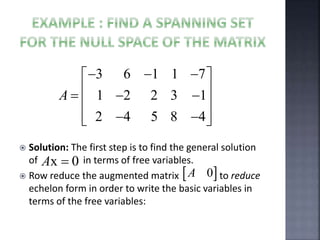
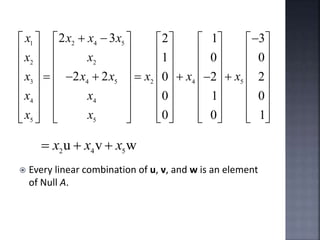
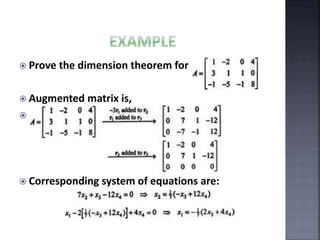
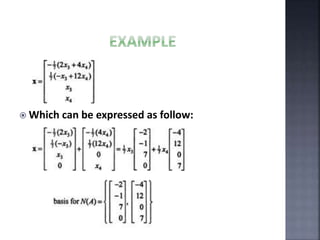
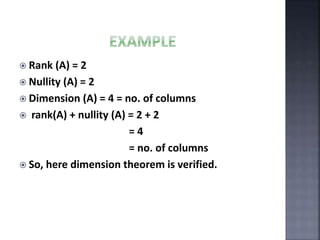
The document outlines the null space and dimension theorem in linear algebra, defining null space and its general solution in terms of free variables. It discusses the decomposition of vectors and the relationship between rank, nullity, and the number of columns in a matrix, ultimately verifying the dimension theorem. The content also includes references to inspiration from a professor and additional resources in linear algebra.