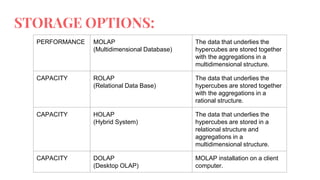
This document discusses different types of OLAP (online analytical processing) systems and tools. It defines OLAP as a multidimensional database where data is stored in a vector to allow for quick analysis. It describes different types of OLAP including MOLAP which stores data in a multidimensional structure, ROLAP which uses a relational database, and HOLAP which combines relational and multidimensional storage. Finally, it lists several major providers of OLAP systems and tools.