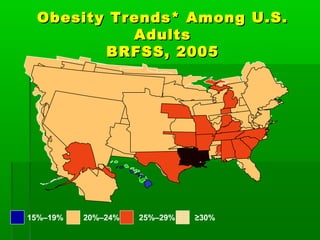
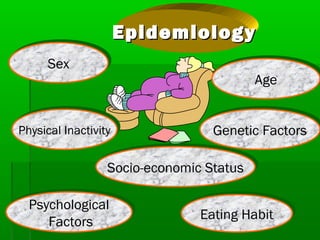
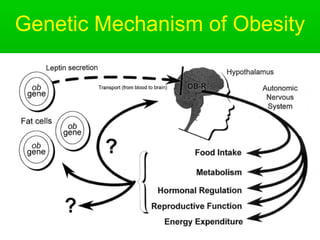
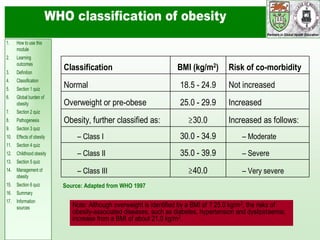
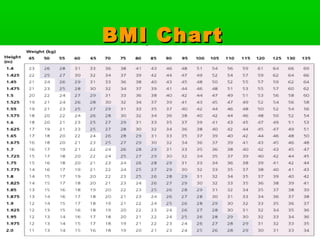
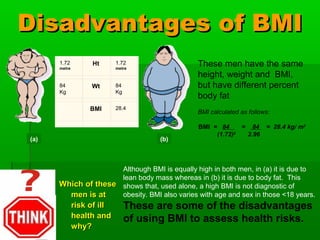
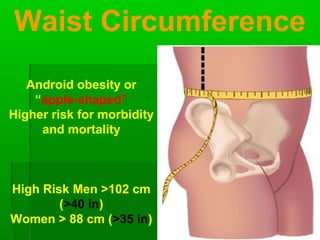
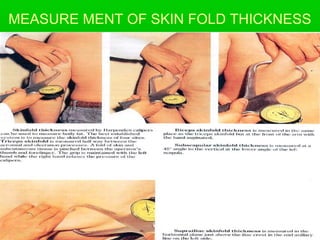
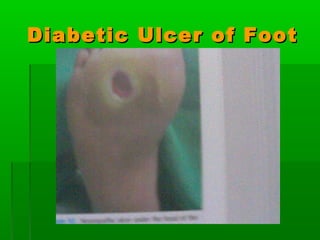
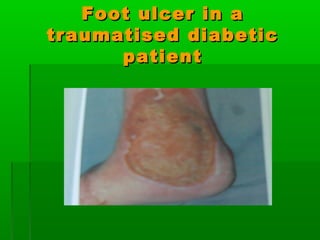
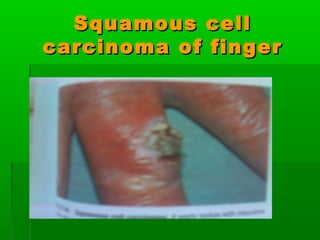
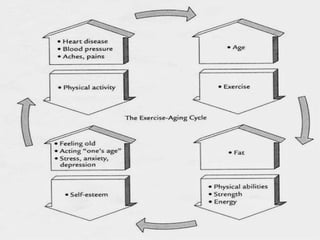
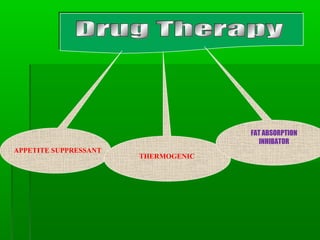
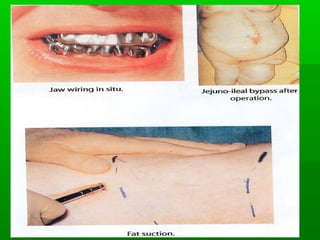
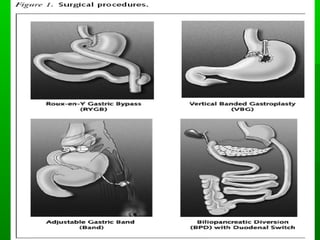
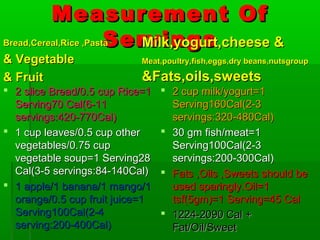
This document discusses obesity, its prevalence, and management. It notes that obesity produces complications like hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease. The prevalence of obesity is increasing globally and is a leading risk factor for death. Obesity is defined as abnormal growth of adipose tissue due to enlarged fat cells or increased fat cell number. The document discusses factors contributing to obesity like diet, physical inactivity, and genetics. It also outlines methods for measuring obesity and classifications based on BMI. Prevention and treatment options for obesity like diet, exercise, and surgery are mentioned.