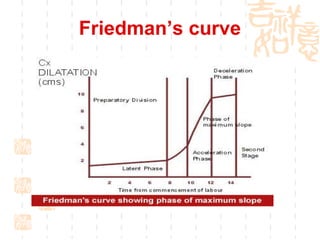
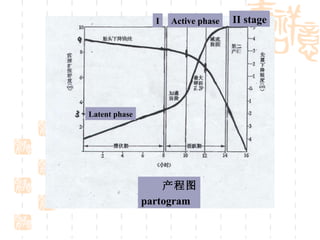
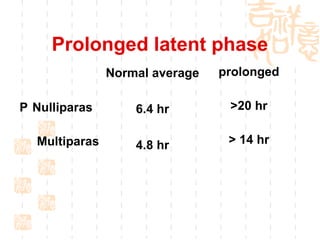
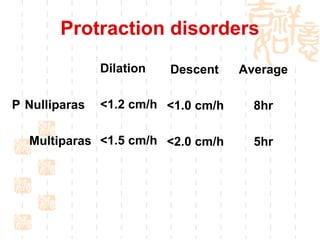
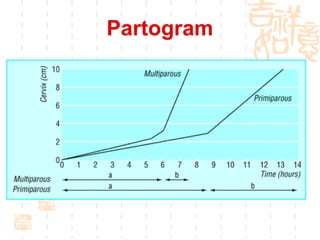
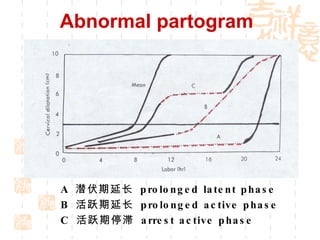
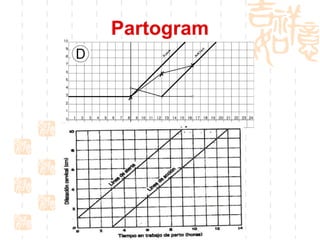
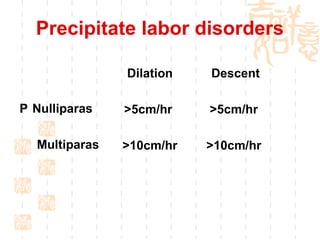
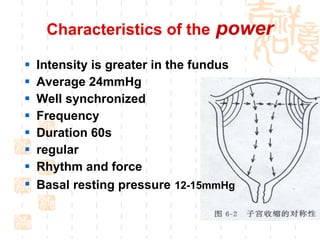
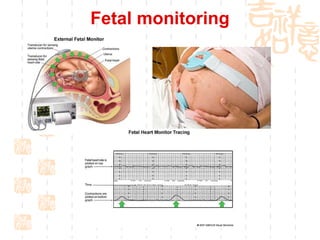
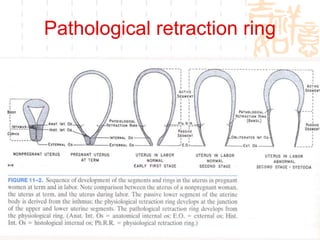
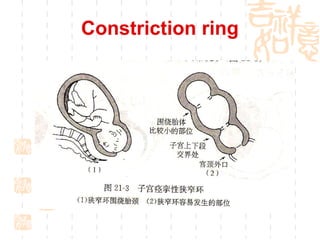
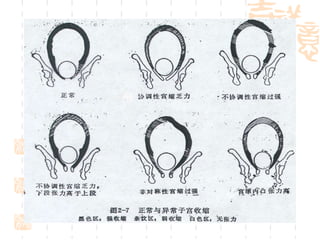
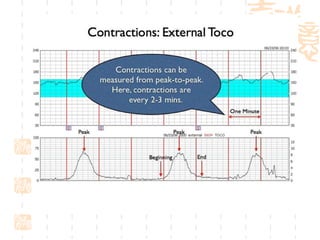
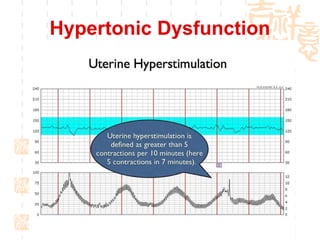
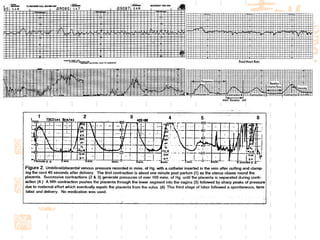
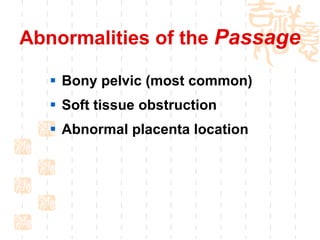
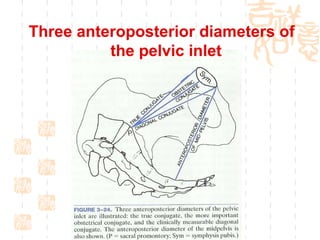
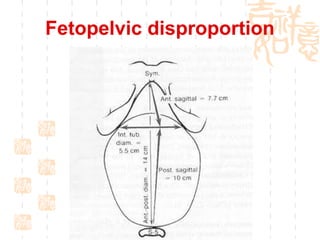
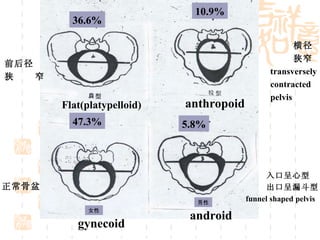
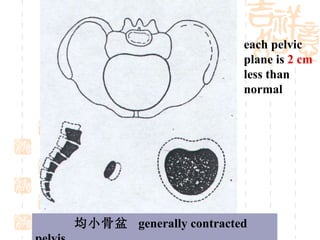
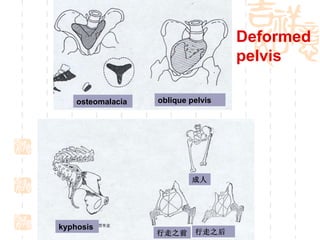
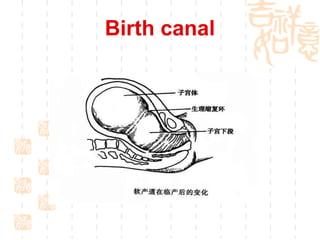
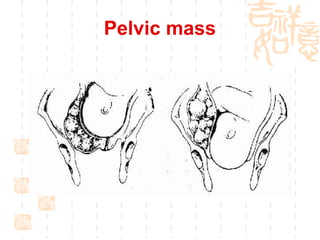
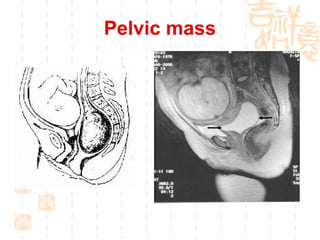
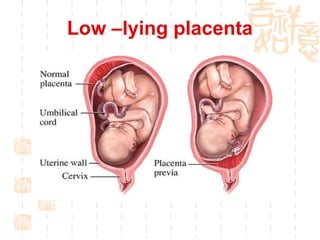
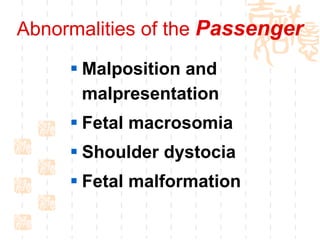
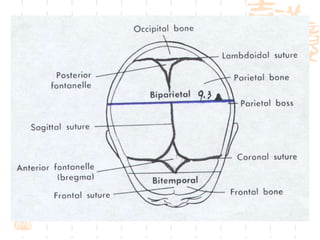
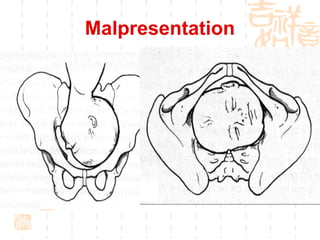
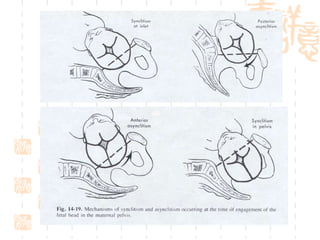
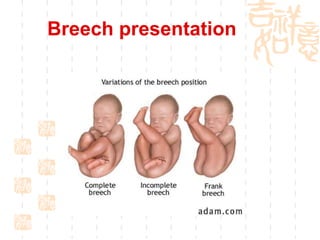
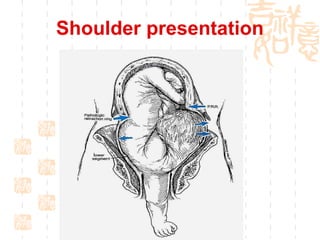
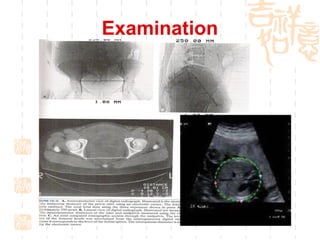
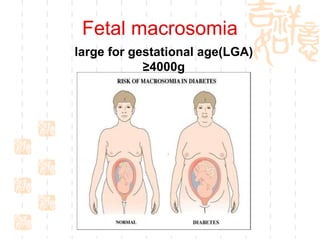
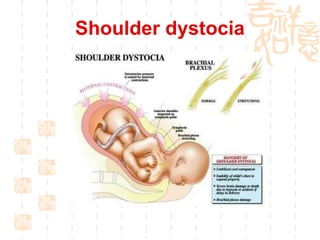
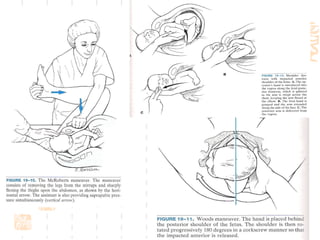
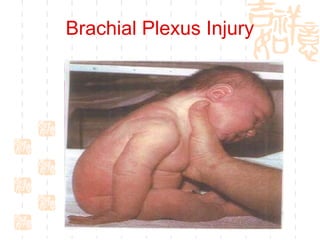
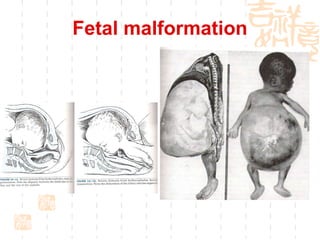
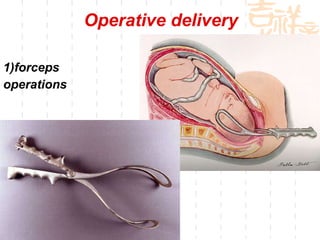
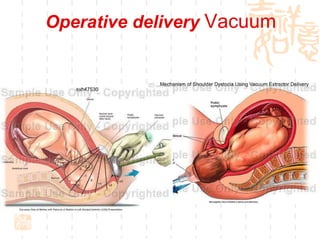
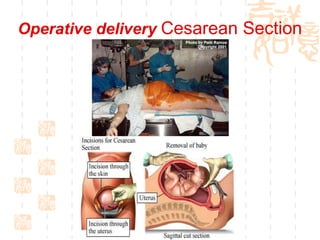
This document summarizes abnormal labor and dystocia. It defines difficult labor as abnormal slow progress and lists the main indications as prolonged latent phase, protraction disorders of the active phase, and arrest disorders of the active phase. It evaluates labor based on cervical dilation and fetal descent, using Friedman's curve as a guideline. It then describes the main types of abnormal labor patterns and dystocia, which can be due to abnormalities of power (uterine dysfunction), passage (pelvic abnormalities), or passenger (fetal malpositions and sizes).