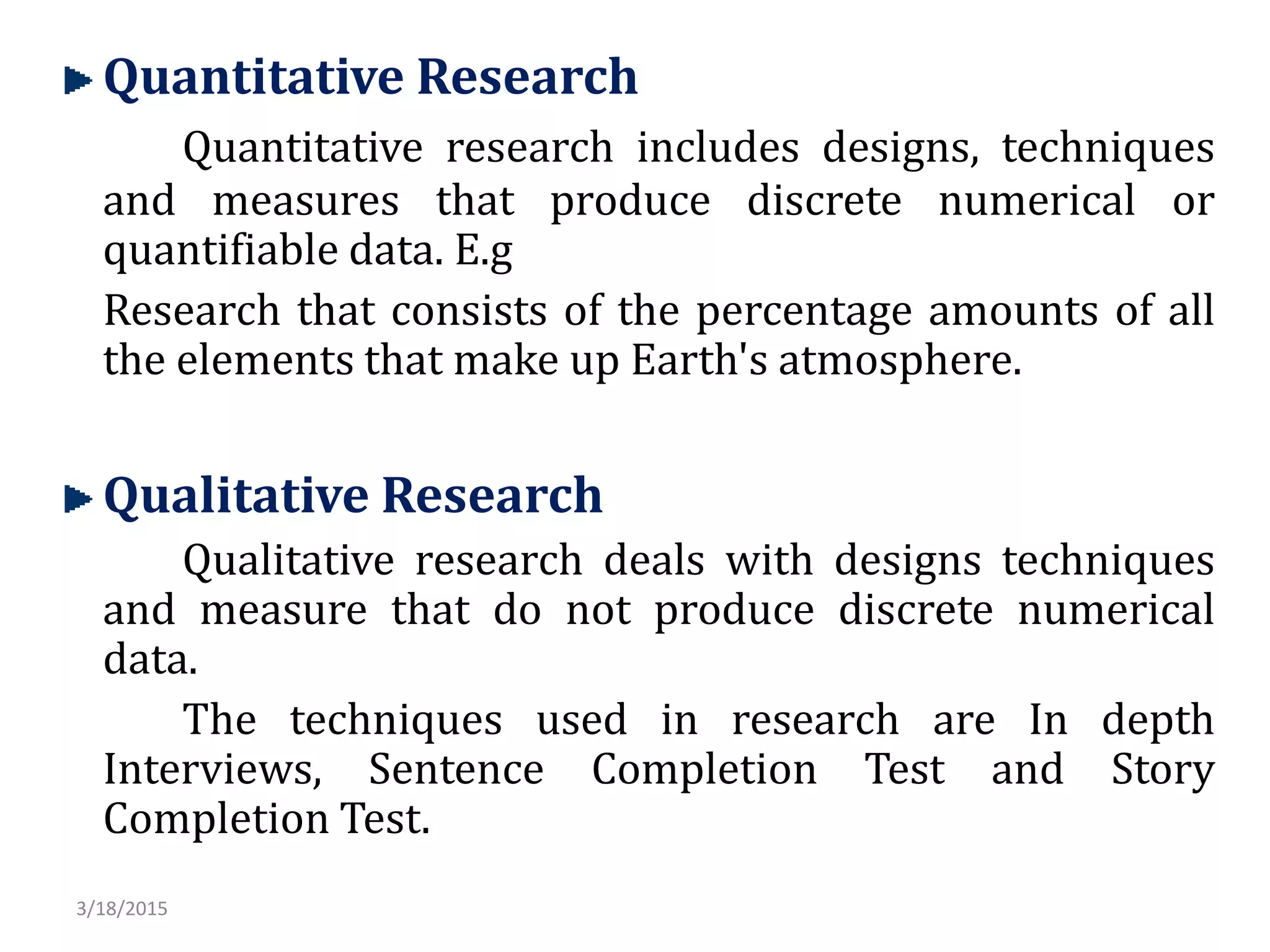
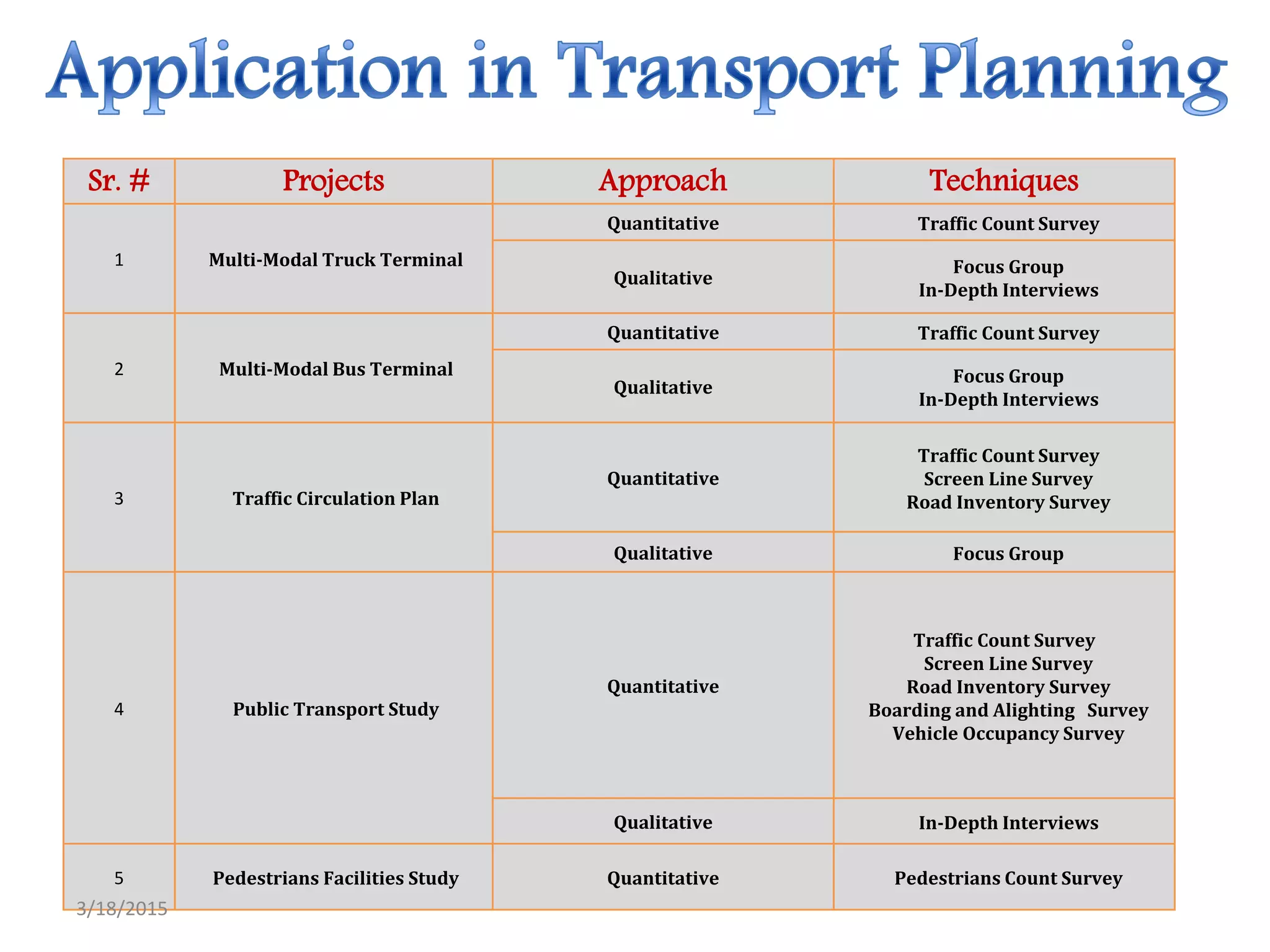
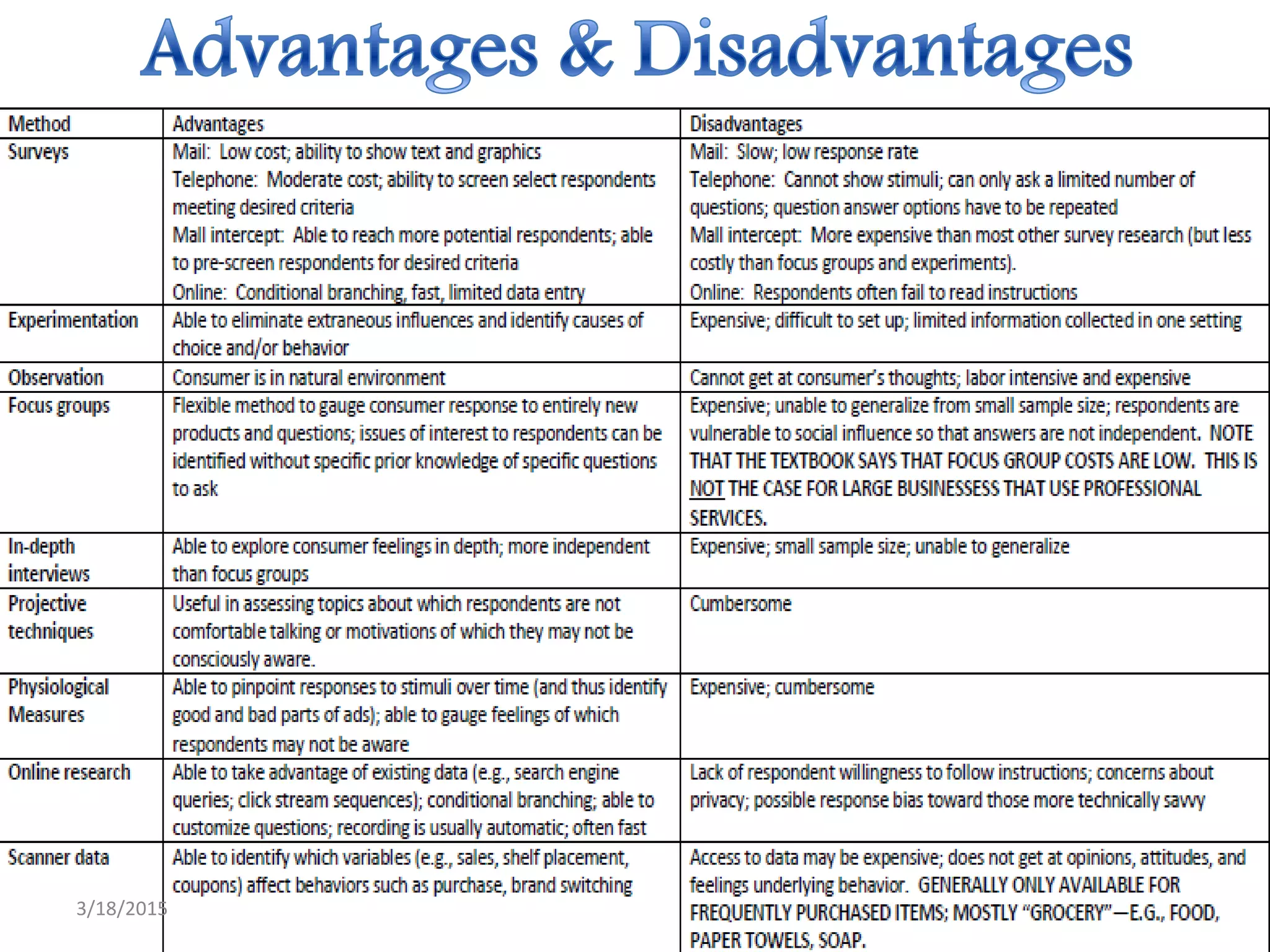
The document defines research and describes its purposes and types. Research purposes include discovering answers, solving problems, and advancing knowledge. The main types discussed are descriptive research, which reports data and characteristics, and analytical research, which analyzes existing facts. Quantitative and qualitative research methods are also outlined. Quantitative involves numerical data while qualitative examines attitudes and opinions. The document also discusses different research approaches like experimental, surveys, and case studies that can be quantitative or qualitative.