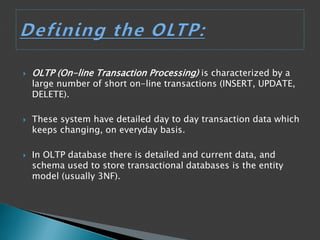
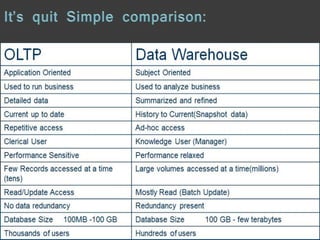
A data warehouse uses a repository to store aggregated, historical data from multiple OLTP databases in a multidimensional schema for online analytical processing (OLAP) through complex queries. In contrast, OLTP systems have detailed, current transactional data stored in a normalized schema to support a large volume of simple queries and updates for daily business tasks. While both involve databases, OLTP focuses on real-time transactions while OLAP supports analysis, planning and decision making through consolidated data from OLTP systems.