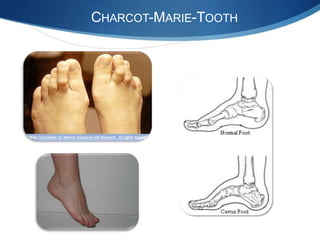
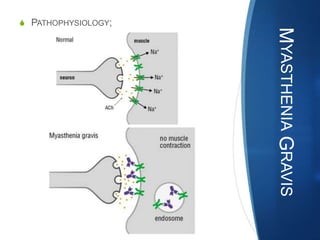
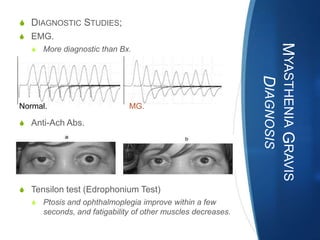
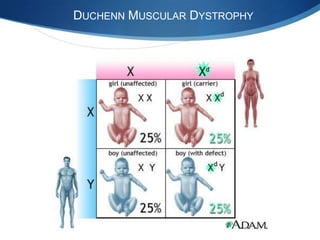
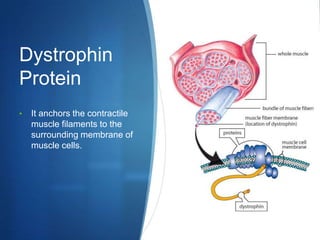
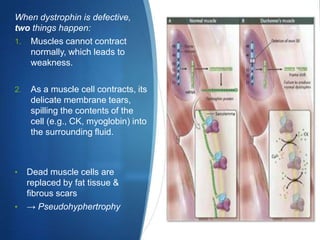
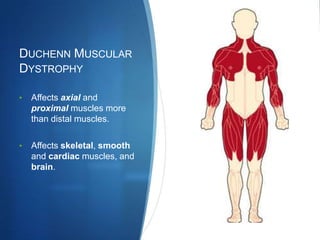
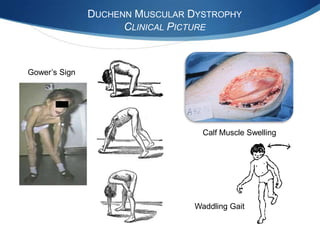
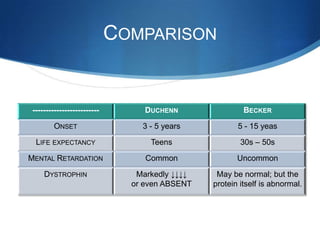
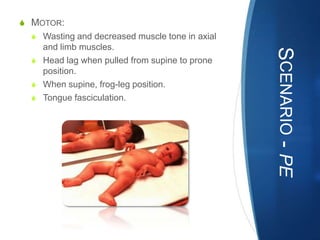
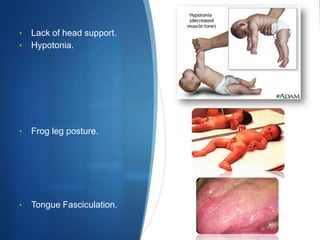
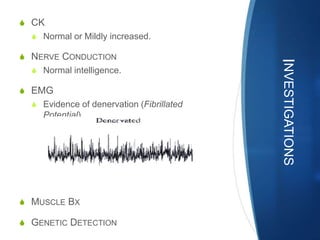
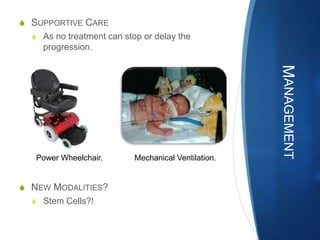
The document discusses various neuromuscular disorders, focusing on specific conditions such as spinal muscular atrophy, Guillain-Barré syndrome, myasthenia gravis, and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. It provides patient histories, clinical pictures, diagnostic workups, and management strategies for each condition. The information highlights the complexities of these disorders, including their symptoms, progression, and treatment options.




















![S COMPLICATIONS;
GUILLIAN-BARRÈ SYNDROME
S Breathing.
S CVS.
S Pain.
S Bowel/Bladder Dysfunctions.
S Blood clots.
S Pressure sores.
S Relapse.
S "10%"
S Death.
S (RDS, Heart Block). [Rare]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/musculardisorders-111203082959-phpapp02/85/Neuro-Muscular-Disorders-40-320.jpg)