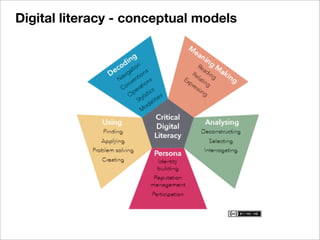
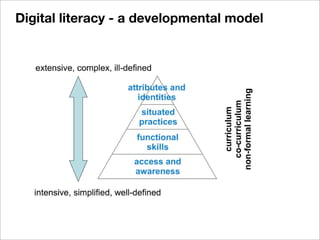
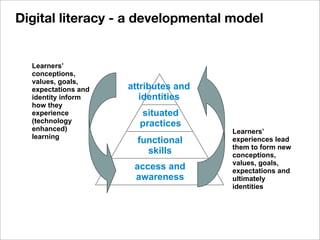
The document discusses the importance of understanding learners' experiences and readiness for online learning, highlighting the role of digital literacy and the need for adaptive teaching strategies. It critiques existing questionnaires aimed at assessing readiness and emphasizes the significance of learner autonomy, proactive behavior, and the equitable distribution of resources. The document also explores the diverse needs and preferences of learners in tech-enhanced environments and advocates for integrating digital literacy into the curriculum through various collaborative practices.