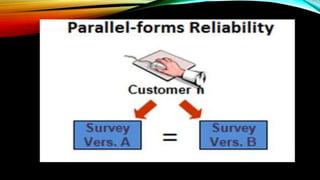
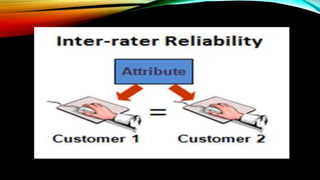
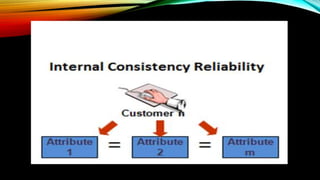
Reliability refers to the consistency of test scores. There are three main types of reliability: stability, equivalence, and homogeneity. Stability measures consistency over time, equivalence uses alternative versions of a test, and homogeneity examines internal consistency. Factors like data collection methods, time intervals, and test administration can influence reliability. To improve reliability, tests should have clear, unambiguous questions and objective scoring. Rater reliability specifically measures consistency between raters or judges.