Embed presentation


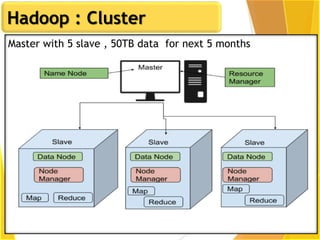
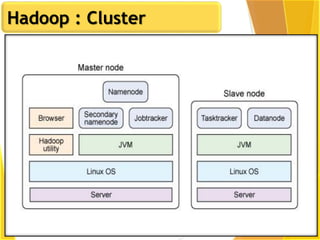
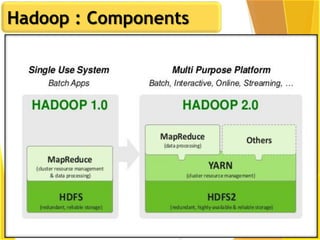


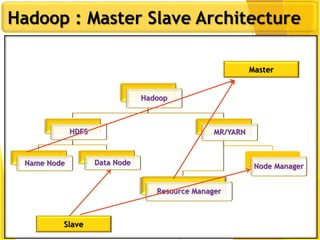
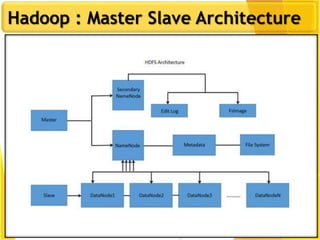
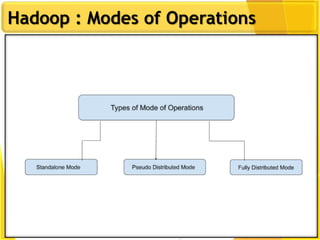
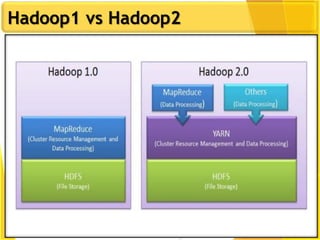

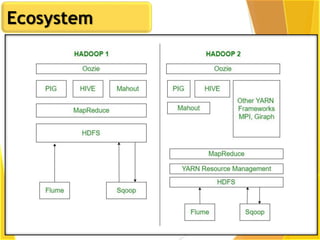
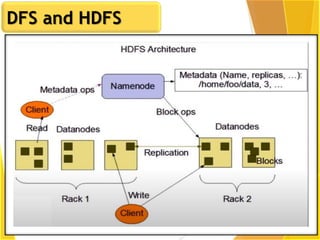
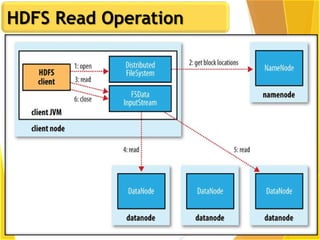
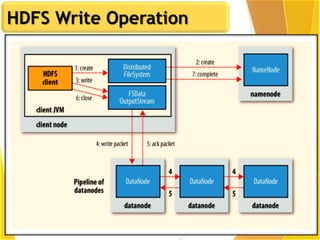
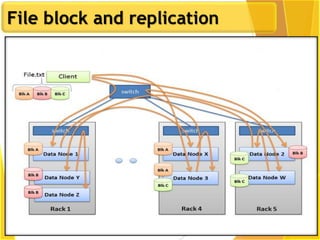


This document provides an overview of Hadoop and Big Data concepts. It introduces Hadoop and its architecture, describing its scalability, cost effectiveness, and resilience. Key Hadoop components are explained, including the NameNode, DataNodes, and Resource Manager. HDFS operations like read and write are also summarized. The document concludes with a thank you.




















