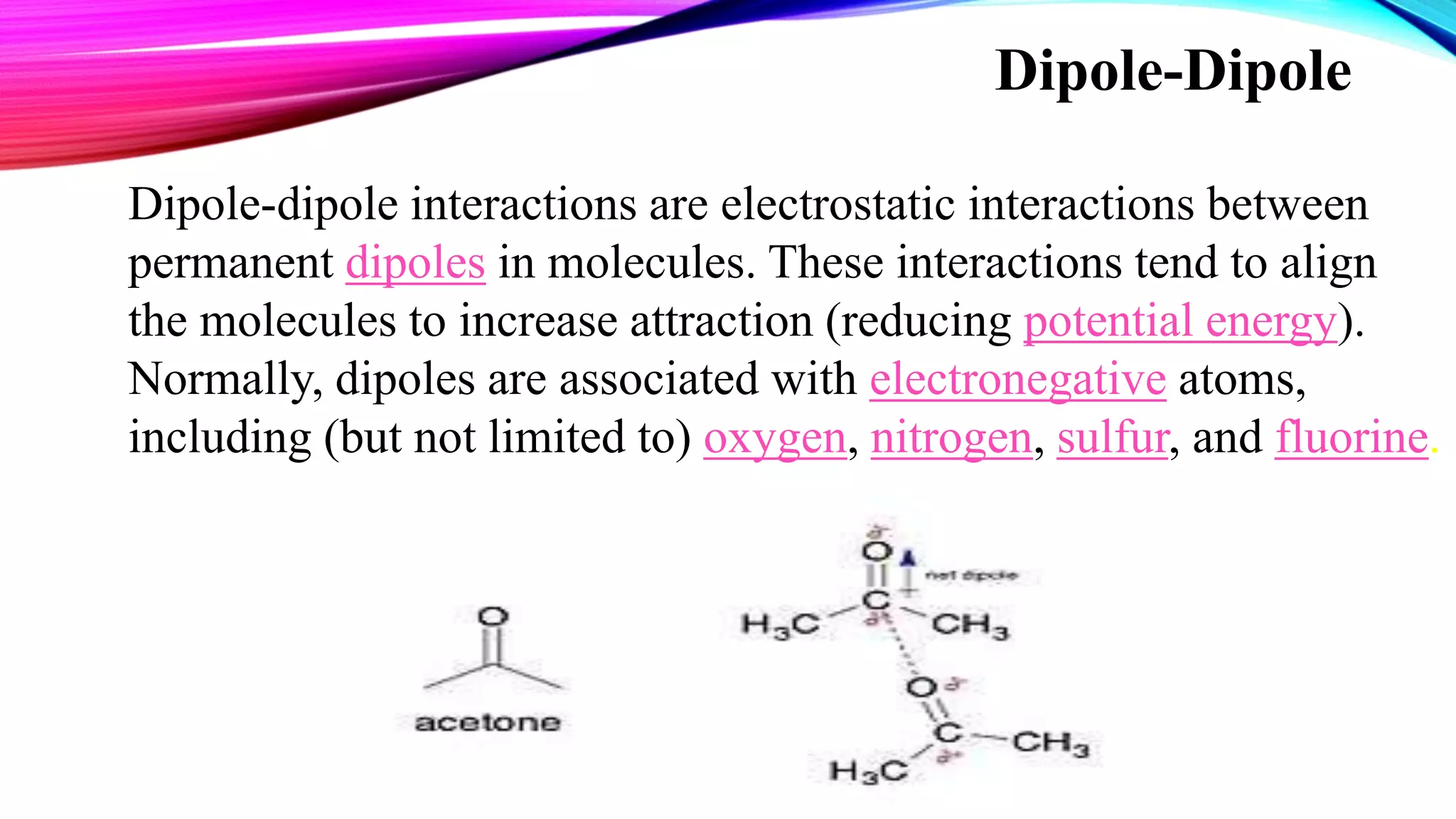
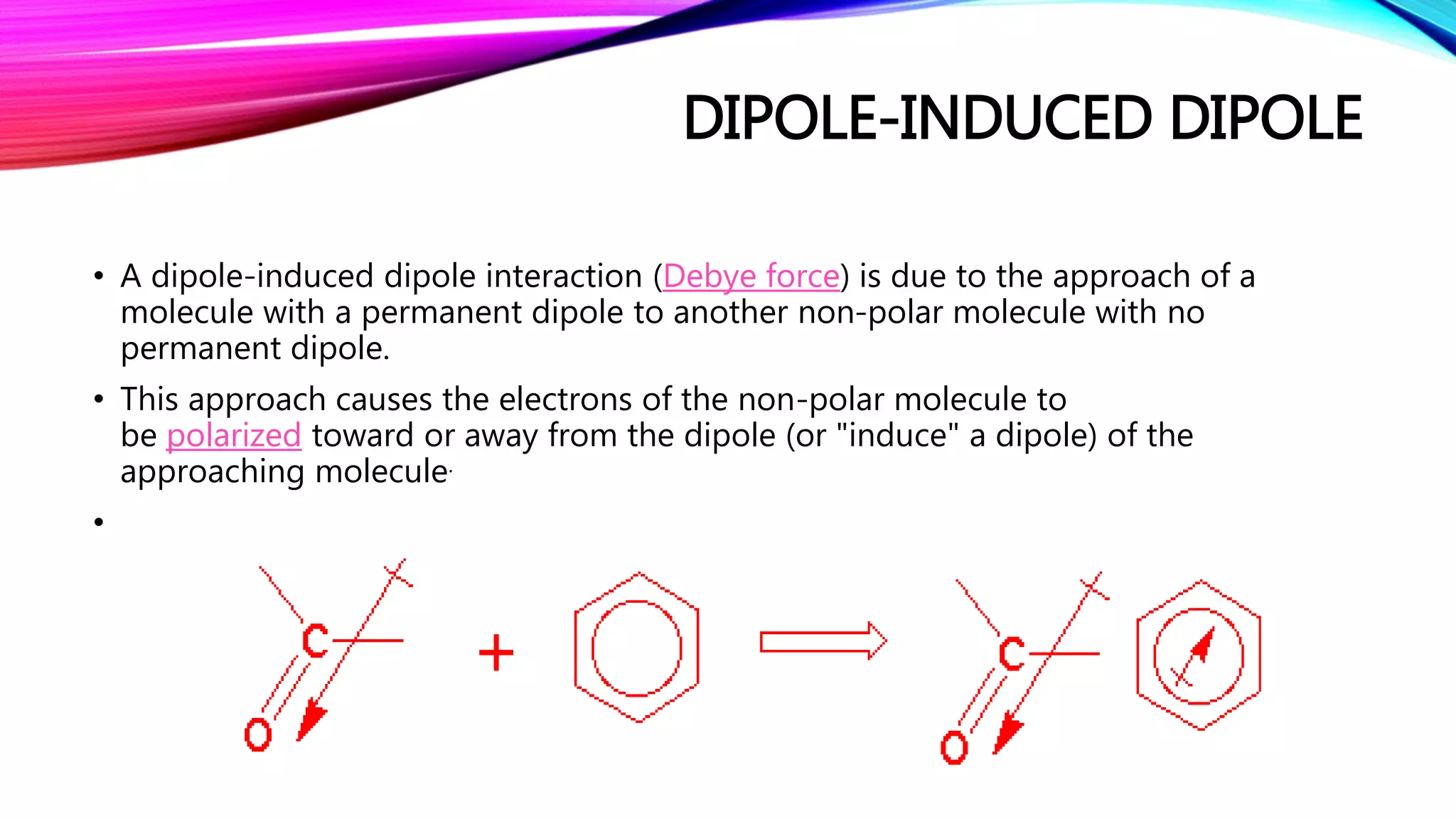
The document discusses non-covalent interactions, which differ from covalent bonds by not involving electron sharing, and are crucial for the structure and function of biological systems. Non-covalent interactions are categorized into electrostatic, van der Waals forces, π-effects, and hydrophobic effects, each with unique characteristics and implications for molecular behavior. These interactions drive processes such as protein folding and molecular recognition, influencing the behavior of supermolecules in supermolecular chemistry.