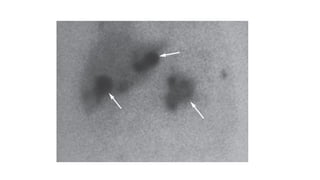
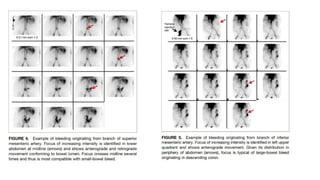
Radioisotope imaging uses radioactive tracers and gamma cameras to produce images of physiological processes. Technetium-99m is commonly used due to its short half-life and gamma ray emissions. Common scans include thyroid scans using iodine-123 or technetium, parathyroid scans using sestamibi, MIBG scans for pheochromocytoma, bone scans, renal scans using DTPA or MAG3, and HIDA scans of the gallbladder. PET scans using fluorodeoxyglucose provide functional imaging combined with anatomical data from CT scans and are useful for cancer staging, treatment response, and detecting recurrence.