Embed presentation
Downloaded 45 times







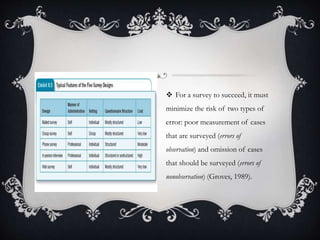


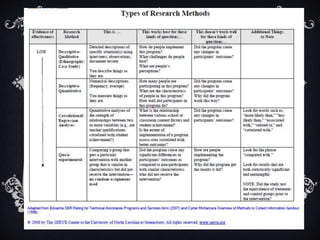
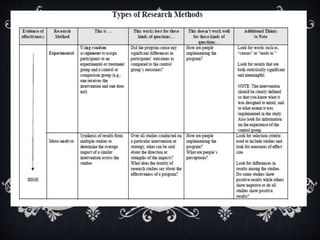

Non-experimental design involves observing and measuring phenomena as they occur without manipulation. It aims to describe variables, propose hypotheses, and provide an overall picture of a phenomenon. Common non-experimental designs include descriptive, correlational, retrospective, prospective, survey, case study, and historical research designs, which involve methods like interviews, questionnaires, observation, and measurement to understand relationships and describe attributes without establishing causality.











