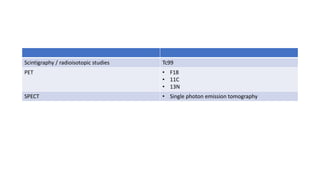
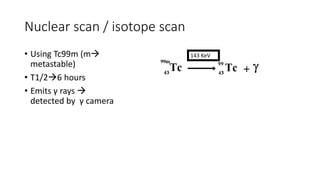
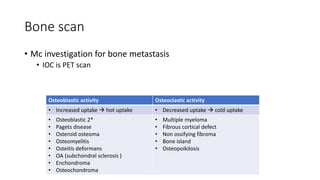
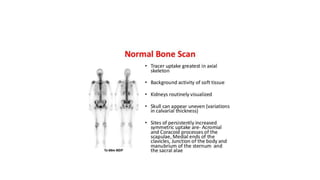
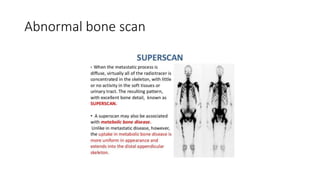
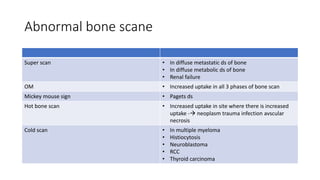
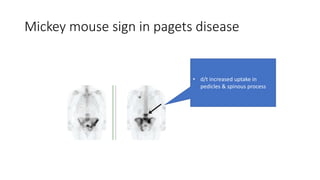
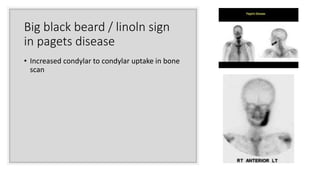
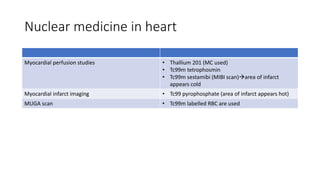
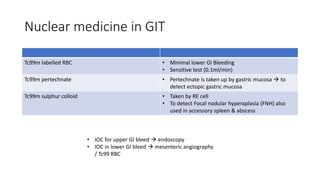
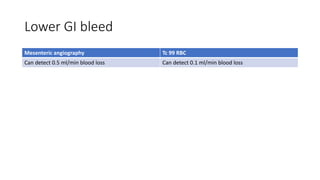
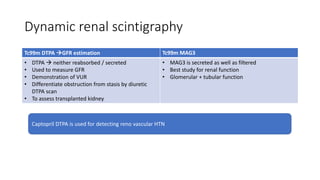
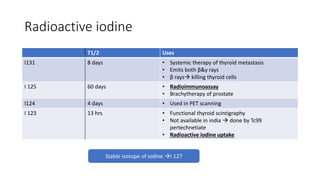
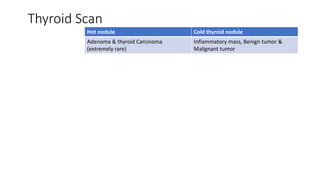
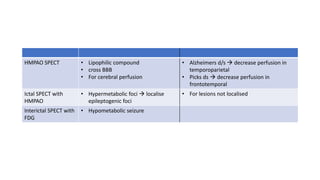
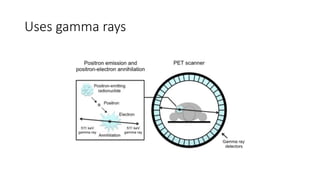
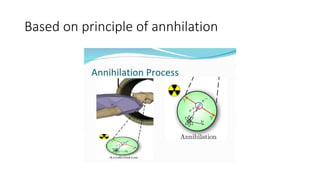
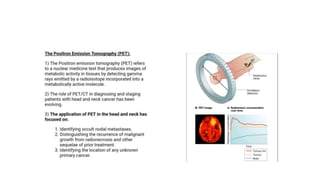
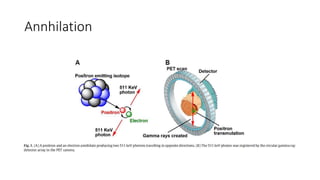
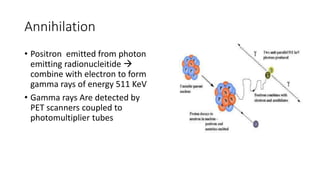
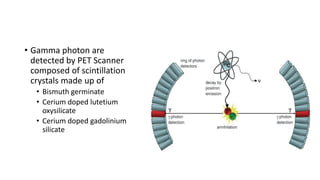
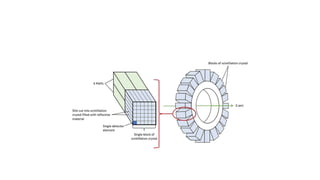
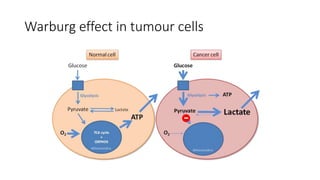
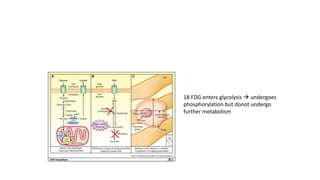
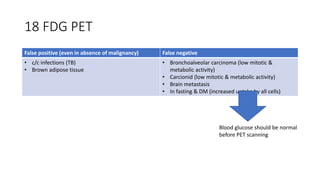
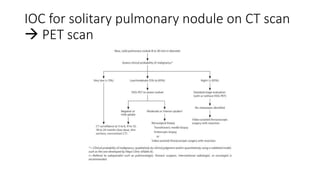
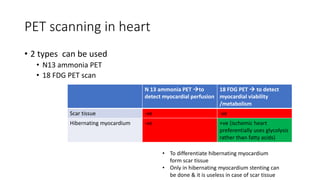
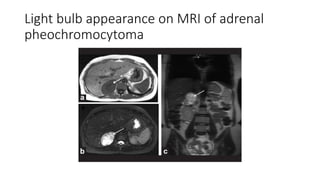
Nuclear medicine uses radiopharmaceuticals and imaging techniques like PET and SPECT scans to assess organ function and detect diseases. Some key applications include using F-18 FDG PET scans to identify cancer metastases based on increased glucose metabolism in malignant cells, Tc-99m sestamibi scans to detect myocardial ischemia, Tc-99m DMSA renal scans to assess kidney function, and somatostatin receptor imaging with radiolabeled octreotide to localize neuroendocrine tumors. PET provides superior detection of bone metastases compared to bone scans or whole-body MRI. Important considerations for nuclear medicine exams include selecting the appropriate radiotracer and ensuring normal blood glucose levels for oncology FDG PET scans