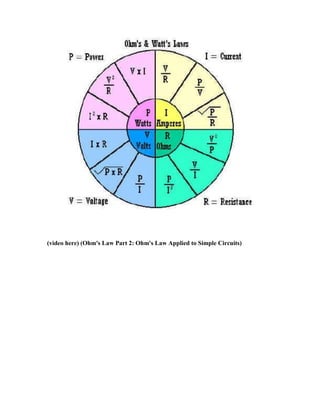
Ohm's Law describes the relationship between resistance, current, and voltage in an electrical circuit. The formula is R (resistance in ohms) = V (voltage in volts) divided by I (current in amperes). Ohm's Law states that the voltage across a conductor is equal to the current through it multiplied by the resistance of the conductor. Understanding Ohm's Law is vital for working with electrical and electronic circuits as it describes how resistance, current, and voltage are interrelated.