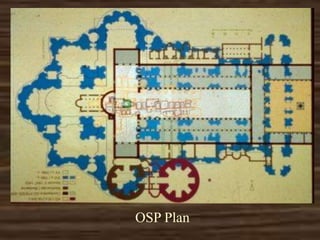
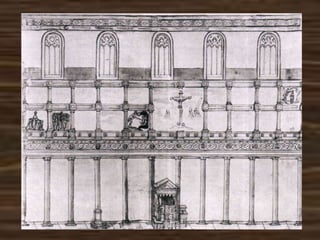
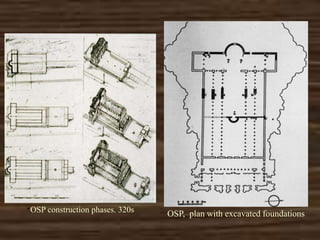
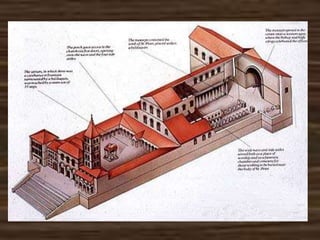
Old St. Peter's Basilica was constructed in Rome between 326-333 AD under Emperor Constantine. It was the first St. Peter's Basilica and was built over the grave of St. Peter. The basilica had a cruciform layout with a nave and aisles inspired by Roman basilicas but adapted for Christian worship. Old St. Peter's Basilica was torn down in the early 16th century to make way for the new St. Peter's Basilica.