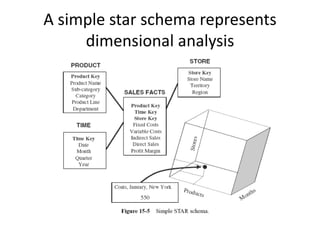
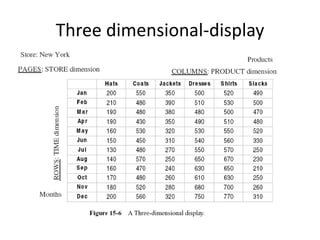
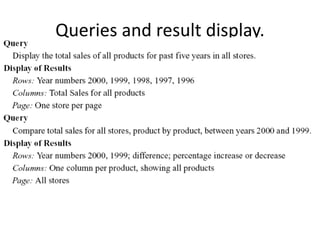
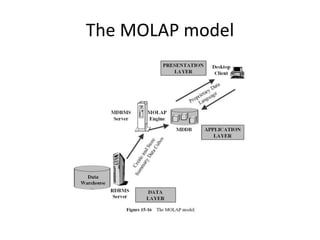
This document summarizes an seminar on online analytical processing (OLAP). It discusses key features of OLAP including dimensional analysis using star schemas and cube representations. It also describes the different OLAP models including MOLAP, ROLAP, and DOLAP. Considerations for implementing OLAP systems are outlined such as data design, tool selection, and implementation steps. The benefits of OLAP for increased productivity, flexibility, and efficient operations are also highlighted.