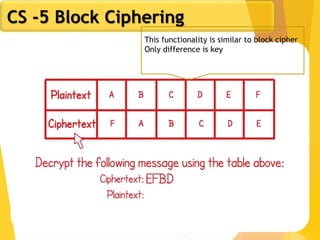
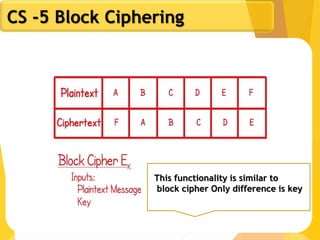
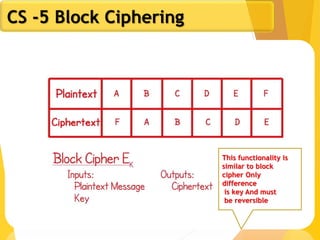
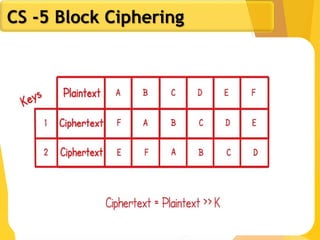
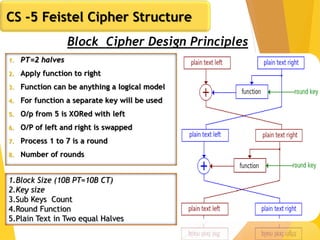
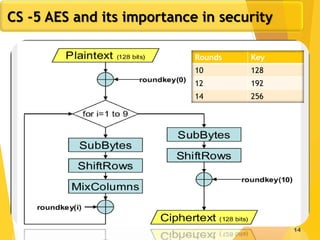
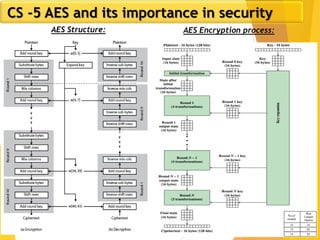
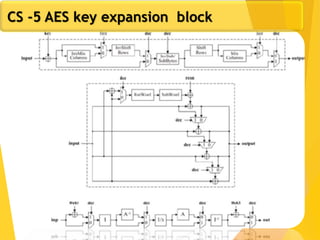
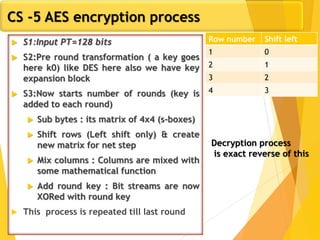
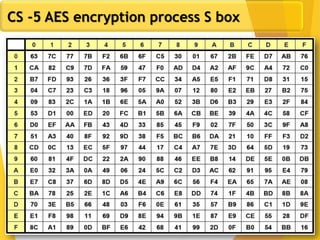
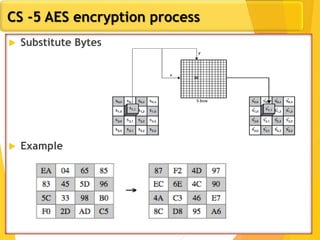
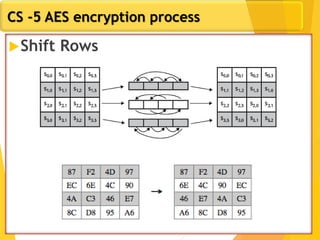
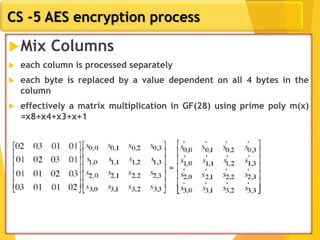
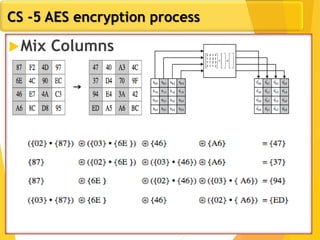
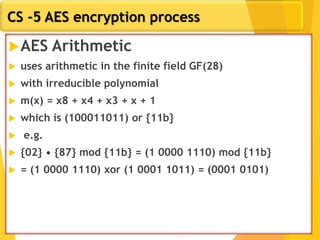
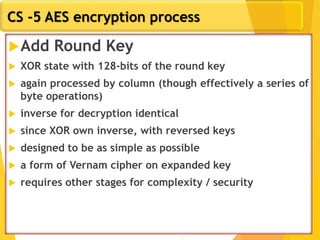
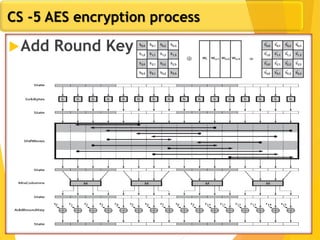
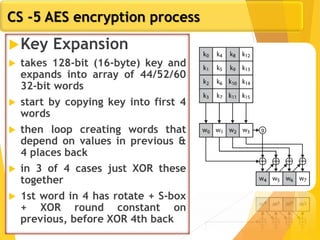
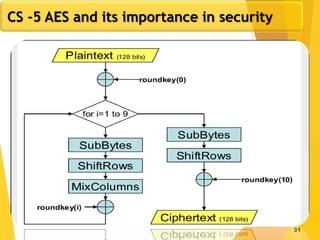
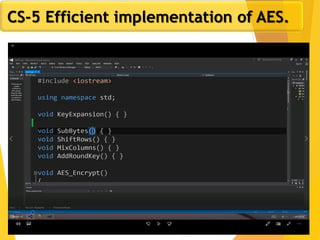
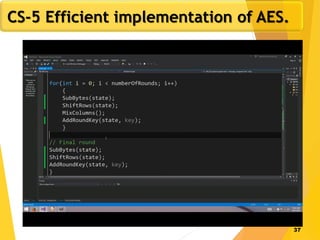
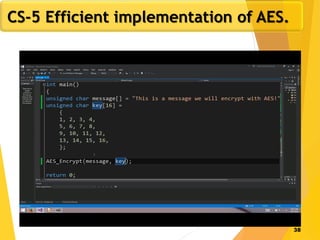
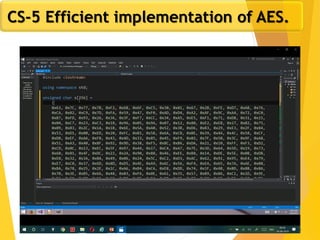
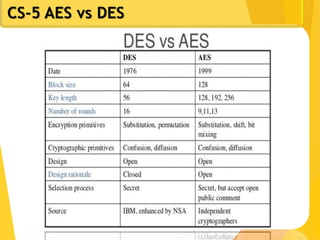
The document covers network security concepts focusing on block ciphering, specifically AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and its significance in security. It details AES structure, including its iterative process, key expansion, and encryption methods, while contrasting it with DES (Data Encryption Standard). The AES is highlighted for its resistance to attacks, speed, and applicability in various commercial platforms.