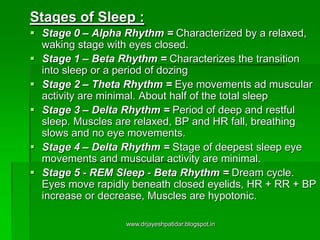
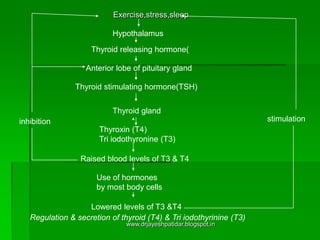
This document discusses neuroendocrinology and the interaction between the nervous and endocrine systems. It focuses on the pituitary gland and thyroid gland. The pituitary gland, also called the "master gland", regulates hormone secretion and has effects on behavior. It interacts with the hypothalamus and controls other endocrine glands. The thyroid gland is stimulated by thyroid stimulating hormone from the pituitary to regulate metabolism and temperature. Abnormal hormone secretion from these glands can impact behavior and mental functioning. The relationship between the immune, endocrine and nervous systems is also explored.