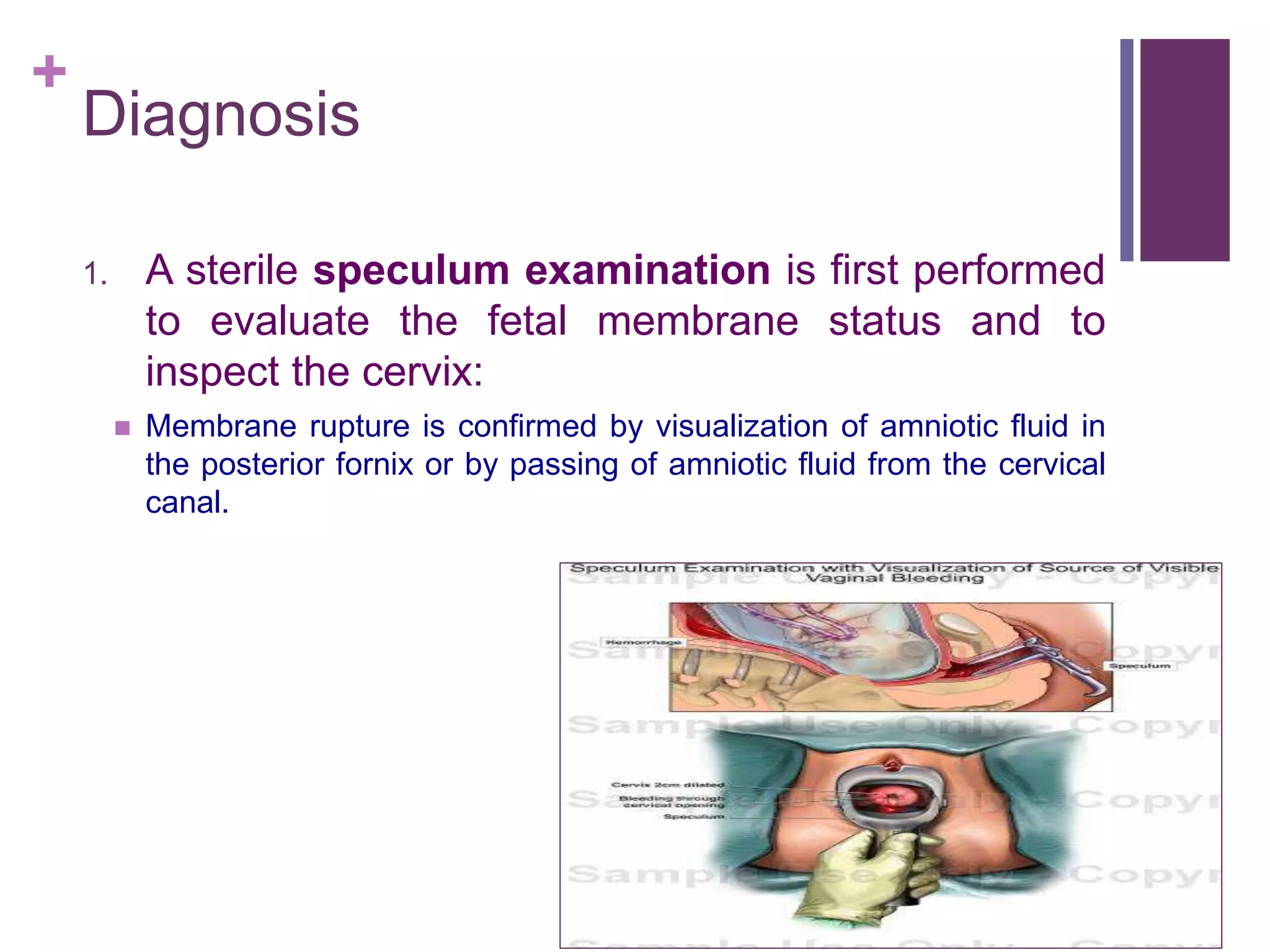
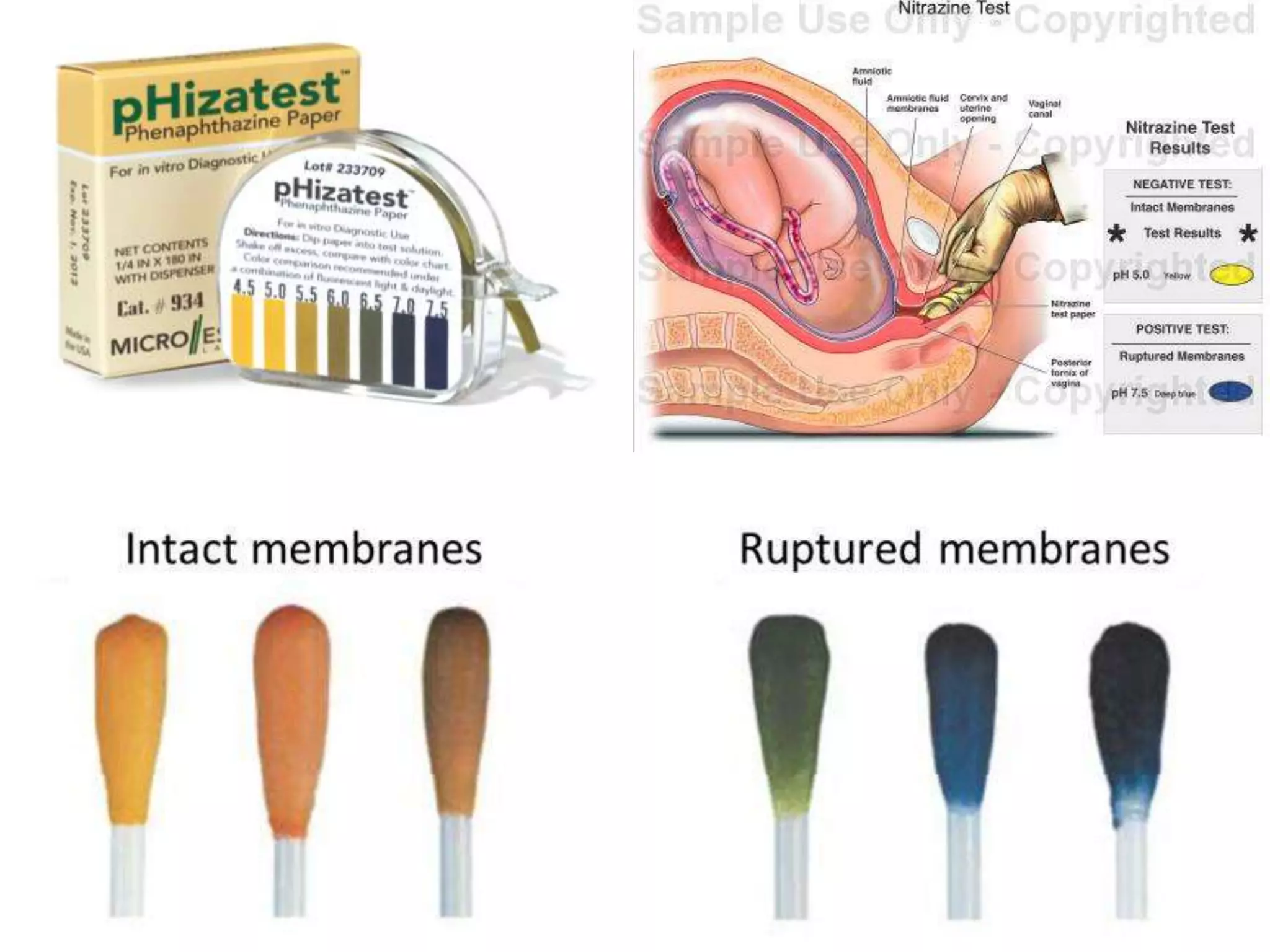
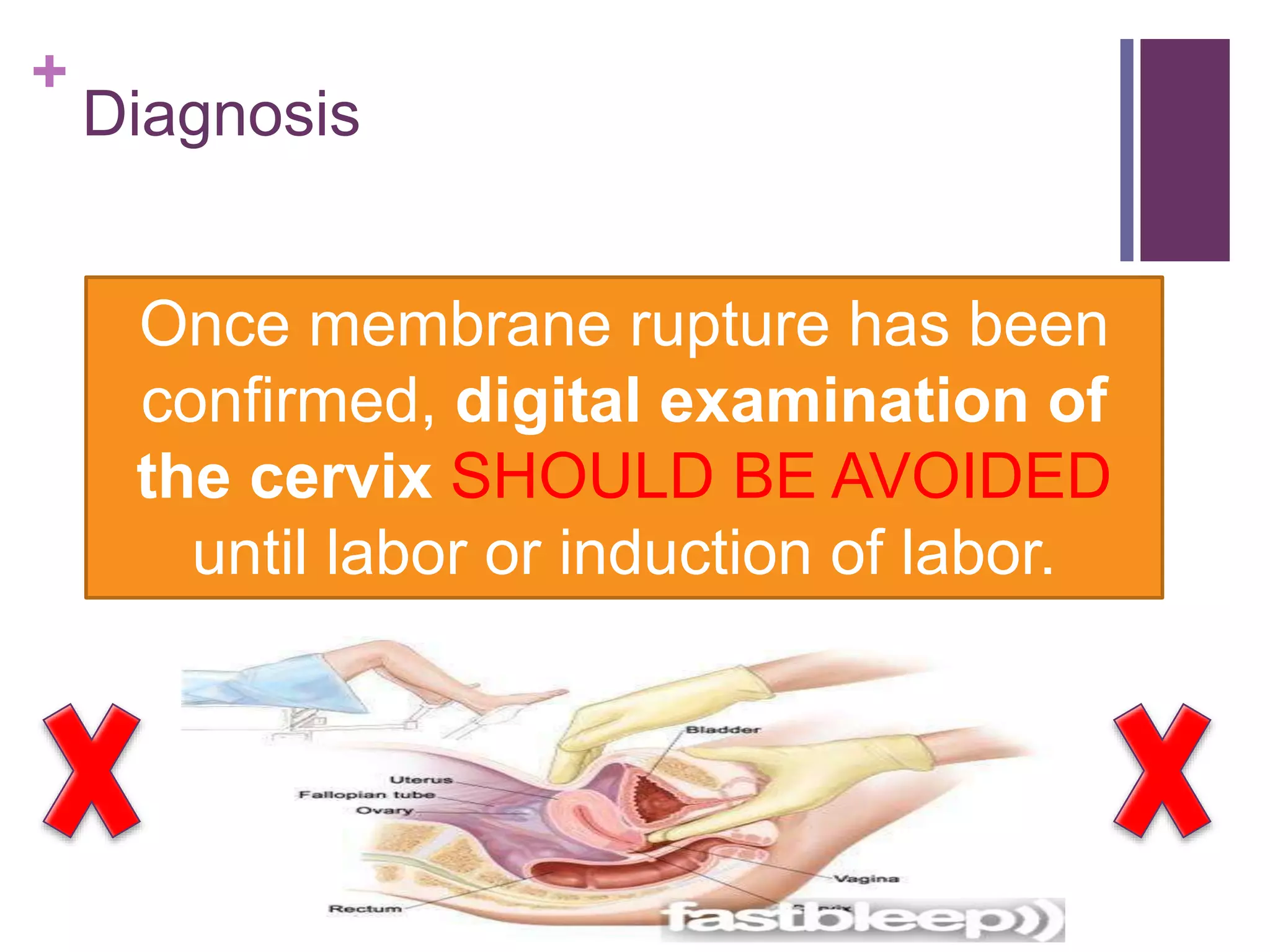
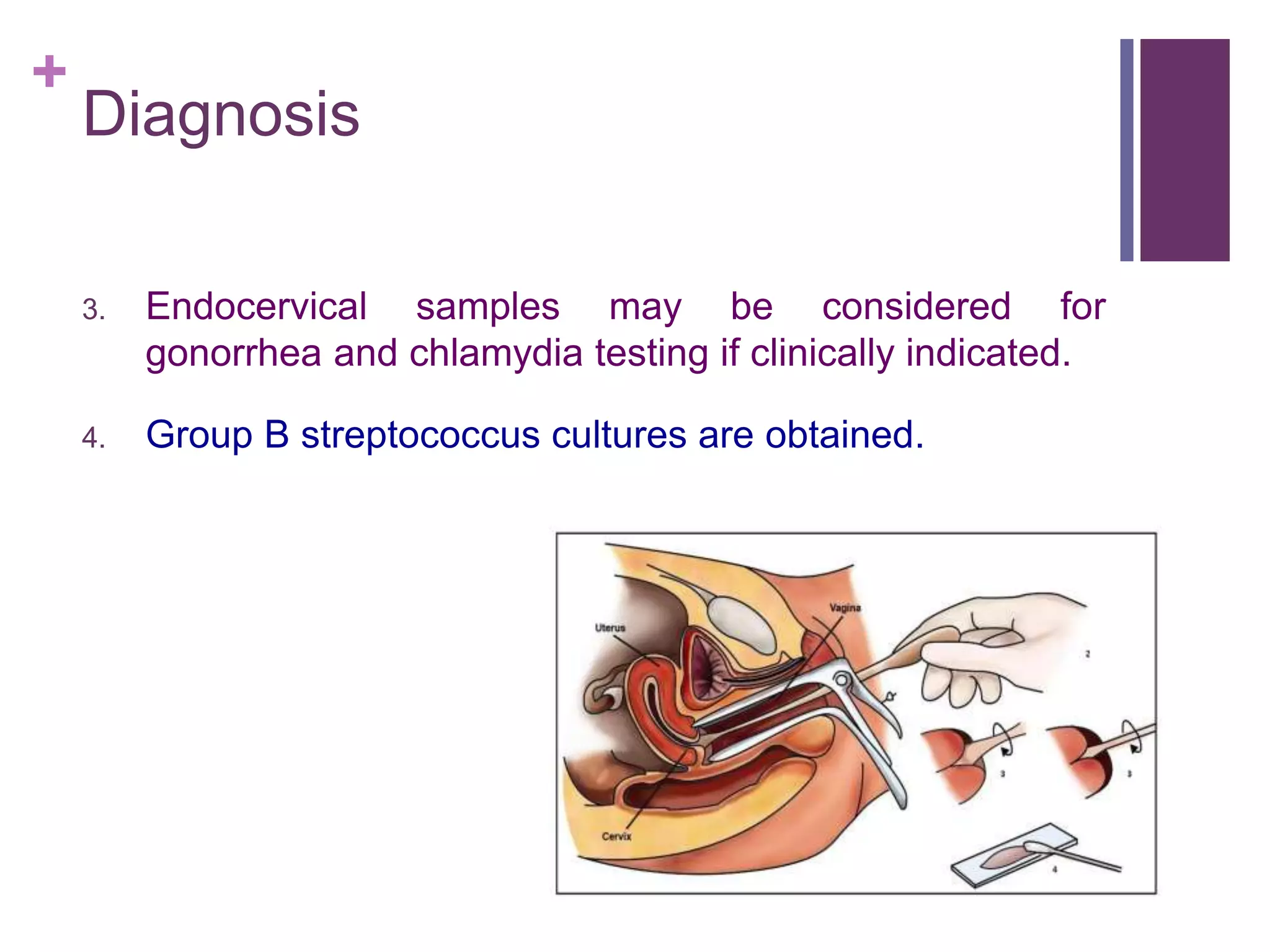
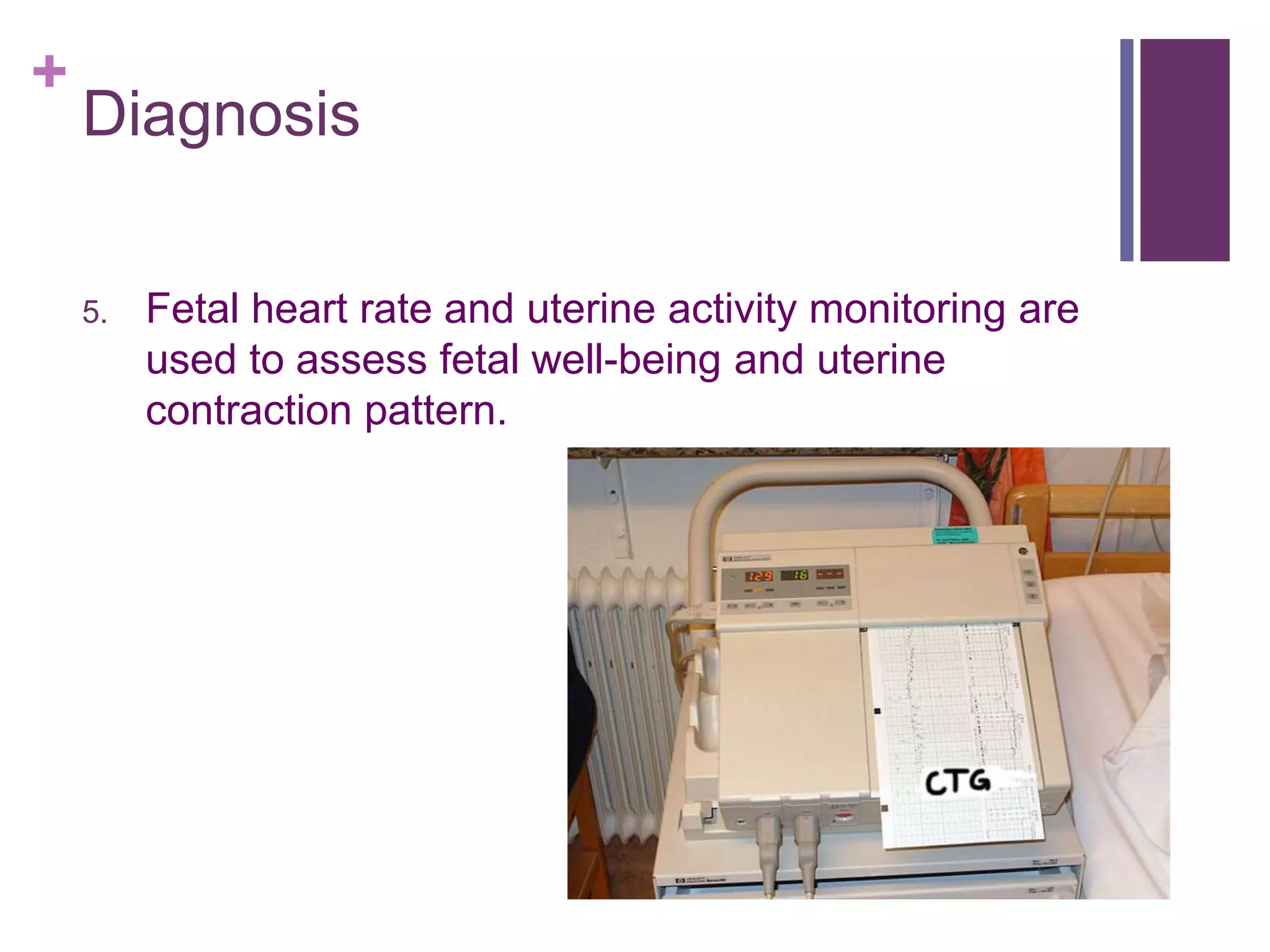
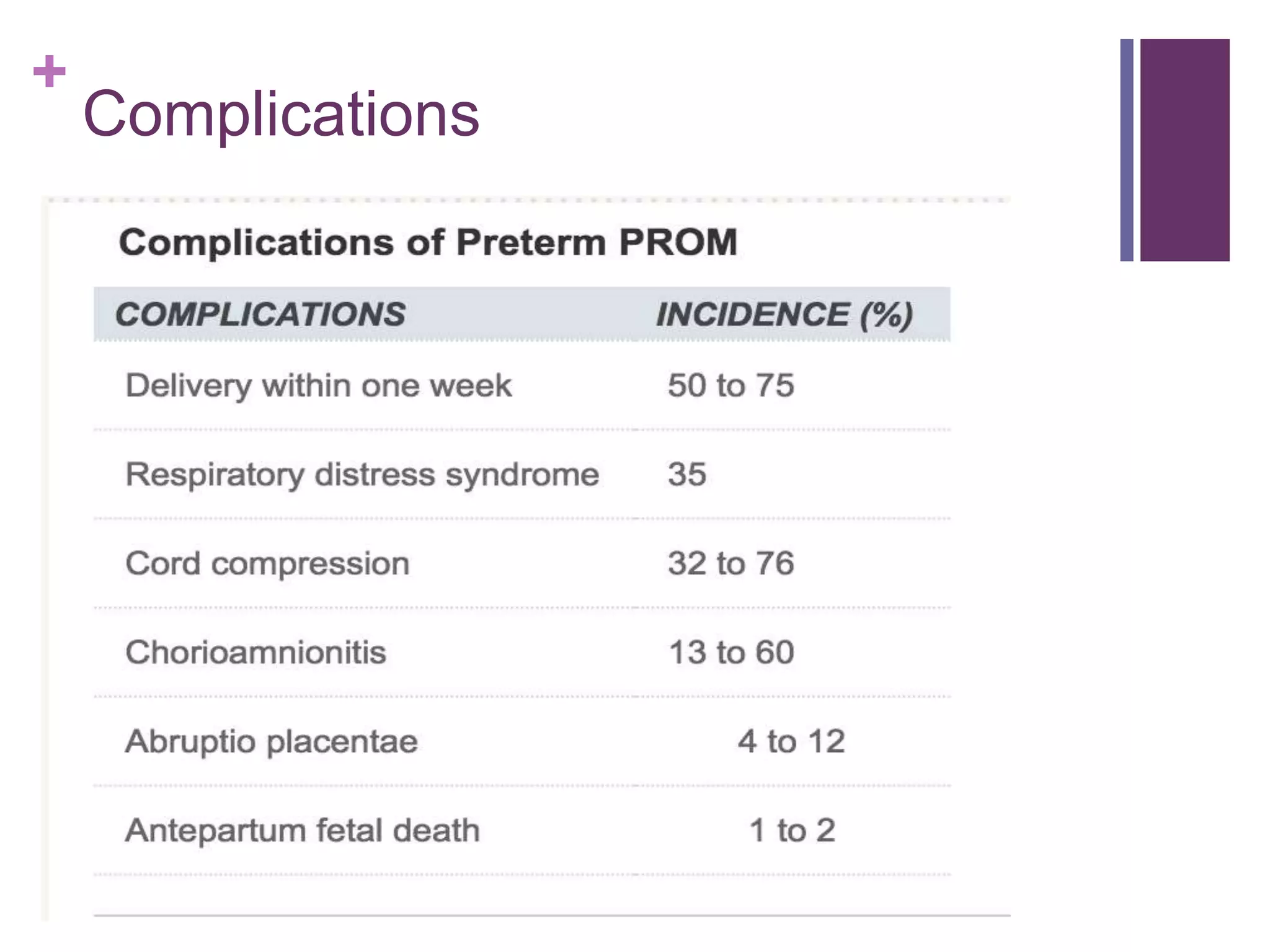
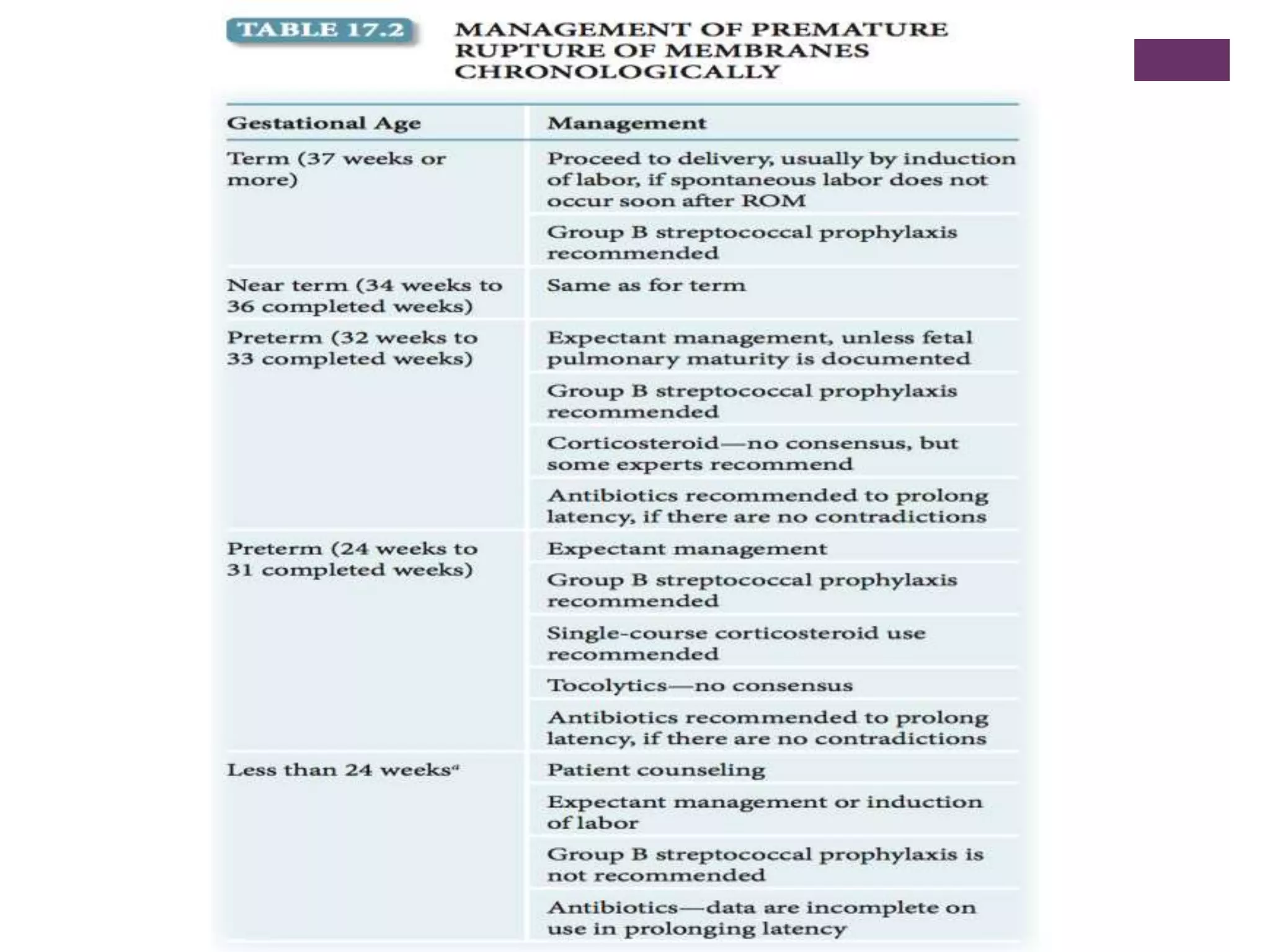
Preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM) occurs when the fetal membranes rupture before 37 weeks' gestation, contributing significantly to neonatal morbidity and approximately 30% of preterm deliveries. Diagnosis involves a sterile examination, nitrazine testing, and monitoring of fetal heart rate, with potential complications and risk factors including intrauterine infections and smoking. Management strategies are critical to address the risks associated with PPROM for both the mother and the fetus.