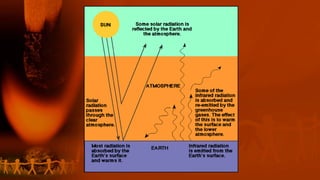
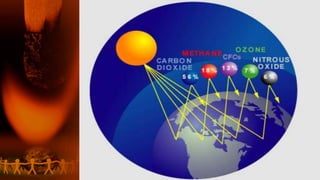
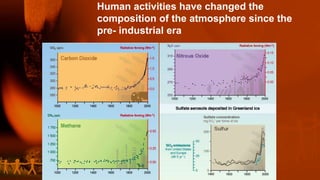
This document discusses global warming and the greenhouse effect. It explains that human activity is increasing greenhouse gases which thickens the layer trapping heat in the atmosphere and gradually increases earth's temperature. The greenhouse effect was discovered in 1824 and the main greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide, methane, CFCs and nitrous oxide. These gases are essential for maintaining a habitable temperature on Earth but human activities like burning fossil fuels have increased their levels since the pre-industrial era. This warming effects ecosystems and humans in various ways like rising sea levels and more extreme weather. Solutions proposed to reduce global warming include using renewable energy, afforestation, energy efficiency and international agreements like the Kyoto Protocol.