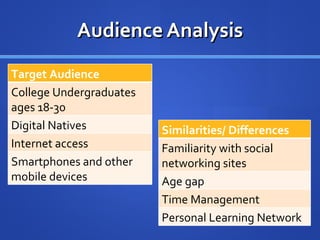
The document outlines a plan to incorporate Twitter into education. It discusses using Twitter to improve communication, interaction and participation between instructors and students. Tutorials, best practices and assignments would be created to teach students how to use Twitter's features like hashtags, retweeting and messaging appropriately and establish personal learning networks. Benefits include increased student engagement, collaboration and connecting with professionals. Formative feedback would be gathered and participation would determine the plan's success.













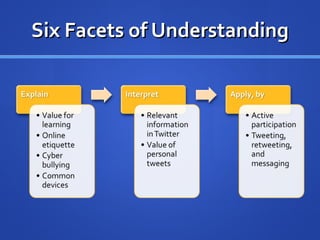
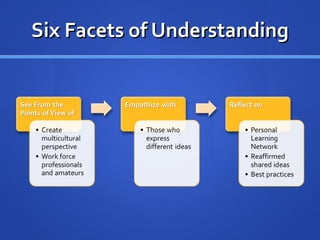


![Learning Activities Explanation [Technology: Twitter, PowerPoint, Video, Internet] ( W ) Discuss social networking Full tutorial lesson on Twitter Personal Learning Network (PLN) Twitter classroom uses ( W, H, E ) Introduction of basics of using Twitter Functions and uses of Twitter Web etiquette Cyber bullying Conduct expectations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twitterpresentation-110429093850-phpapp01/85/Integrating-Twitter-into-Education-18-320.jpg)

![Learning Activities Interpretation [Technology: Twitter, Internet] ( W, H ) (Discussion) Define Social Networking Applications towards education. Allow students to discuss their views of social networking. ( W, E ) Discuss Twitter etiquette to the students. Discuss conduct and content of tweets. Keep direct messages private. Explore tweeting, retweeting, and replying. Ask questions on Twitter during class.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twitterpresentation-110429093850-phpapp01/85/Integrating-Twitter-into-Education-20-320.jpg)
![Learning Activities Perspective [Technology: Twitter, Internet] ( R ) Conduct a survey Twitter Take a class poll and discuss opinions and feedback on twitter learning experiences ( E ) Follow a news feed or a world event Gain perspective of other users on Twitter Learn value of information ( R,E ) Research cyber bullying and its implications on victims and social networking](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twitterpresentation-110429093850-phpapp01/85/Integrating-Twitter-into-Education-21-320.jpg)
![Learning Activities Empathy [Technology: Twitter, Internet] ( R, T ) Explore jobs that use Twitter Learners will list 3 jobs Describe in detail Present person on Twitter that holds that job title](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/twitterpresentation-110429093850-phpapp01/85/Integrating-Twitter-into-Education-22-320.jpg)