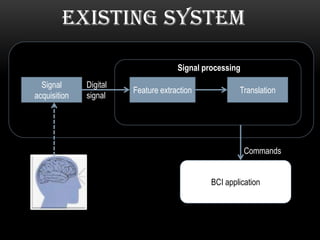
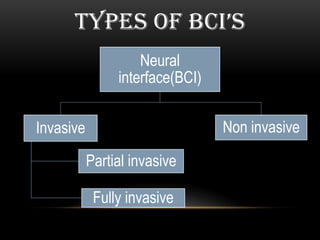
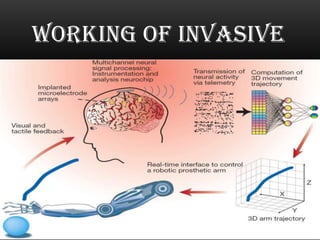
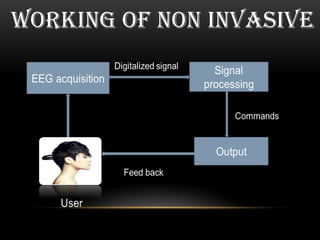
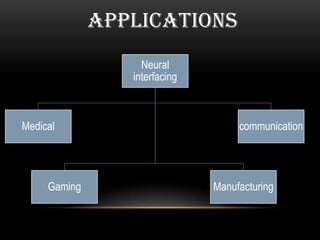
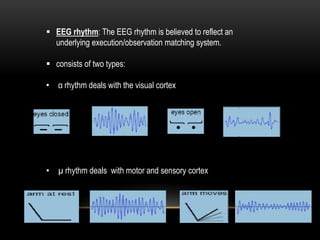
This document discusses neural interfacing systems, including their objective to link the nervous system to the outside world by stimulating or recording neural tissue. It describes types of invasive and non-invasive neural interfaces and their workings. Applications mentioned include assisting those with disabilities, gaming, manufacturing, and communication. Methods covered are P300 detection, EEG rhythms, and conclusion discusses advantages like helping disabled individuals and disadvantages like risk factors and noise sensitivity.