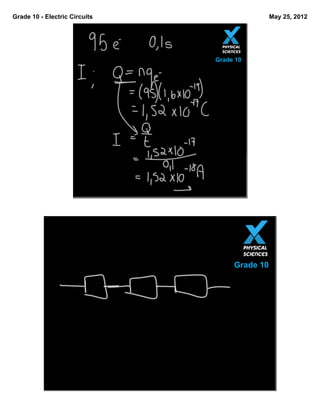
This document covers key concepts in electric circuits for grade 10 students. It defines potential difference as the work done per unit charge. It also defines current as the rate at which charges move past a fixed point, and resistance as anything that slows the flow of charge. Several sample problems are provided to calculate potential difference, current, energy, resistance, and time values. Key terms like coulomb, resistor, and potential difference are defined.





![Grade 10 - Electric Circuits May 25, 2012
Grade 10
Problem
Define the following:
1] Resistor
2] Coulomb
3] Potential difference
Grade 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/grade10-electriccircuits-130608085258-phpapp02/85/Grade-10-electric-circuits-6-320.jpg)