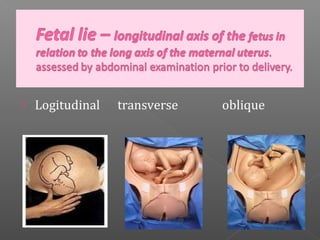
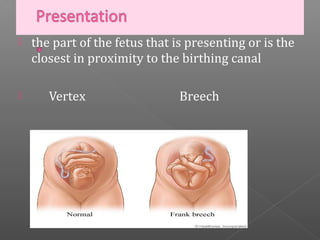
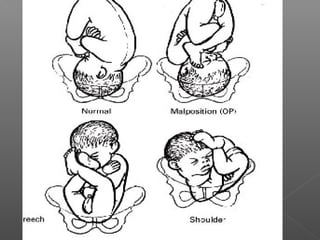
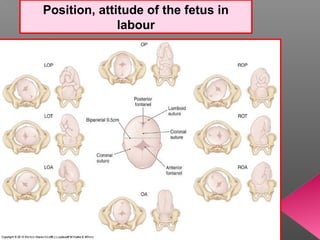
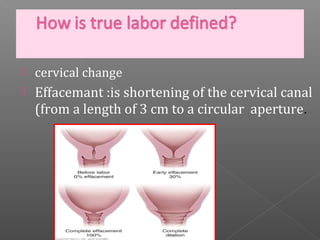
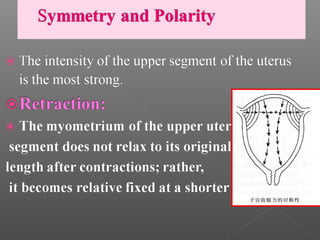
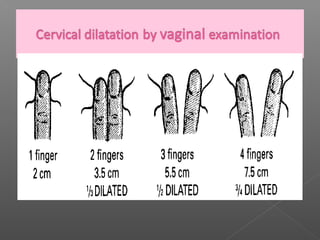
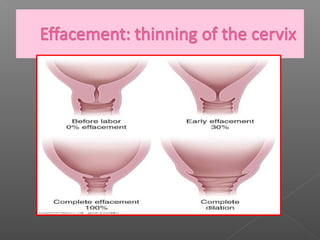
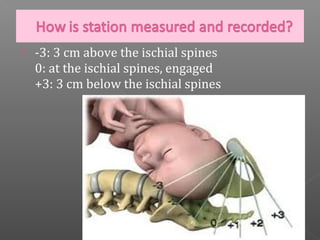
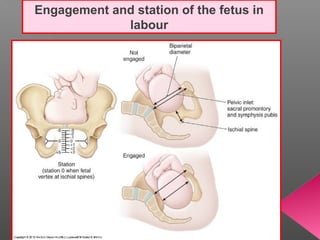
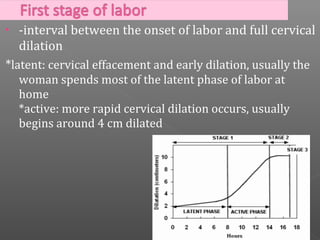
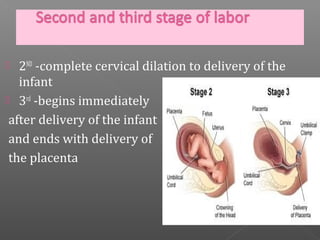
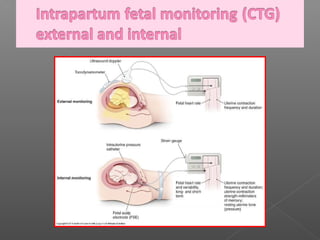
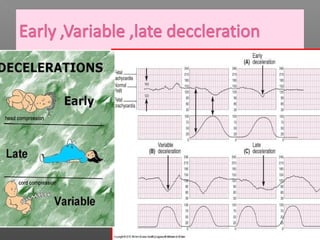
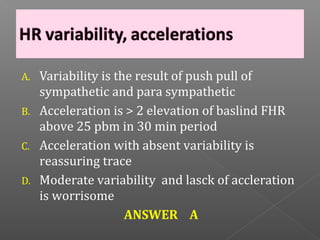
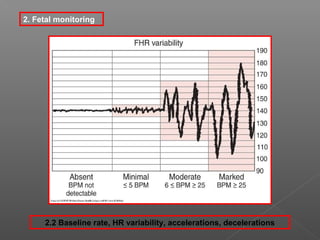
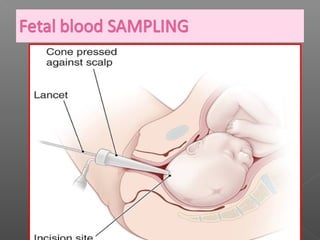
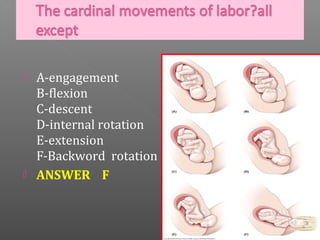
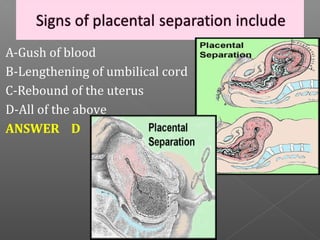
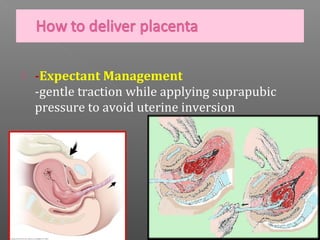
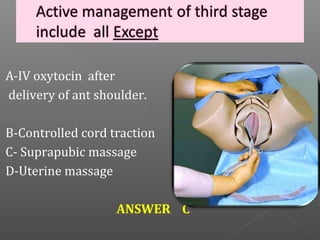
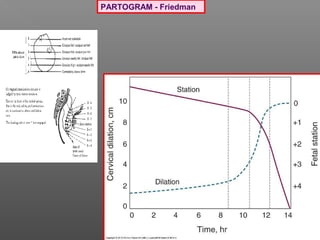
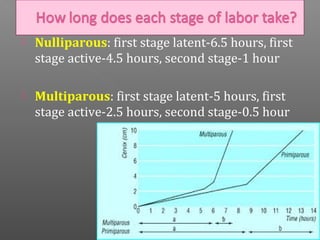
Normal labor occurs between 37-42 weeks gestation. Preterm labor is before 37 weeks and postdate pregnancy is after 42 weeks. The longitudinal axis of the fetus relates to the long axis of the maternal uterus. The part of the fetus closest to the birth canal is the presenting part. Cervical dilation and effacement indicate the progression of labor. Contractions increase in intensity, frequency and duration as labor progresses.