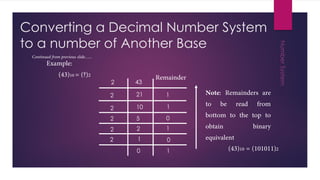
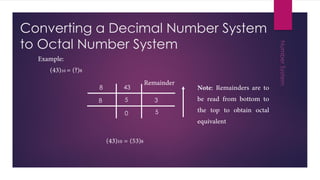
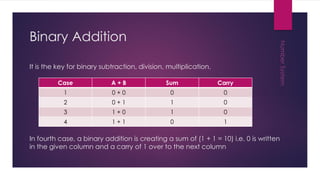
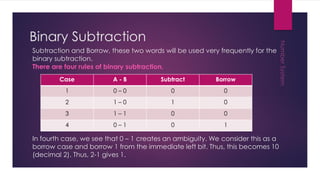
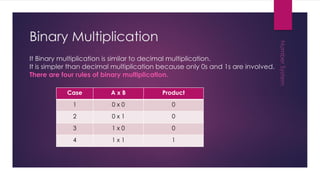
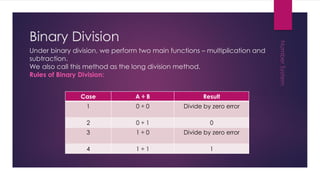
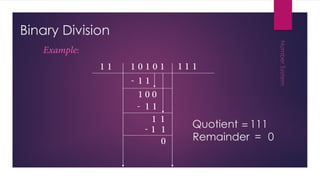
This document discusses different number systems including non-positional, positional, decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal systems. It provides examples of converting between these systems, such as converting the octal number 3450 to decimal. Binary arithmetic operations including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are also covered. The key steps and rules for performing each binary operation are outlined.