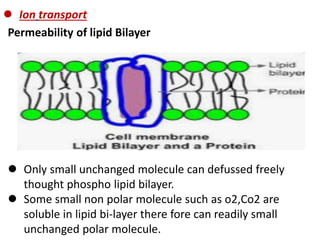
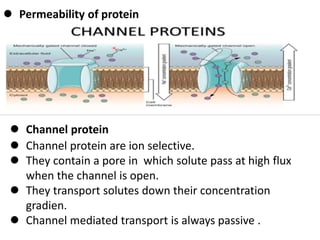
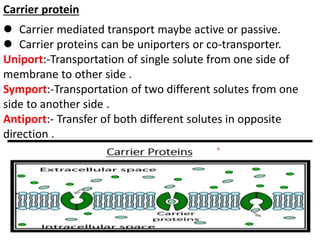
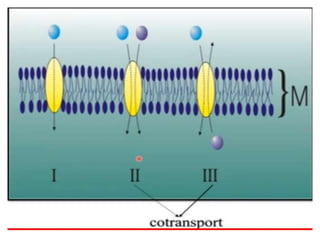
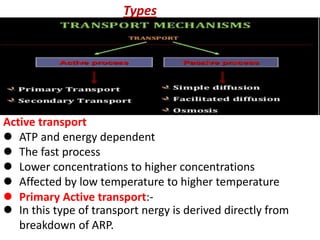
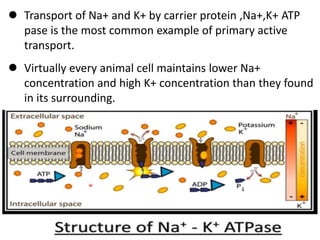
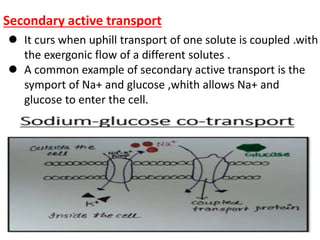
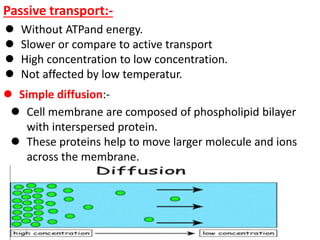
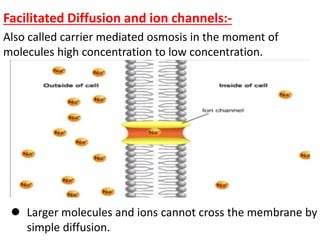
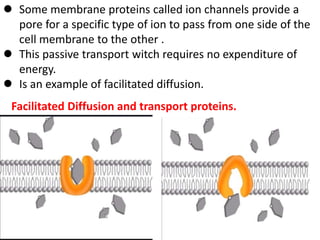
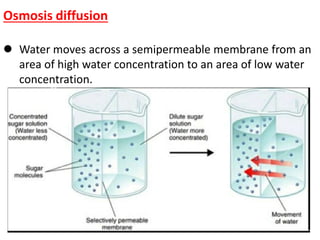
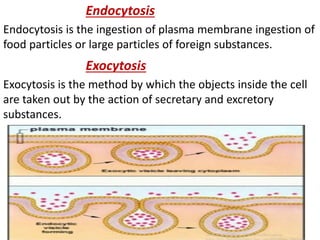
Ion transport through cell membranes occurs through passive and active transport mechanisms. Passive transport includes simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, and osmosis. Simple diffusion allows small, nonpolar molecules to freely pass through the phospholipid bilayer. Facilitated diffusion uses channel and carrier proteins to transport ions and larger molecules down their concentration gradients without expending energy. Osmosis allows for the diffusion of water through semipermeable membranes. Active transport moves solutes against their concentration gradients and requires energy in the form of ATP hydrolysis. Primary active transport uses ATP and carrier proteins like Na+/K+ ATPase to pump ions. Secondary active transport couples the uphill transport of one solute to the downhill flow of another.