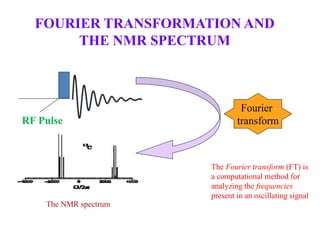
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy exploits the magnetic properties of certain nuclei to study the physical, chemical, and biological properties of matter. NMR provides detailed information about molecular structure through analysis of spectra. 1H NMR spectra reveal the number and environment of hydrogen atoms in a molecule based on signal frequency (chemical shift) and splitting patterns. 13C NMR spectra similarly provide information about carbon atoms, though the low natural abundance of 13C and long relaxation times make these spectra less sensitive. NMR spectroscopy is a powerful nondestructive analytical technique for elucidating molecular structure.