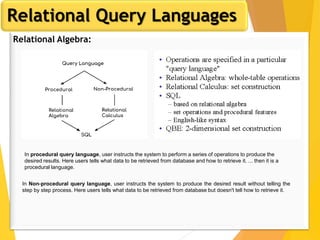
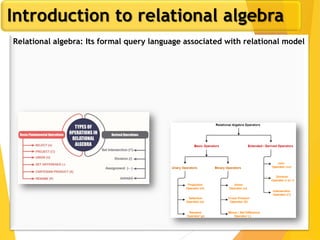
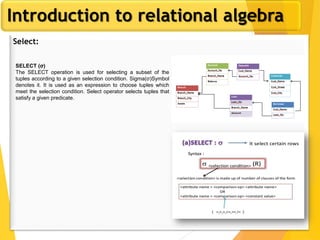
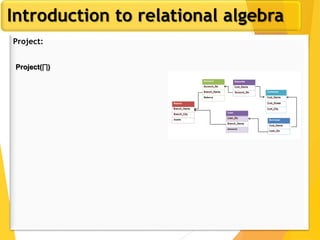
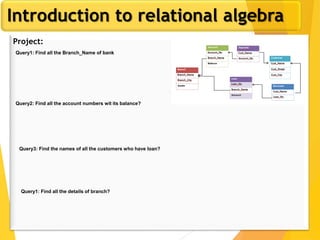
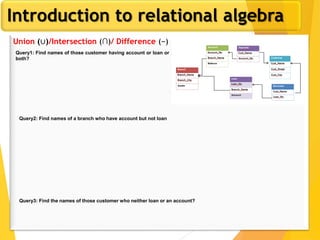
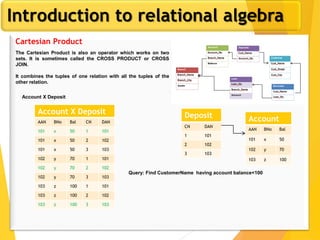
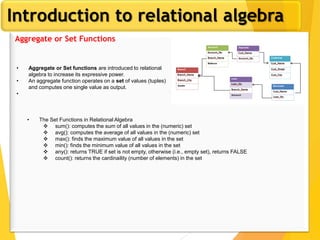
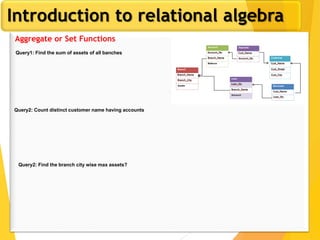
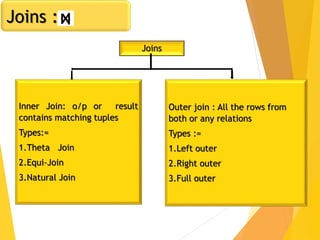
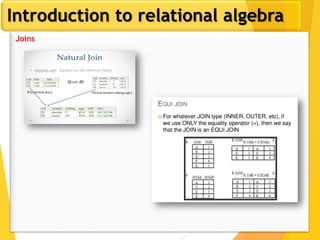
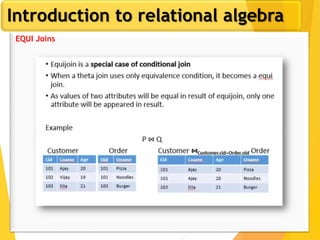
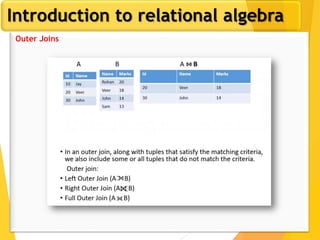
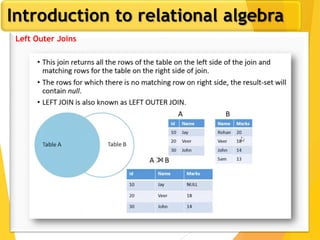
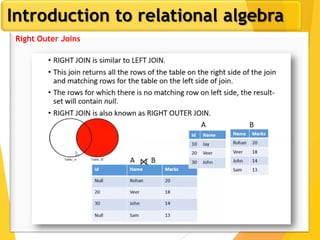
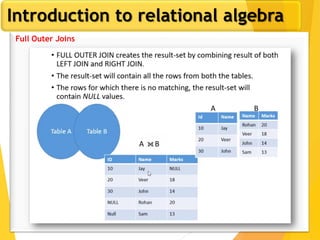
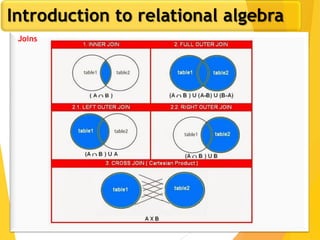
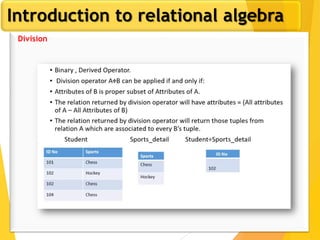
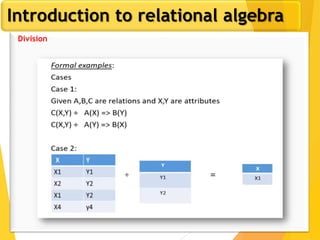
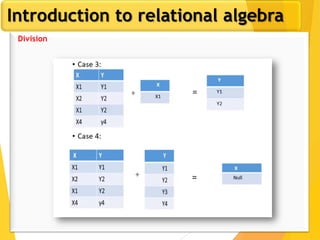
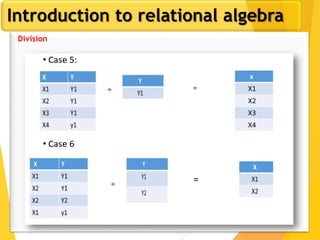
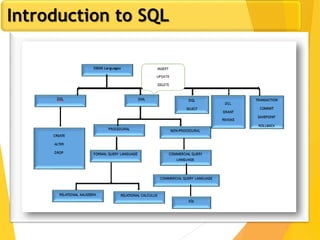
The document covers Chapter 3 of database design and applications, focusing on relational query languages, specifically relational algebra and SQL. It introduces key concepts such as selection, projection, set operations, joins, and aggregate functions within relational algebra. The document also distinguishes between procedural and non-procedural query languages, providing examples of various queries and operations.