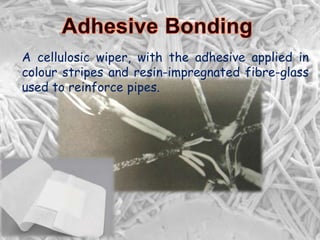
A non-woven fabric is made directly from fibres without creating yarn first. It is produced by bonding or interlocking fibres using mechanical, chemical, thermal, or solvent bonding. Non-woven fabrics have a higher production rate than woven or knitted fabrics and are cheaper to manufacture. While they can be engineered for specific properties, non-wovens do not match the aesthetics of conventional fabrics. Current major uses of non-wovens include geotextiles, medical products, disposable goods, and filters.