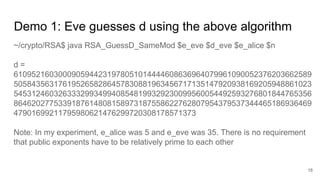
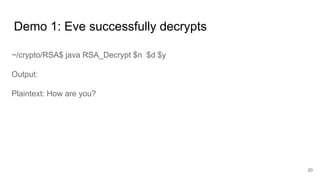
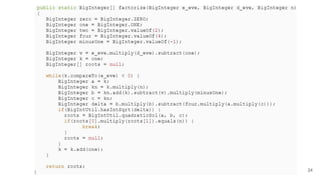
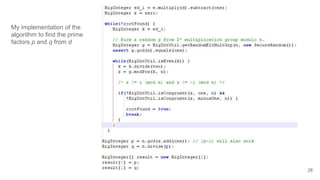
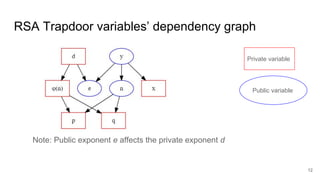
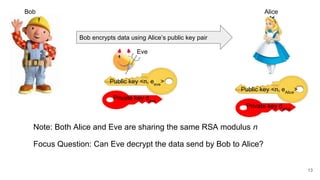
This document analyzes the security implications of sharing the same RSA modulus n between two users. It presents three algorithms that an attacker could use to break RSA encryption if the public keys for two users share the same n value. Algorithm 1 works if the public exponents are relatively prime. Algorithm 2 works for small public exponents by factoring n. Algorithm 3 directly factors n from the private exponent. The conclusion is that RSA is breakable if n is not unique per user.












![Algorithm 1: In case ealice
is relatively prime to V
We known eeve
.deve
≡ 1(mod φ(n)); Thus, V = eeve
.deve
- 1 is a multiple of φ(n)
Since ealice
is relatively prime to V, Eve can find d from the following:
ealice
.d ≡ 1(mod V) ⇒ ealice
.d = 1 + kV for some integer k.
Eve will use this d to decrypt the ciphertext y send from Bob to Alice as follows:
yd
mod n = ( 𝓍 ) mod n = 𝓍1+kV
mod n = 𝓍 𝓍kV
mod n = 𝓍 mod n; [Note 𝓍kV
mod n
= 1;Euler’s theorem]
Thus, Eve got the secret message 𝓍 by simply performing yd
mod n
16
ealice
d](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analysisofsharedrsamodulus-190126220309/85/Analysis-of-Shared-RSA-Modulus-16-320.jpg)