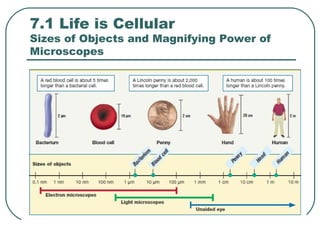
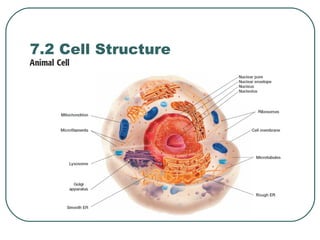
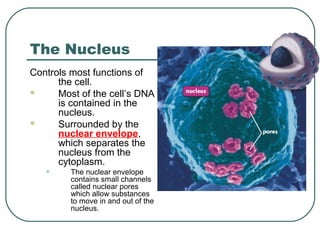
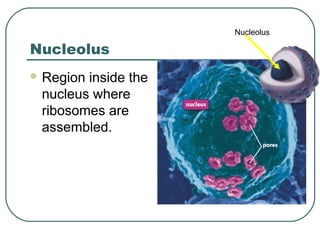
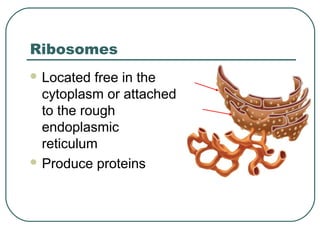
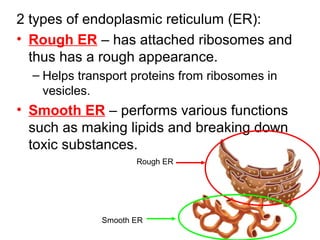
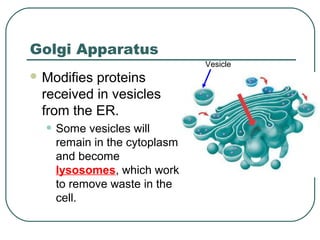
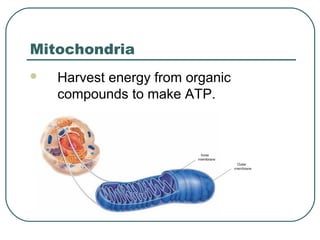
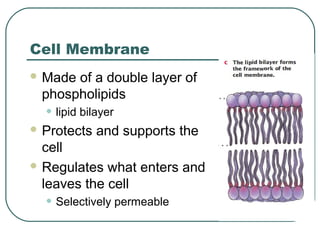
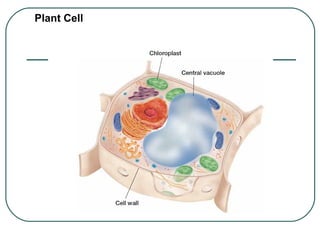
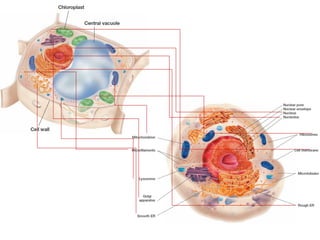
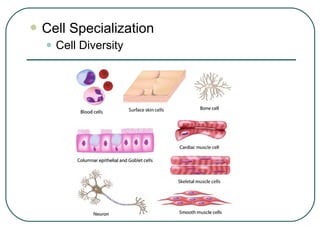
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things. There are two main types of cells - prokaryotic cells which lack internal structures and eukaryotic cells which have internal membranes and structures called organelles. The organelles each have specific functions like the nucleus which controls cell processes, mitochondria which produce energy, and the endoplasmic reticulum and golgi apparatus which modify and transport proteins. Plant cells have additional structures like a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a central vacuole which allow them to perform photosynthesis and store nutrients.