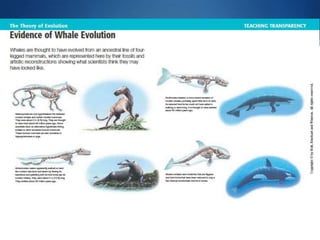
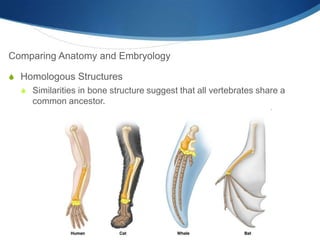
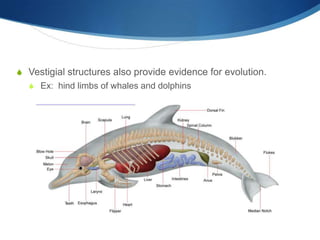
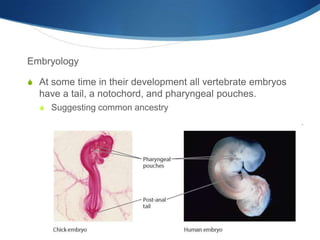
Charles Darwin developed the theory of evolution by natural selection based on observations he made during a 5-year voyage. He noticed that related species varied between locations and over time, suggesting descent from common ancestors. Darwin proposed that variations within species provided different adaptations for survival and reproduction, and that natural selection led populations to change over generations as favorable traits increased. His 1859 book On the Origin of Species outlined evolution based on struggle for existence, variation and adaptation, and survival of the fittest. Fossil, anatomical, embryological, and genetic evidence now provide strong support for evolution through natural selection.