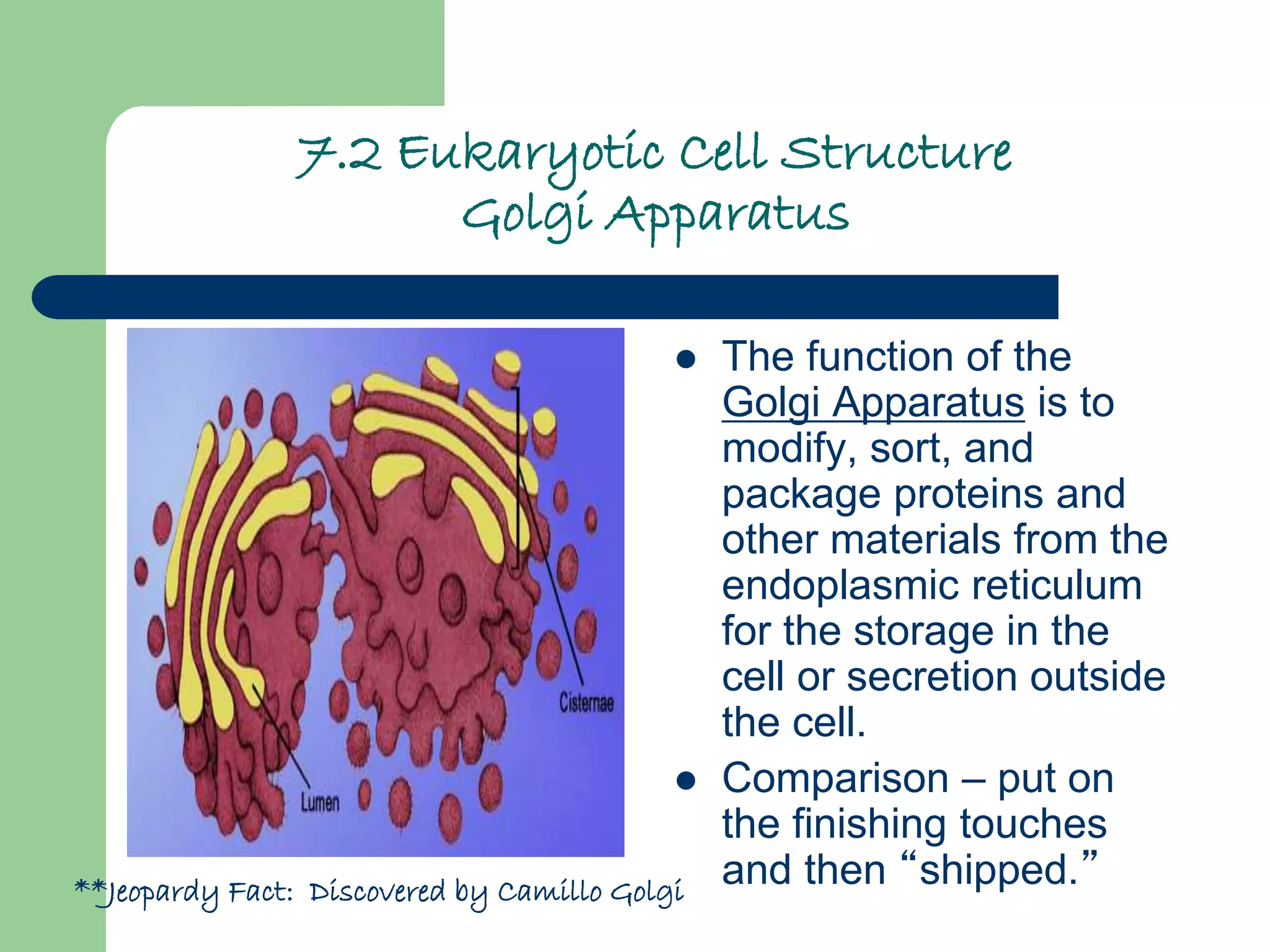
The document summarizes key concepts about cell structure and function from Chapter 7 of a biology textbook. It begins by describing the early discoveries of cells in the 1600s by Hooke and Leeuwenhoek. It then outlines the Cell Theory developed in the 1830s-1850s. The rest of the document details the structures and functions of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, including organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and cell membrane. It explains cellular processes like diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion and active transport across the cell membrane.