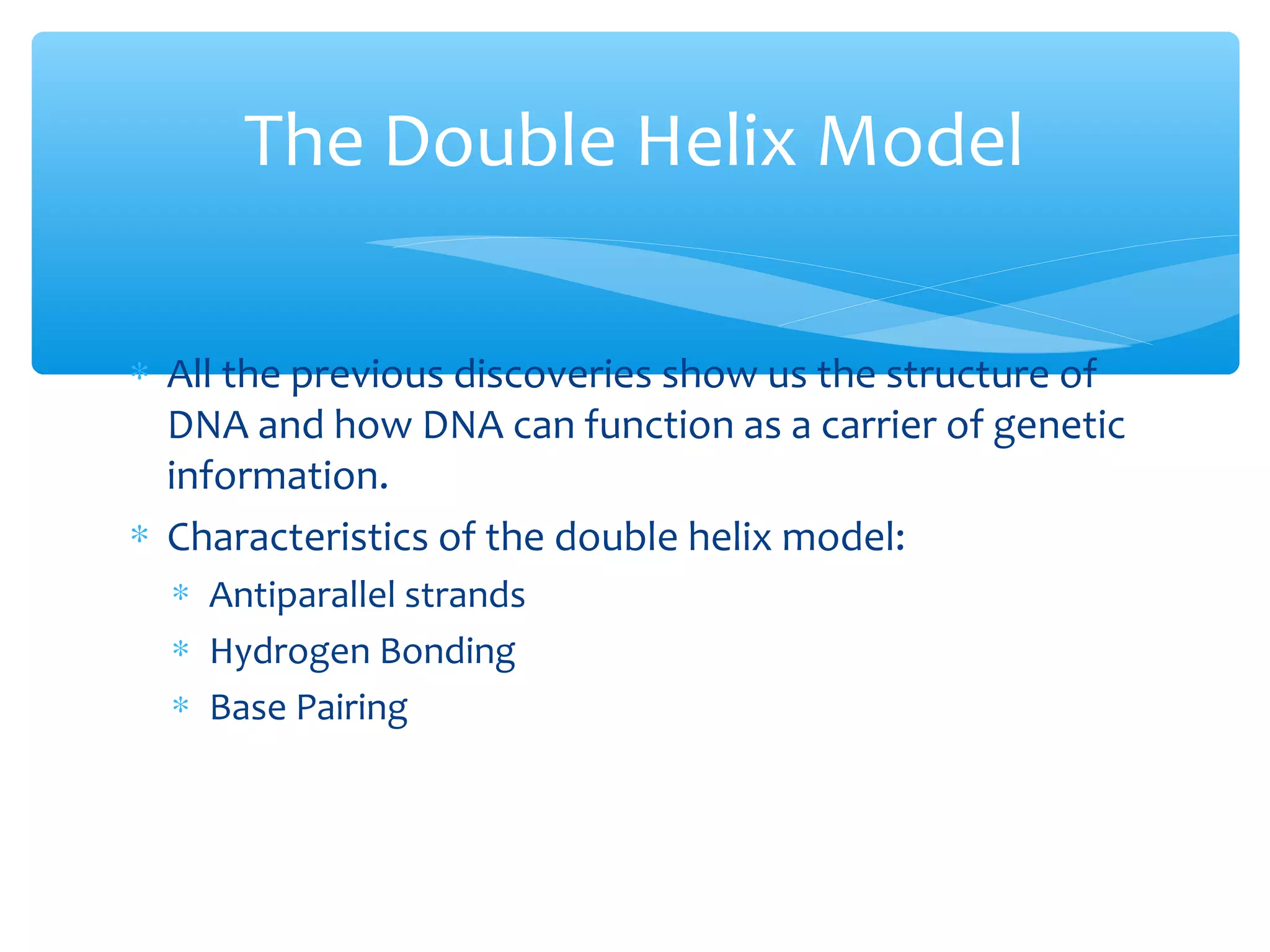
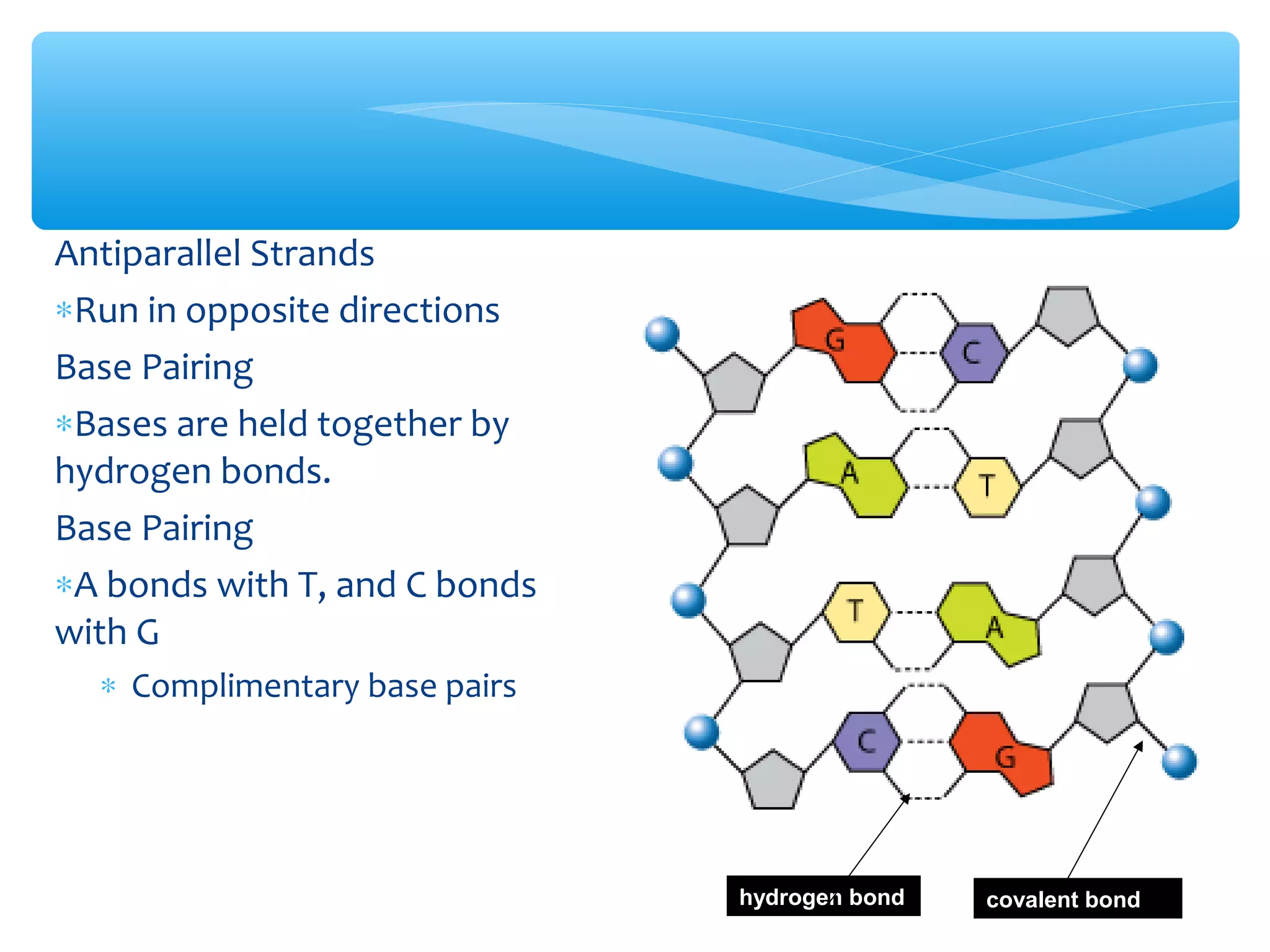
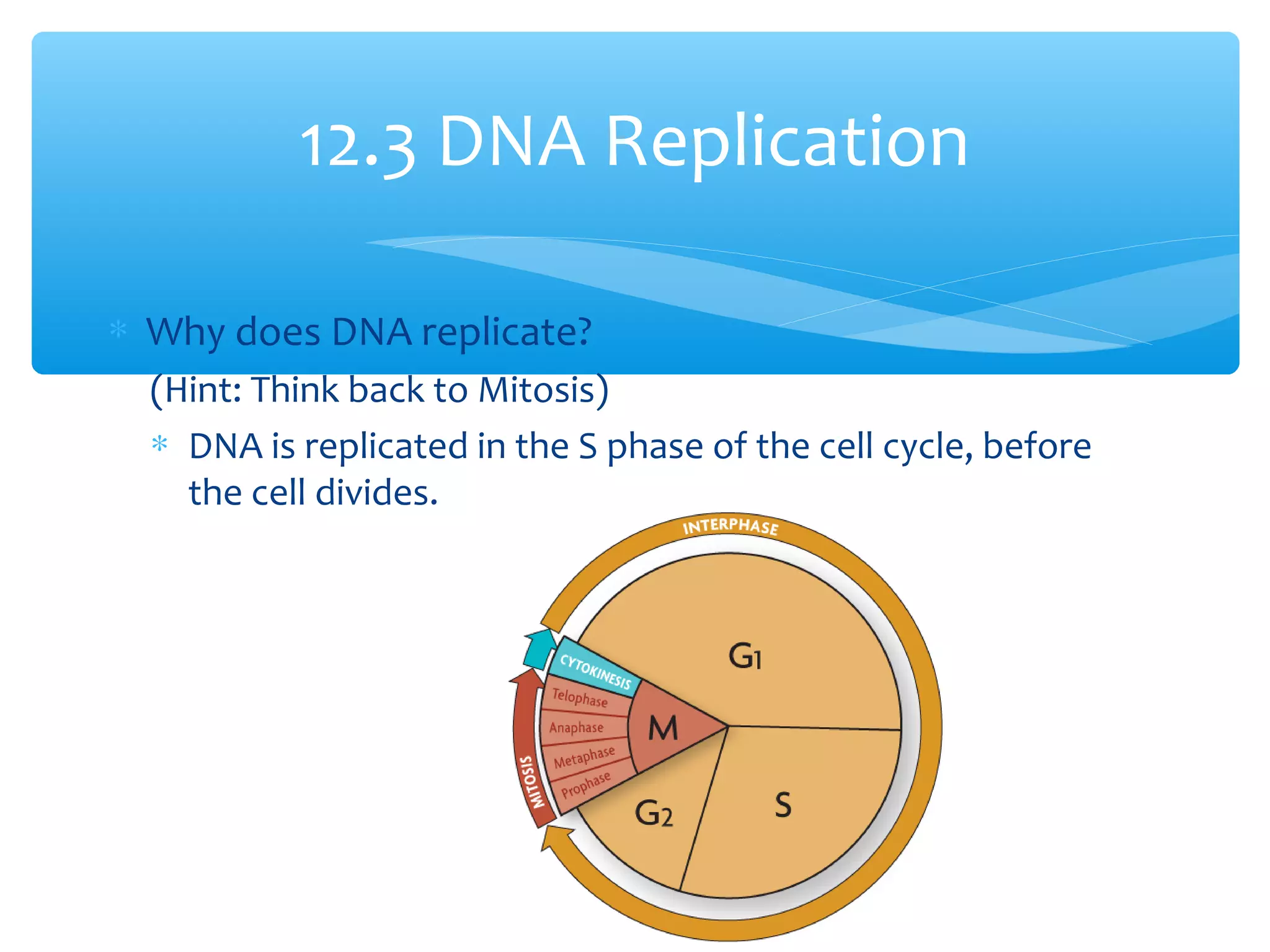
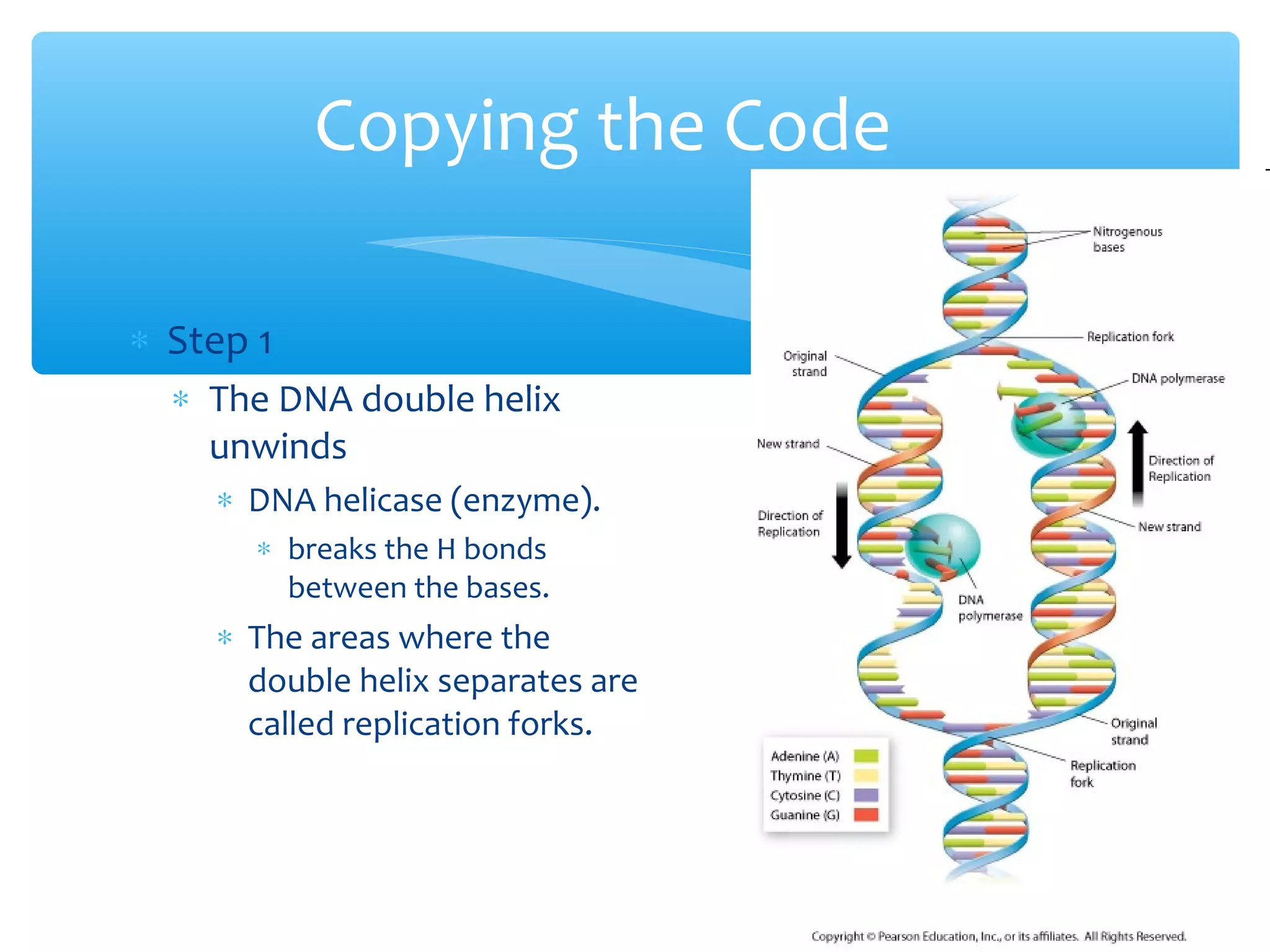
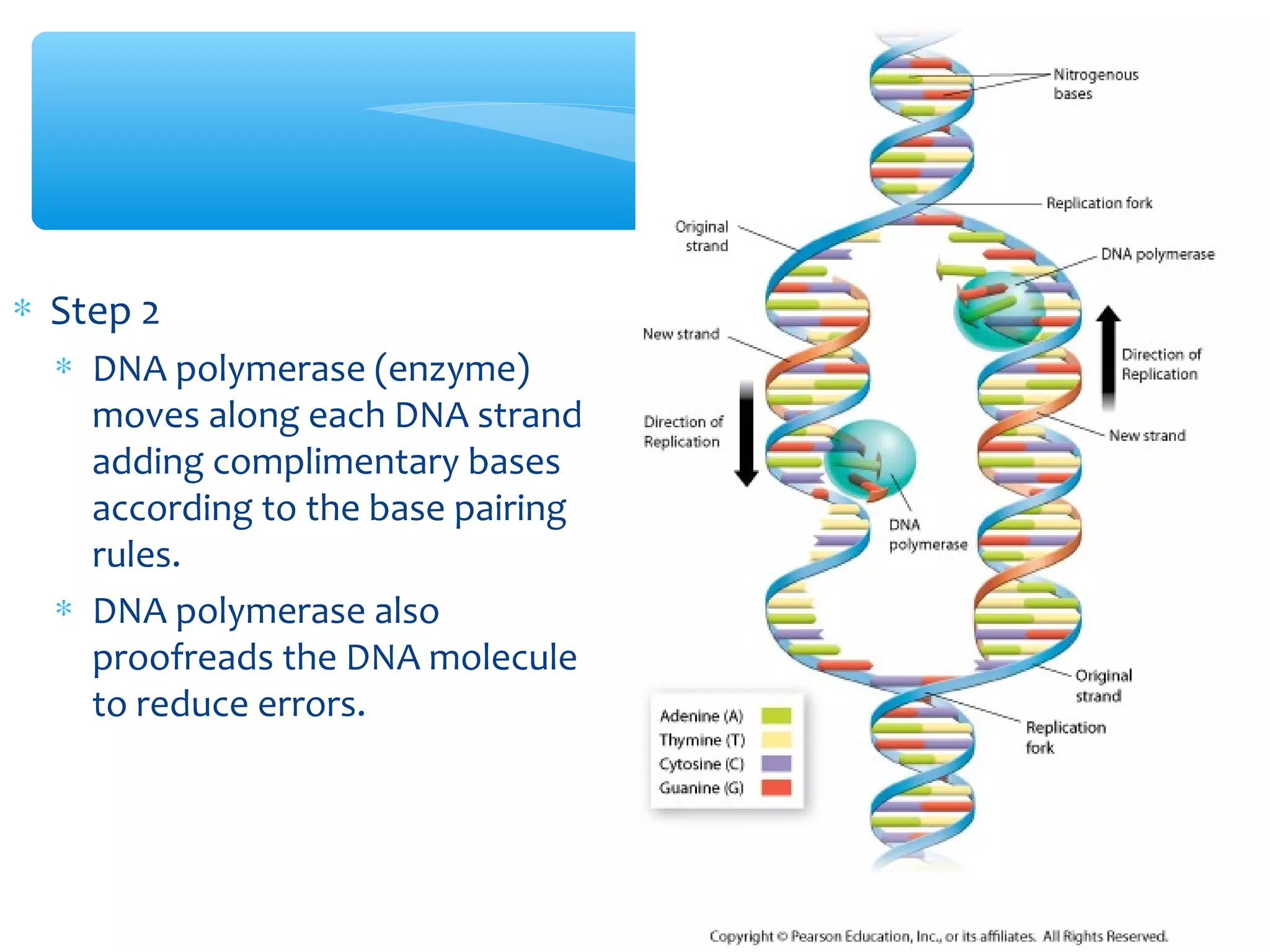
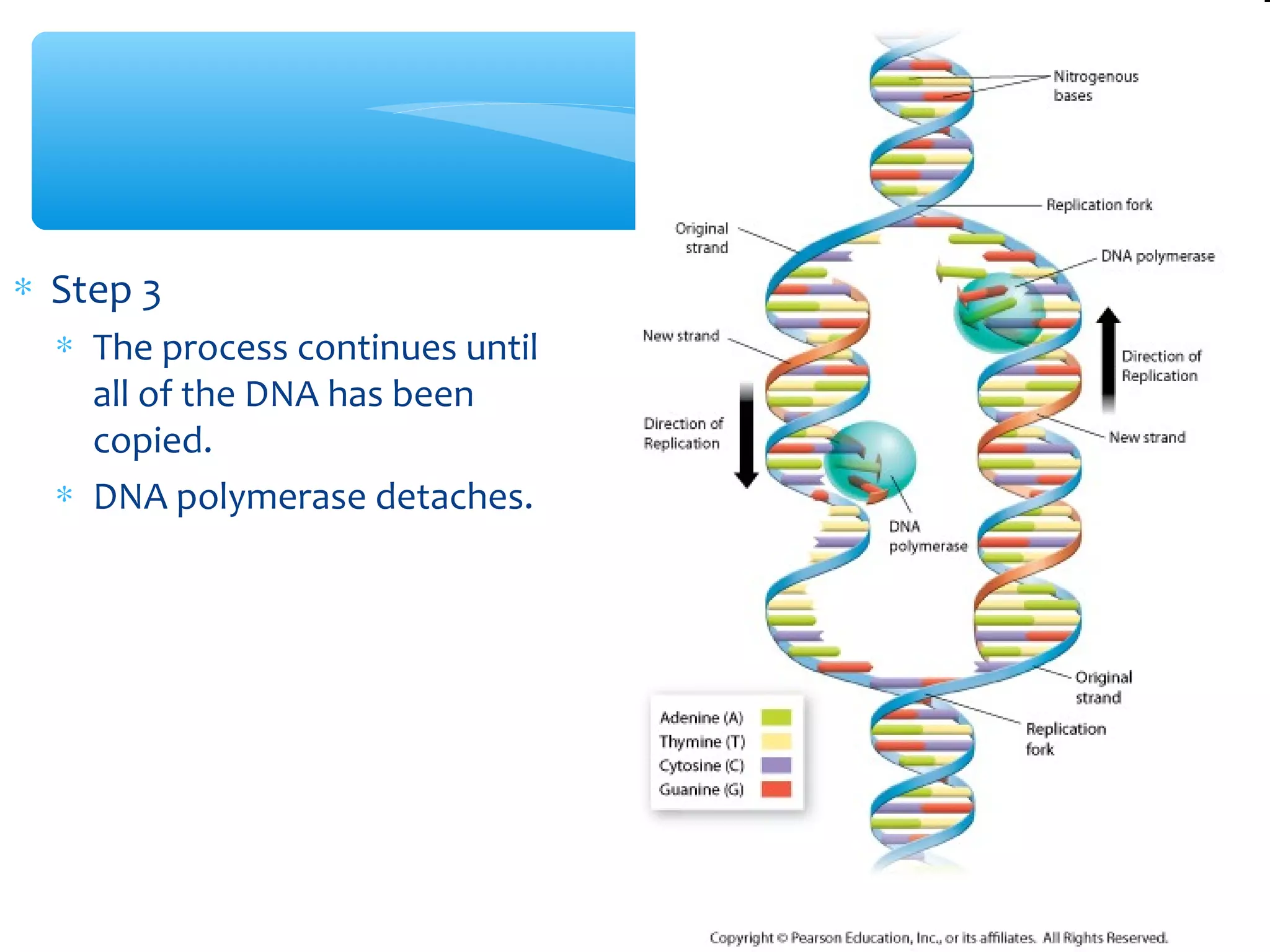
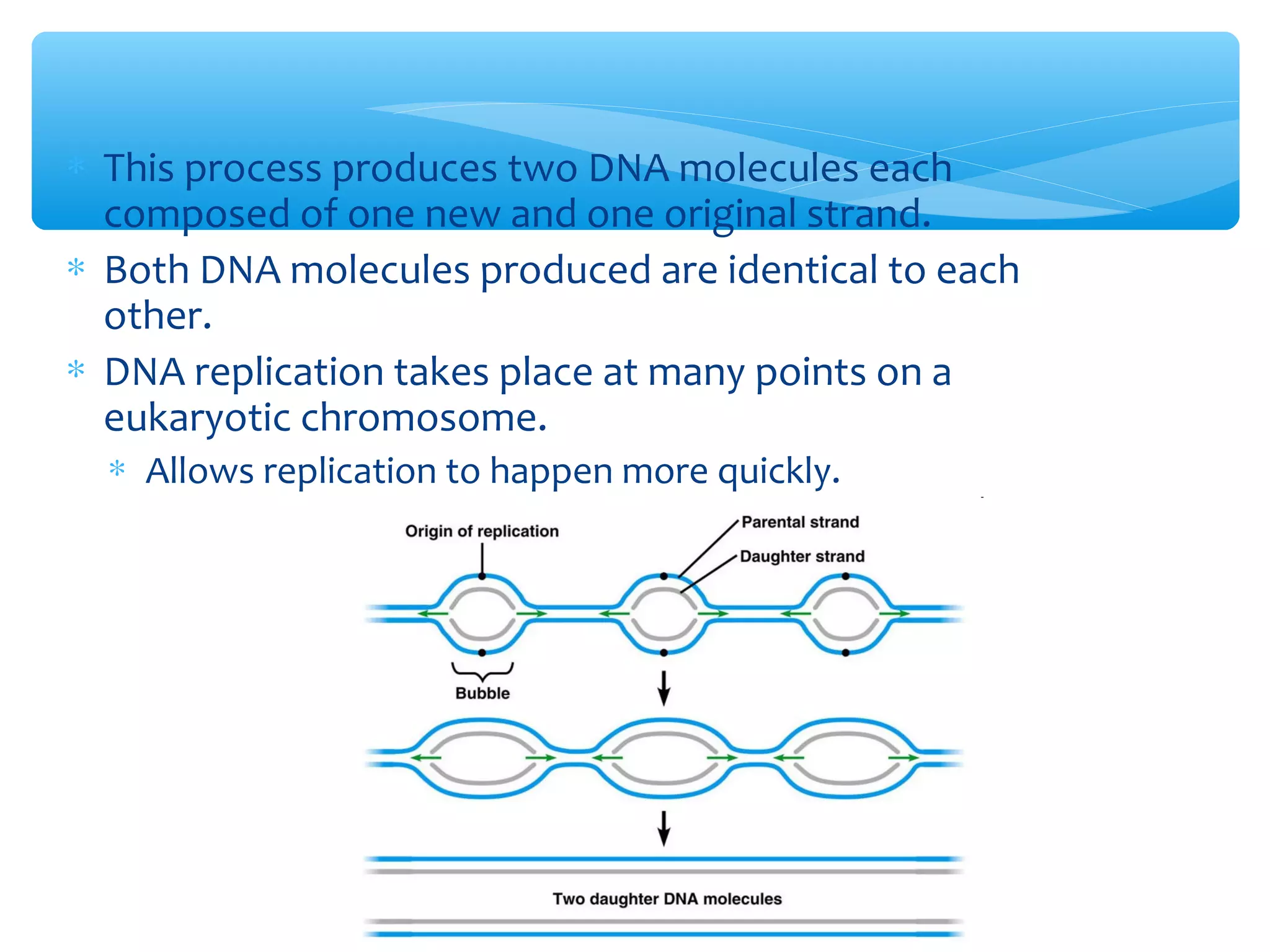
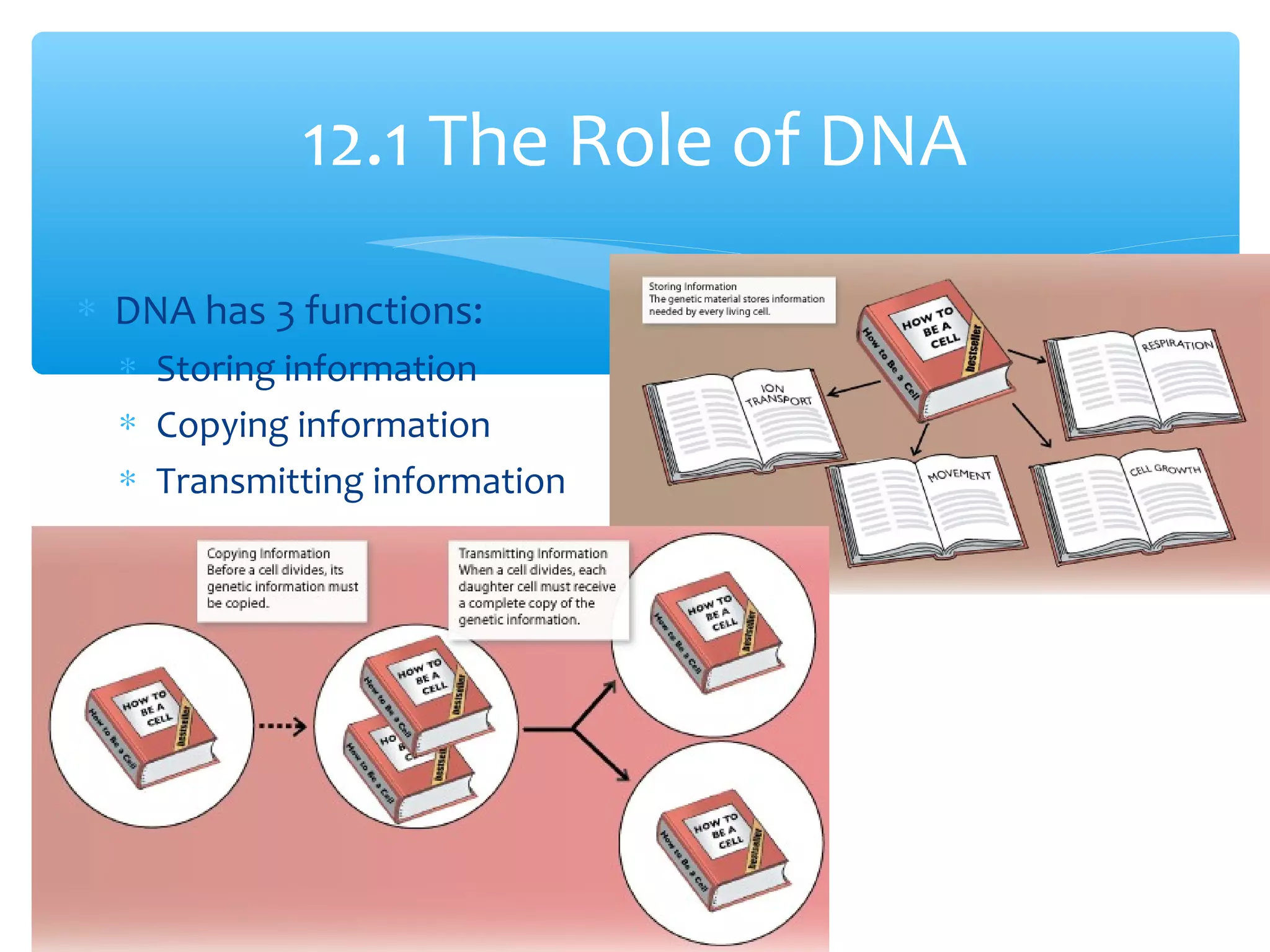
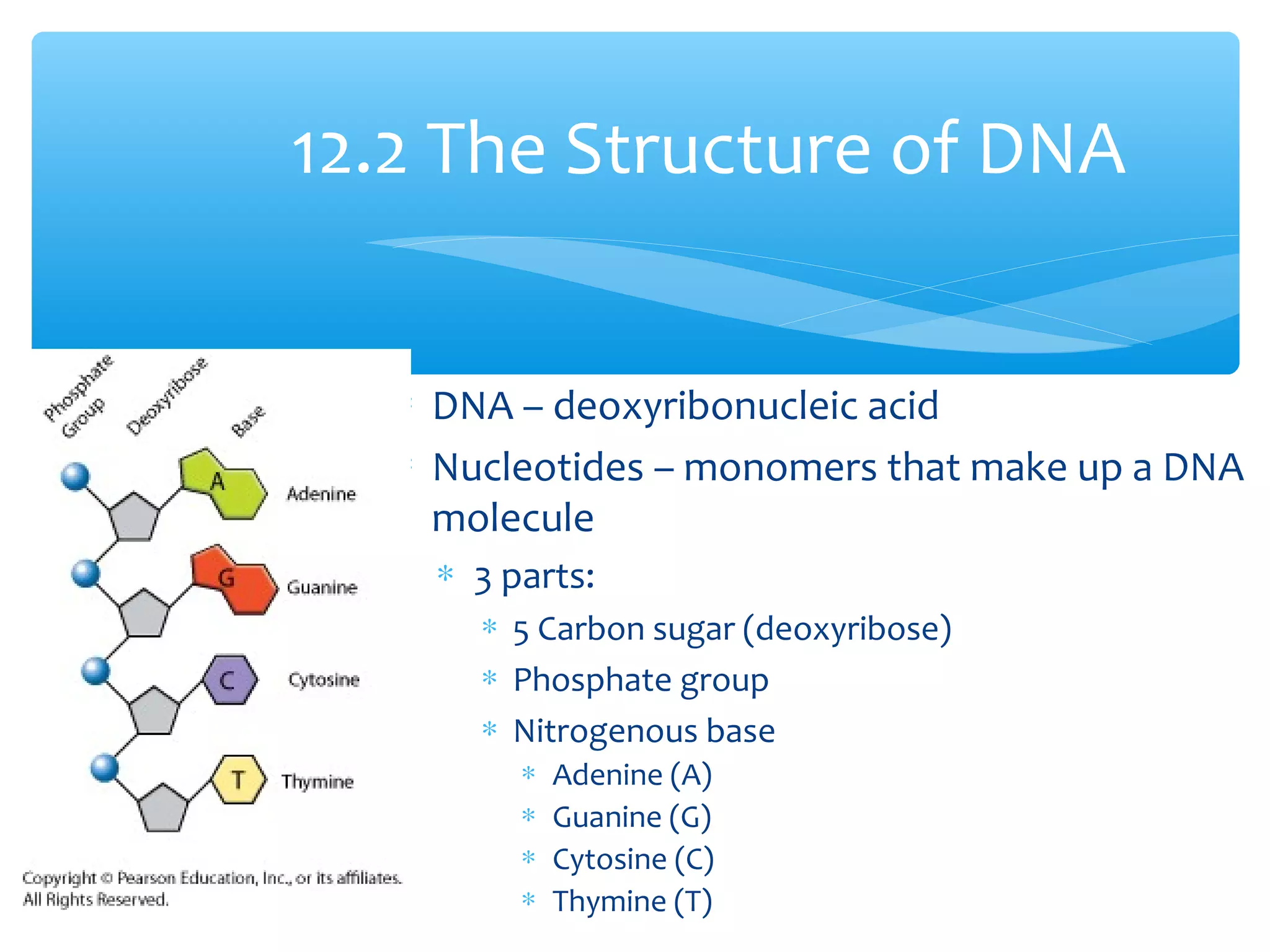
DNA has three main functions: storing genetic information, copying that information during cell division, and transmitting the information from parent to offspring. DNA is made up of nucleotides containing a sugar, phosphate, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. The structure of DNA was discovered to be a double helix with the bases on each strand bonding with their complement on the other strand (A pairs with T and C pairs with G). DNA replication copies the DNA through unwinding of the helix, addition of complementary bases by DNA polymerase, and production of two identical DNA molecules, each with one original and one new strand.

![∗Edwin Chargaff (1949)
∗Chargaff’s Rule
∗[A]=[T]
∗[C]=[G]
Solving the Structure of DNA
Adenine Thymine Guanine Cytosine
35%
45%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/notesch12-website-140408100525-phpapp01/75/Notes-ch12-DNA-4-2048.jpg)