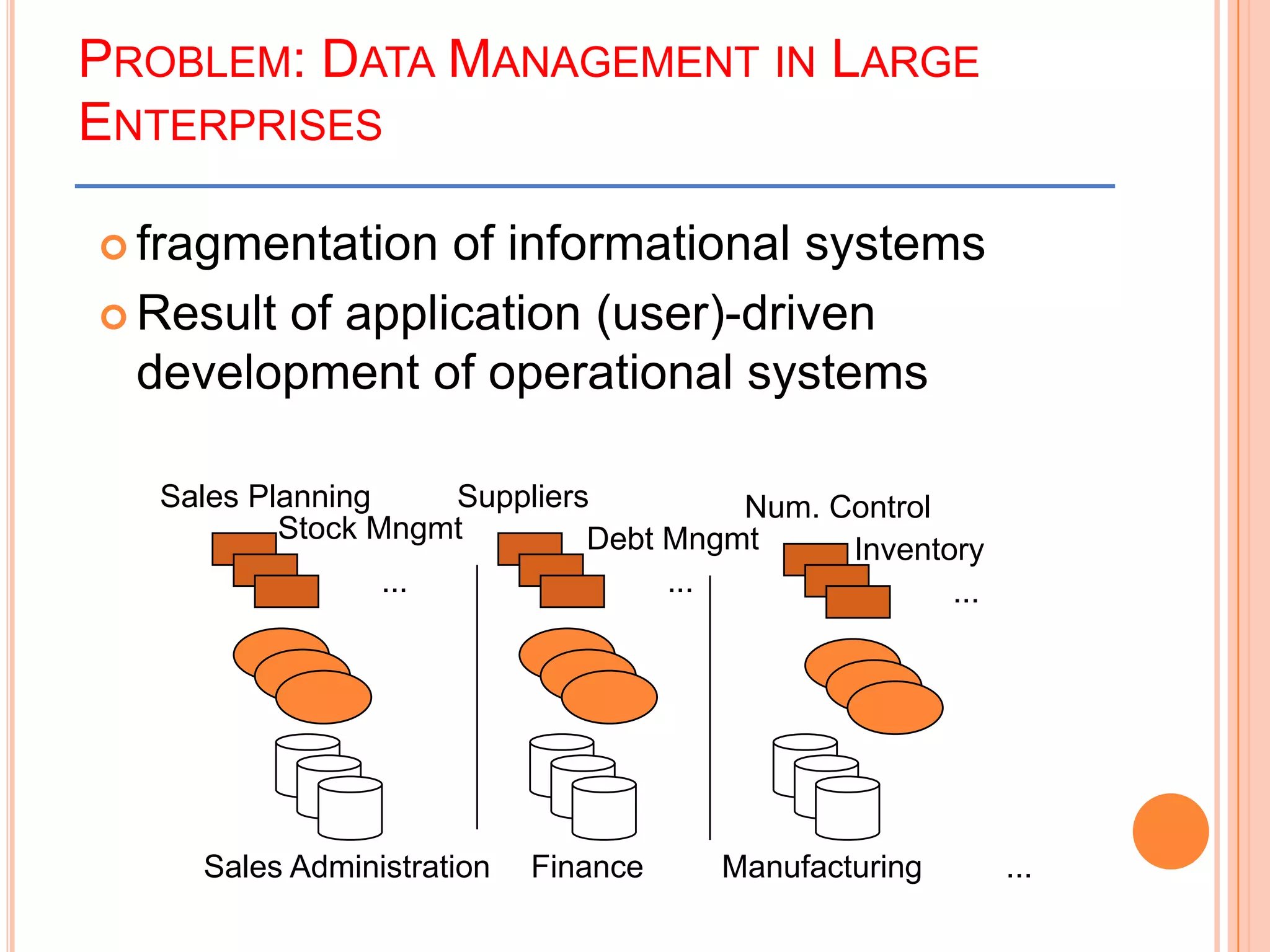
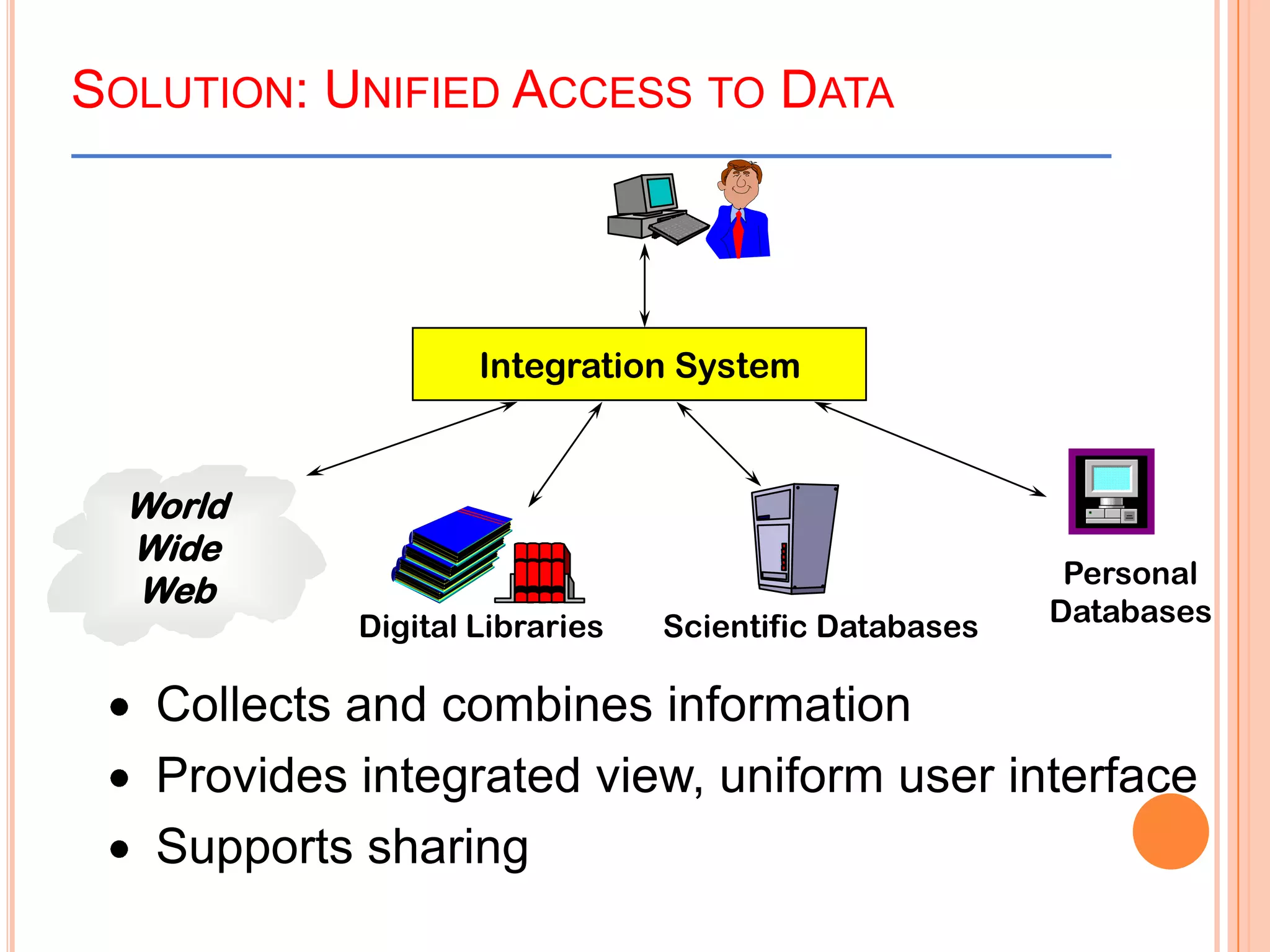
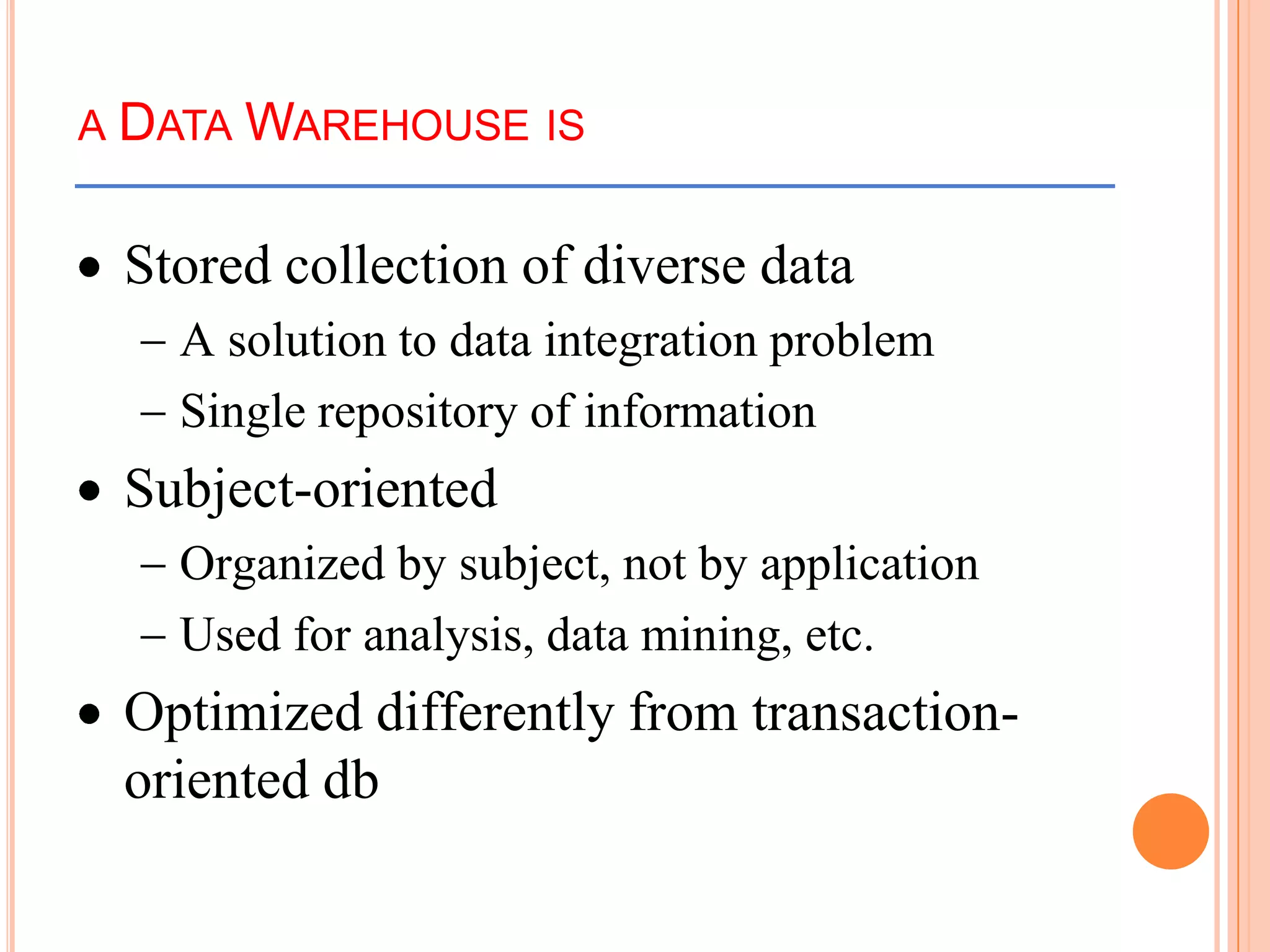
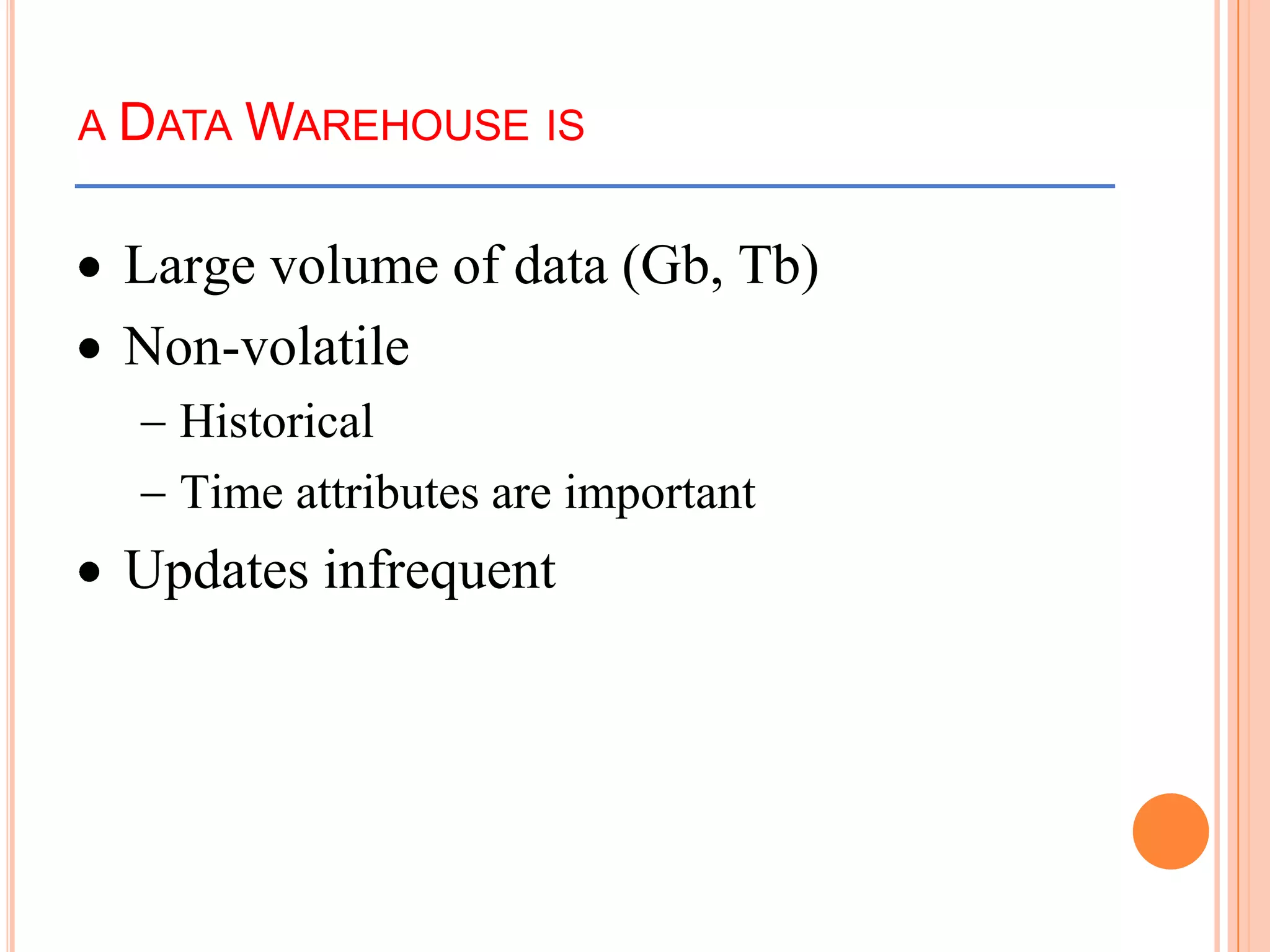
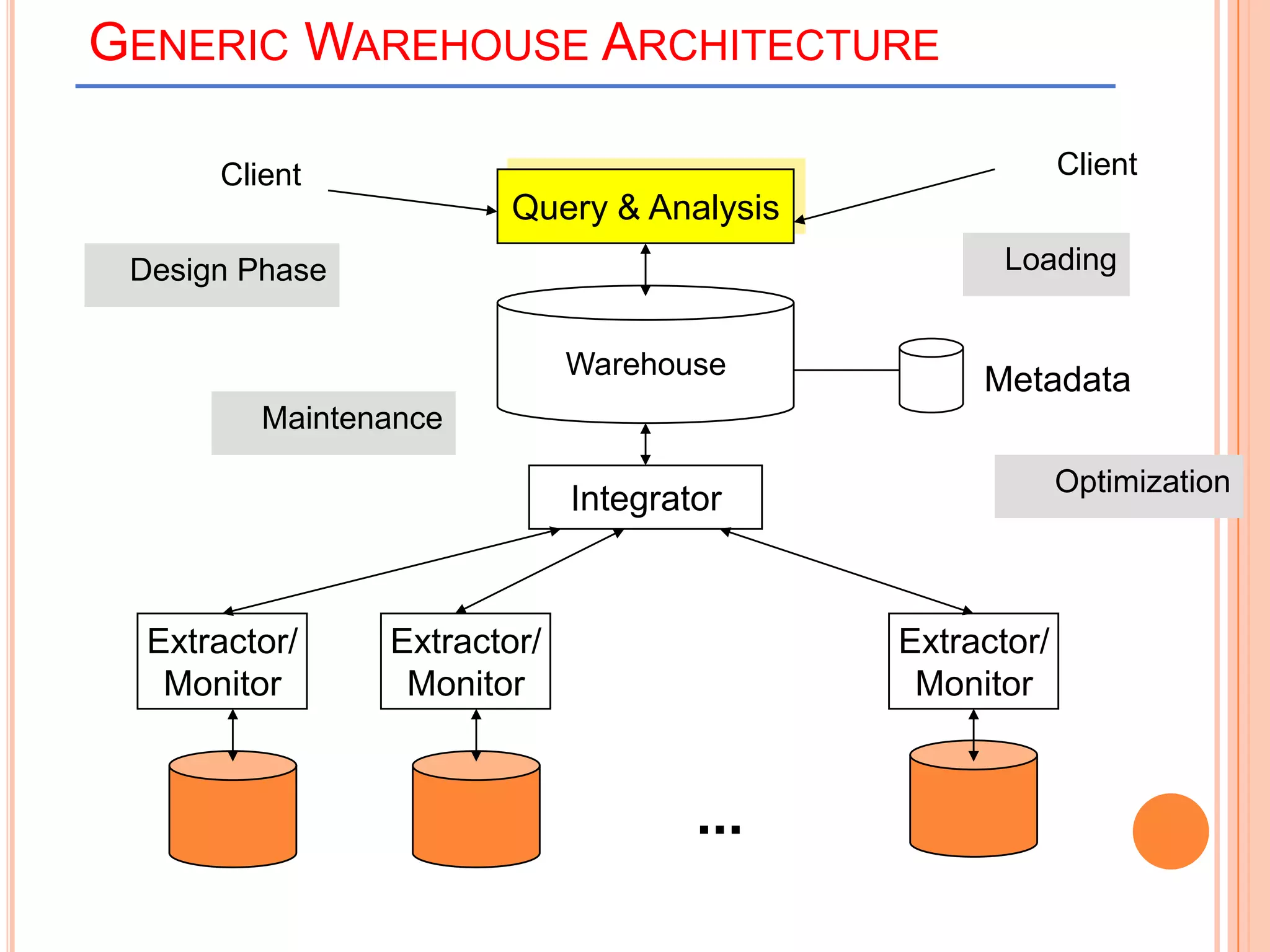
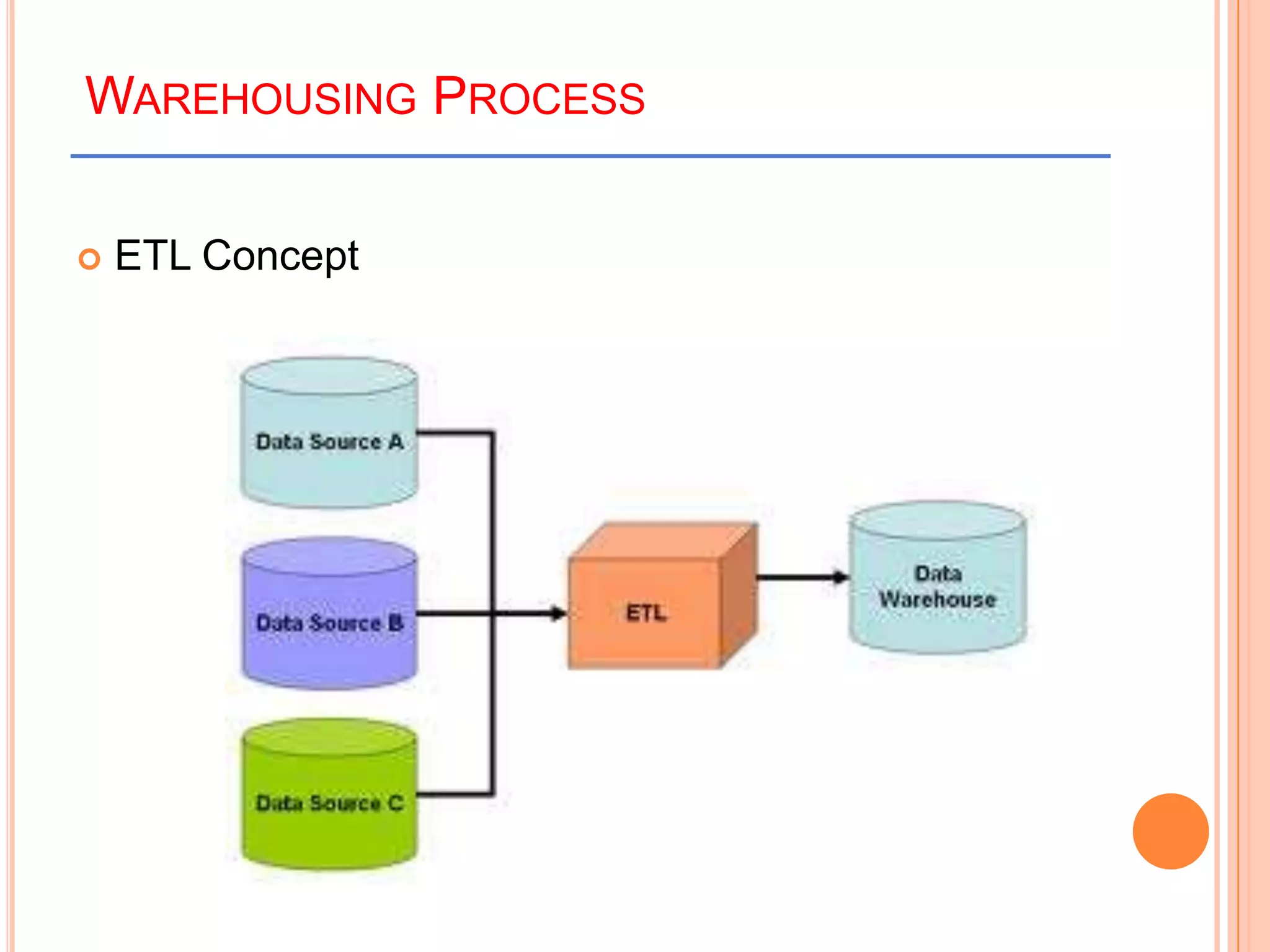
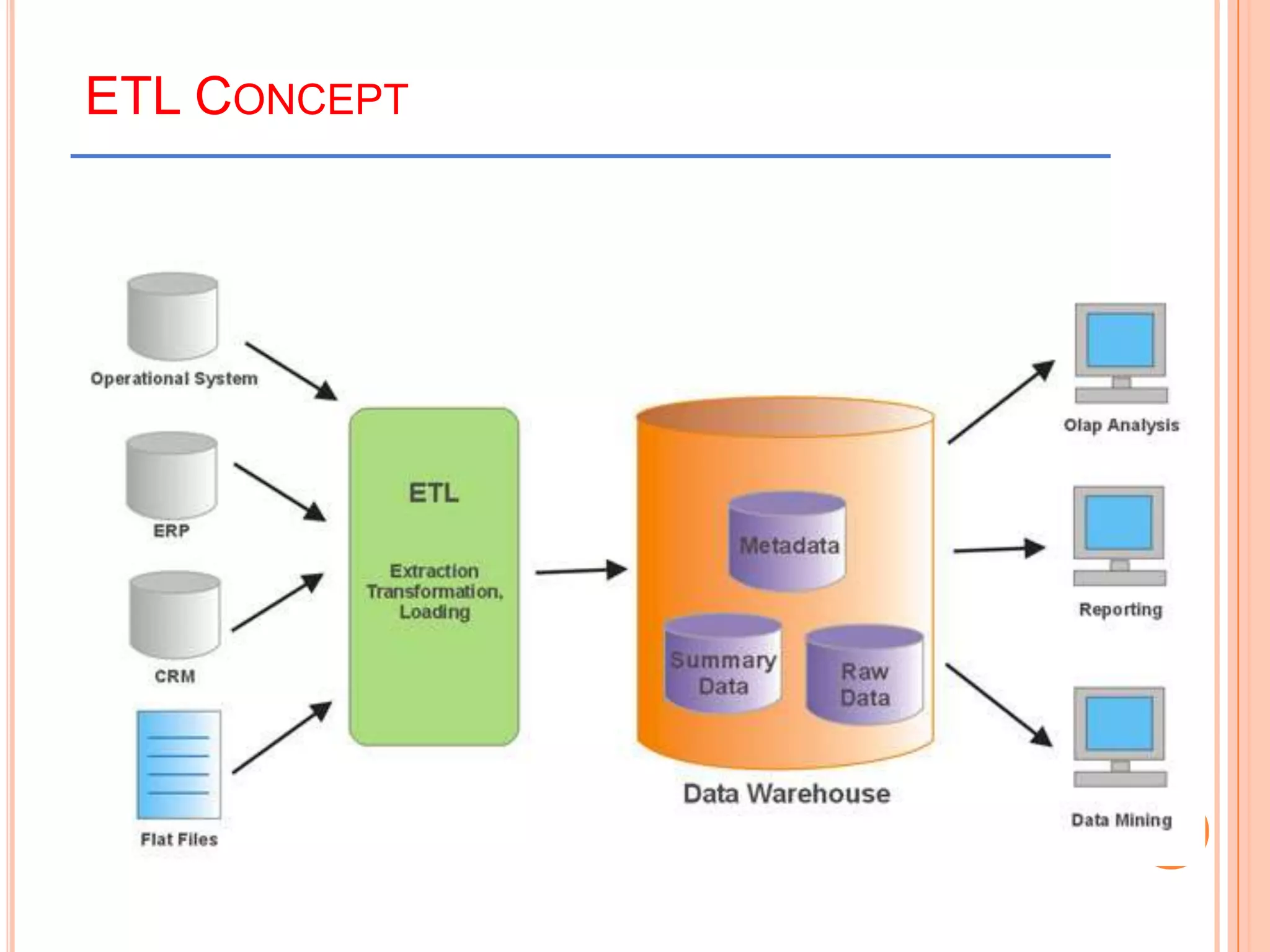
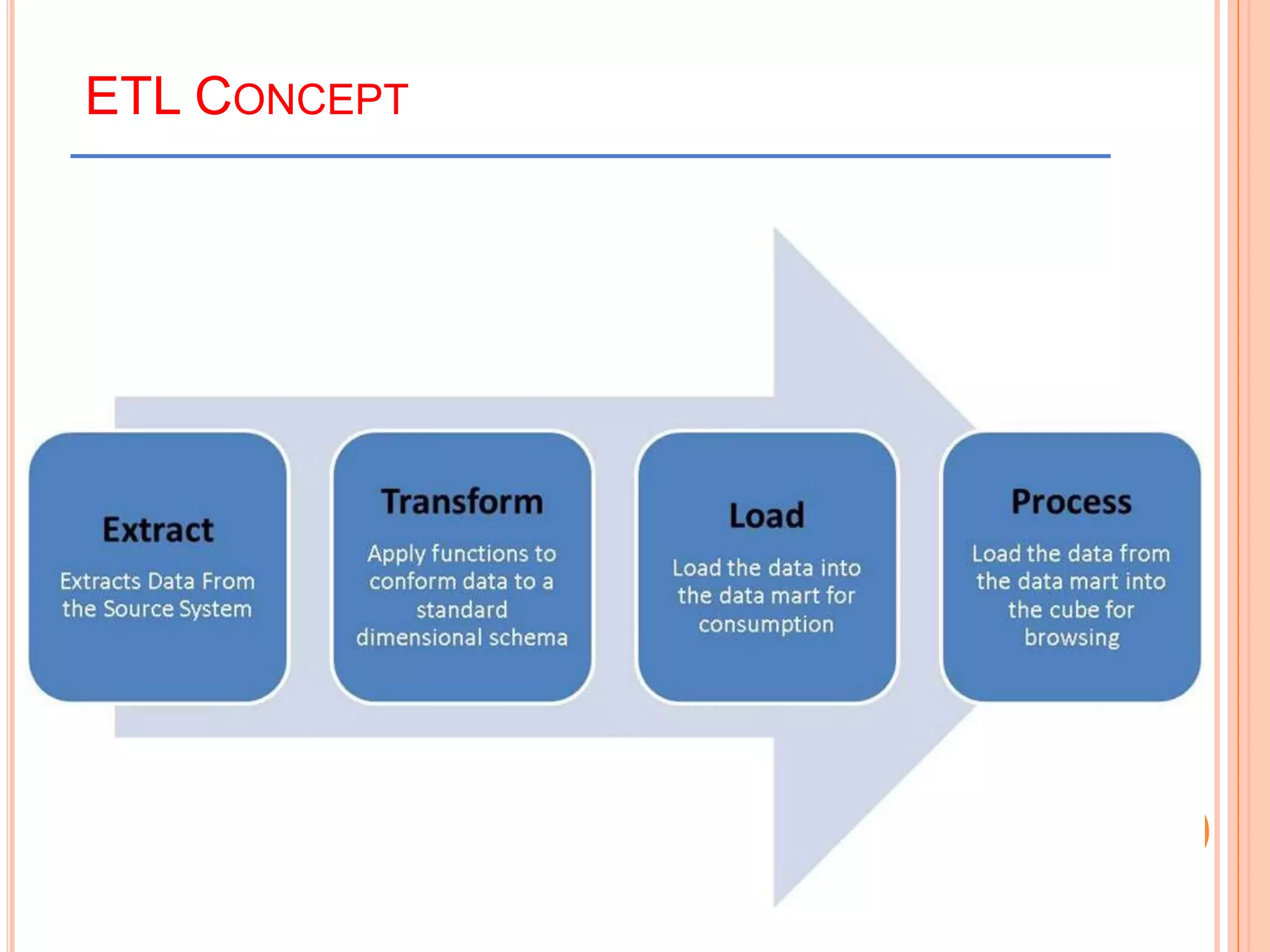
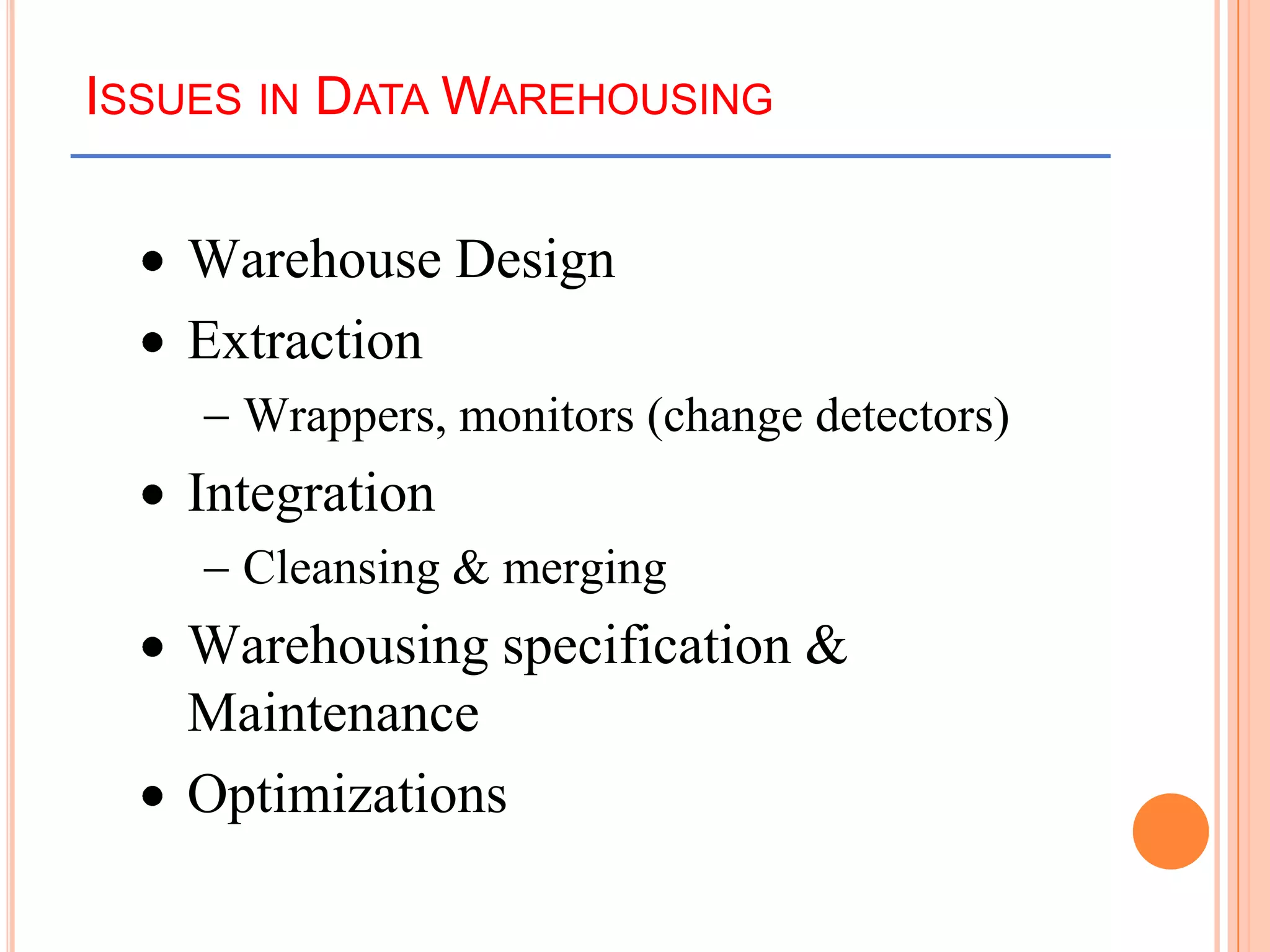
This document provides an introduction to data warehousing. It defines key concepts like data, databases, information and metadata. It describes problems with heterogeneous data sources and fragmented data management in large enterprises. The solution is a data warehouse, which provides a unified view of data from various sources. A data warehouse is defined as a subject-oriented, integrated collection of historical data used for analysis and decision making. It differs from operational databases in aspects like data volume, volatility, and usage. The document outlines the extract-transform-load process and common architecture of data warehousing.