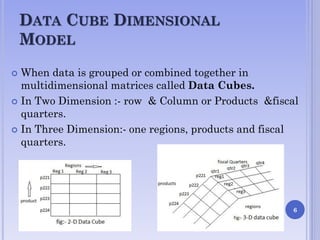
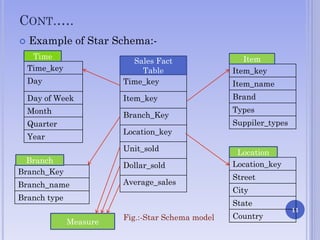
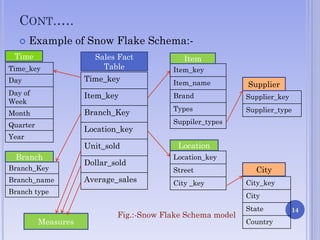
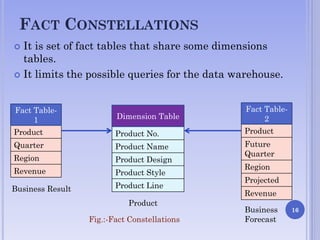
The document presents on multidimensional data models. It discusses the key components of multidimensional data models including dimensions and facts. It describes different types of multidimensional data models such as data cube model, star schema model, snowflake schema model, and fact constellations. The star schema model and snowflake schema model are explained in more detail through examples and their benefits are highlighted.
![MULTIDIMENSIONAL DATA MODEL(MDDM)
Content:-
1. Introduction of MDDM.
2. Component of MDDM.
3. Types of MDM.
[A]. Data Cube Model.
[B]. Star Schema Model.
[C]. Snow Flake Schema Model.
[D]. Fact Constellations.
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multidimentionaldatamodel-121012060705-phpapp02/85/Multidimentional-data-model-2-320.jpg)


![TYPES OF MDDM
[A]. Data Cube Model.
[B]. Star Schema Model.
[C]. Snow Flake Schema Model.
[D]. Fact Constellations.
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/multidimentionaldatamodel-121012060705-phpapp02/85/Multidimentional-data-model-5-320.jpg)