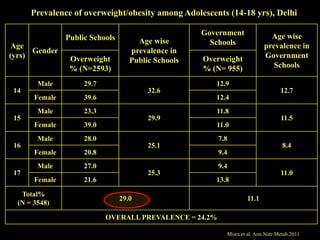
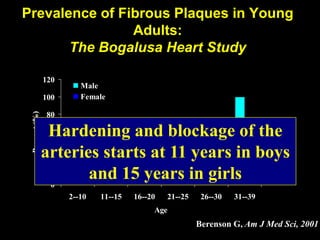
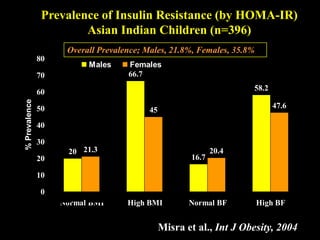
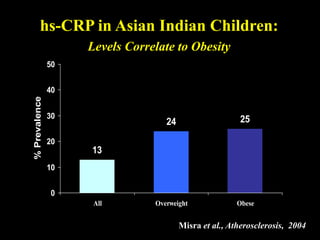
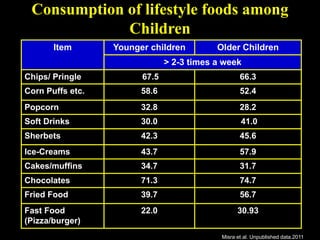
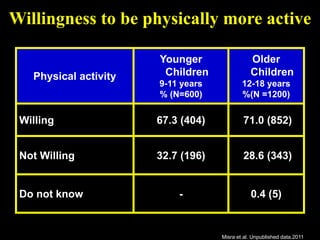
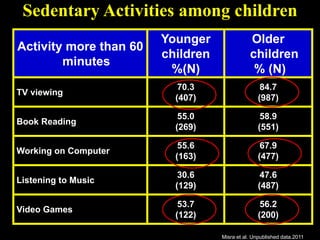
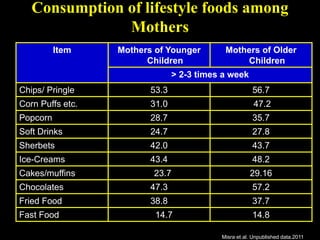
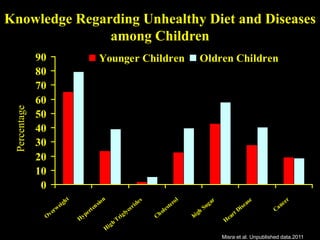
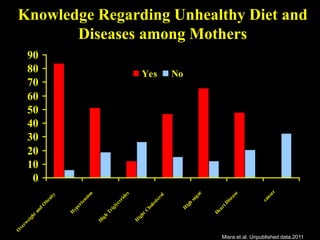
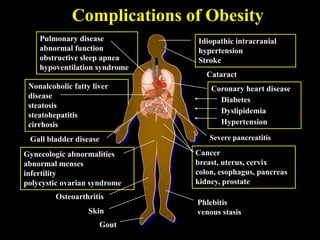
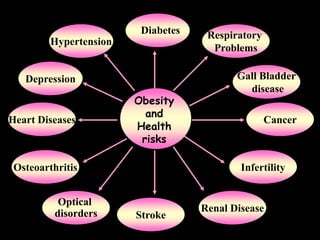
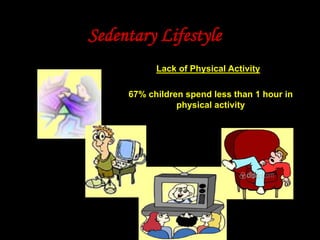
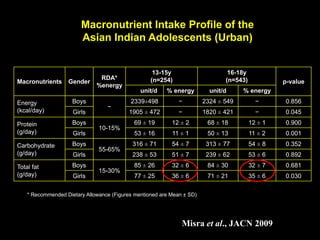
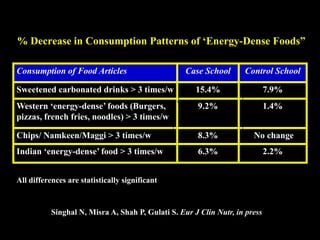
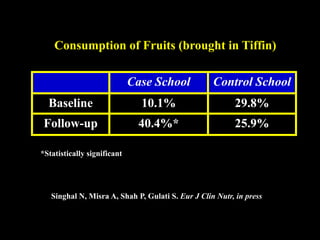
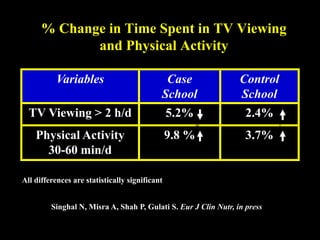
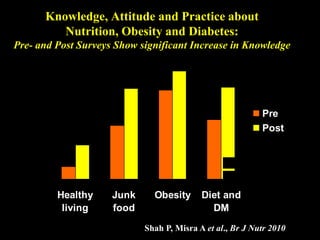
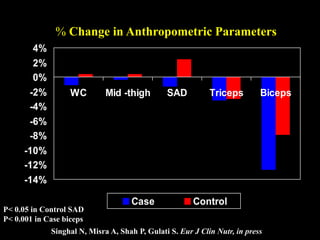
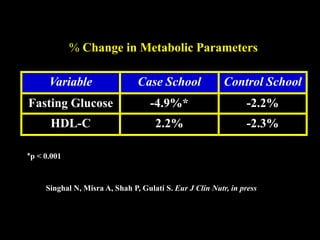
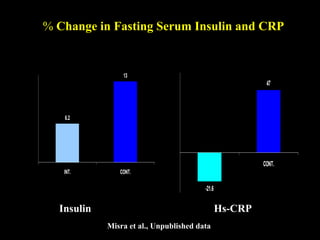
This document discusses obesity in India from the perspective of experts Dr. Anoop Misra and Dr. Seema Gulati. It presents data showing rising rates of overweight and obesity among Indian adolescents. It dispels common myths about obesity, noting that excess weight in childhood often leads to health issues like diabetes and heart disease. While obesity was once seen as a problem only of developed nations, the data shows its growing prevalence in India and other developing areas. The experts attribute this to unhealthy diets high in processed foods and low physical activity levels among Indian youth. They call for initiatives to increase awareness about obesity prevention and healthy lifestyles.