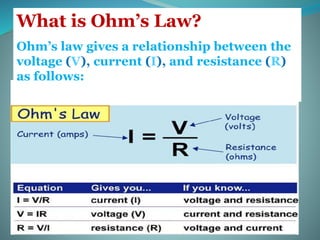
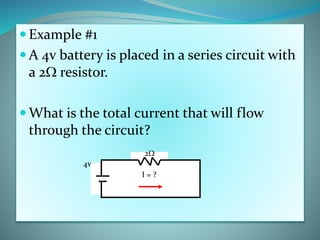
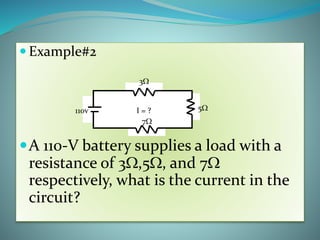
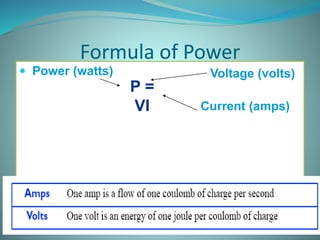
This document defines key electrical terms like voltage, current, and resistance. It explains that voltage is measured in volts and is the amount of energy per charge moving electrons. Current is measured in amperes and is the rate of charge flow. Resistance is measured in ohms and is the opposition to current flow. Ohm's Law is introduced, which gives the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance as V=IR. Examples are given to show how to use Ohm's Law to calculate current in different circuit scenarios. The document concludes by providing practice problems for readers to solidify their understanding of these concepts.