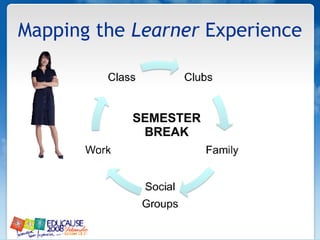
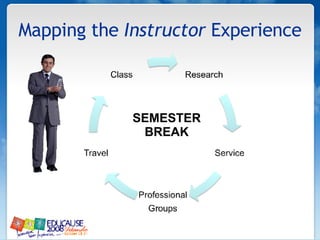
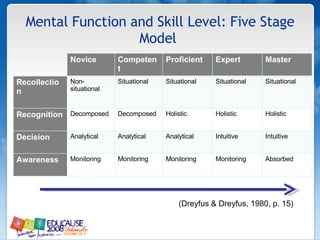
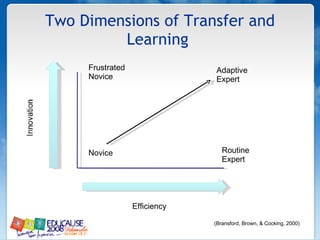
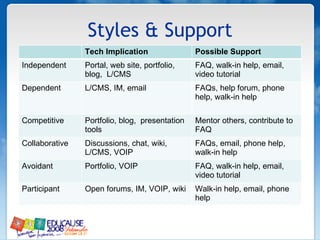
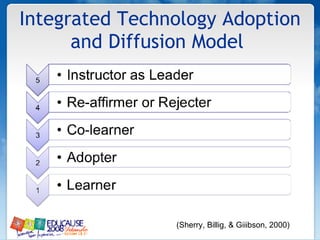
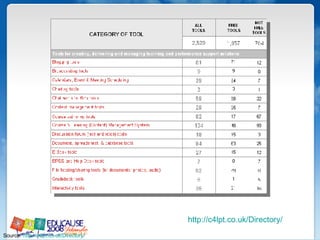
The document discusses understanding faculty members and learners in the context of web 2.0 technologies. It covers mapping learner and instructor experiences, examining people, data and things involved. It also discusses learners' technology abilities and needs, as well as challenges of emerging technologies for faculty development.