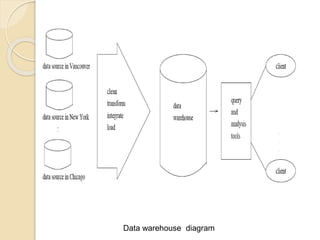
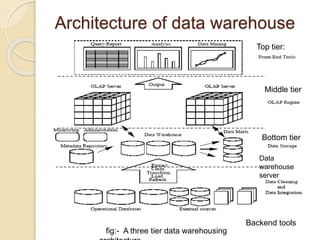
This document provides an overview of data warehousing. It defines data warehousing as collecting data from multiple sources into a central repository for analysis and decision making. The document outlines the history of data warehousing and describes its key characteristics like being subject-oriented, integrated, and time-variant. It also discusses the architecture of a data warehouse including sources, transformation, storage, and reporting layers. The document compares data warehousing to traditional DBMS and explains how data warehouses are better suited for analysis versus transaction processing.